GC-MS for New Analytical Scientists
Endorsed by

This learning path will equip you with the knowledge and understanding to run GC-MS methods. System setup, fundamental scientific knowledge, and in-depth insights into instrumentation are covered.
12 Modules
12 Items
GC-MS Introduction
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is a hyphenated technique which combines the separating power of gas chromatography (GC) with the detection power of mass spectrometry (MS). This module will explore the instrument acquisition methods used and examine the type of data that can be produced from such systems.
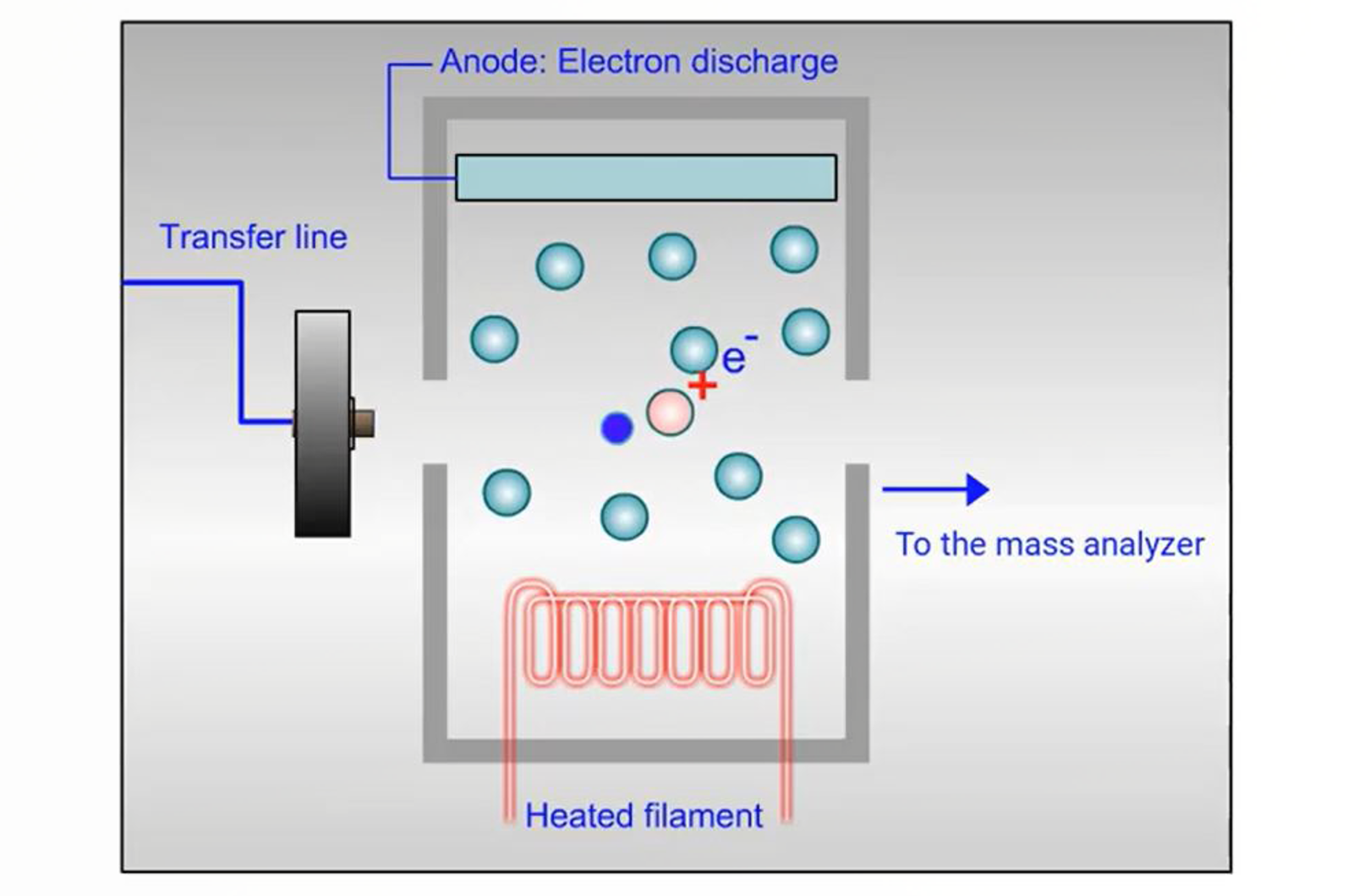
GC-MS Ionization
An introduction to the ionization processes which occur in GC-MS. Ionization is the process whereby electrons are either removed or added to atoms or molecules to produce ions.

GC Considerations
This module explores the main GC considerations when using MS detectors. The choice of column phase and dimensions are considered, as well as the effects of carrier gas flows on the MS vacuum system.
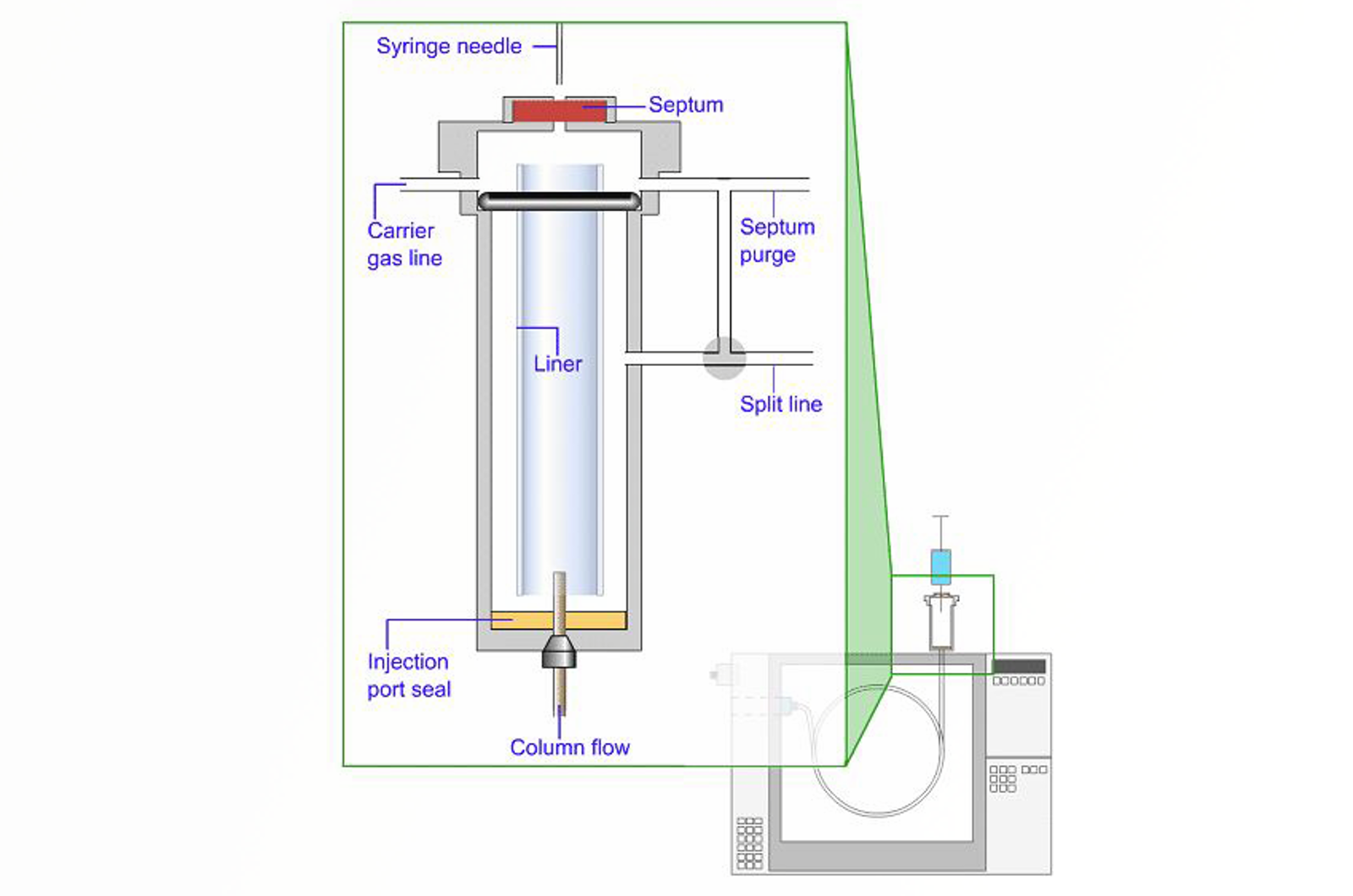
GC-MS Sample Introduction
Perhaps the most difficult step in any GC-MS analysis is the sample introduction. Solid or liquid samples need to be converted to the gas phase and then efficiently transported onto the GC column. The primary aim with all sampling techniques is to ensure a representative and homogeneous gaseous aliquot of the sample under investigation is delivered to the GC column. This module will explore the main GC considerations when using MS detectors.
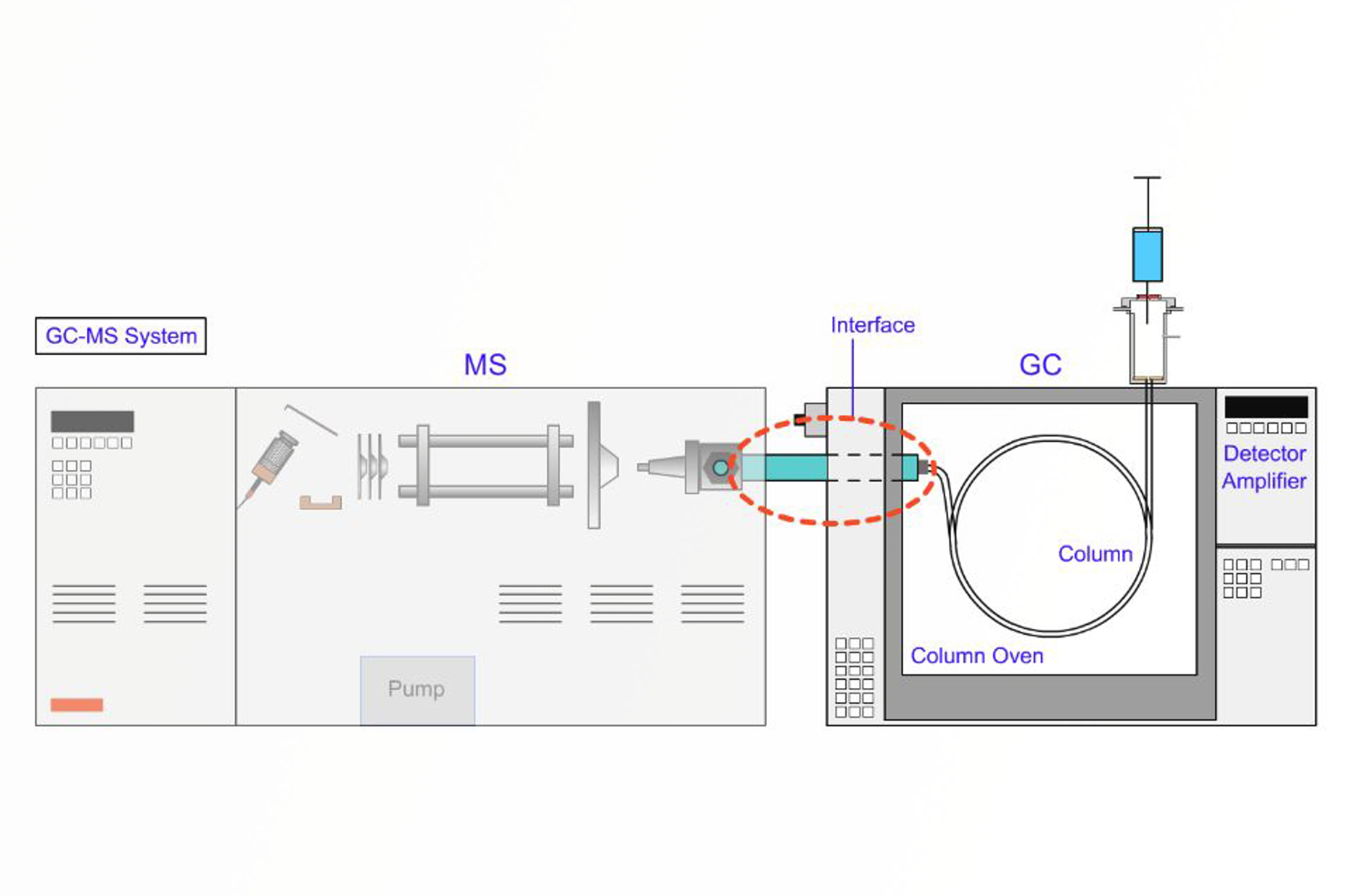
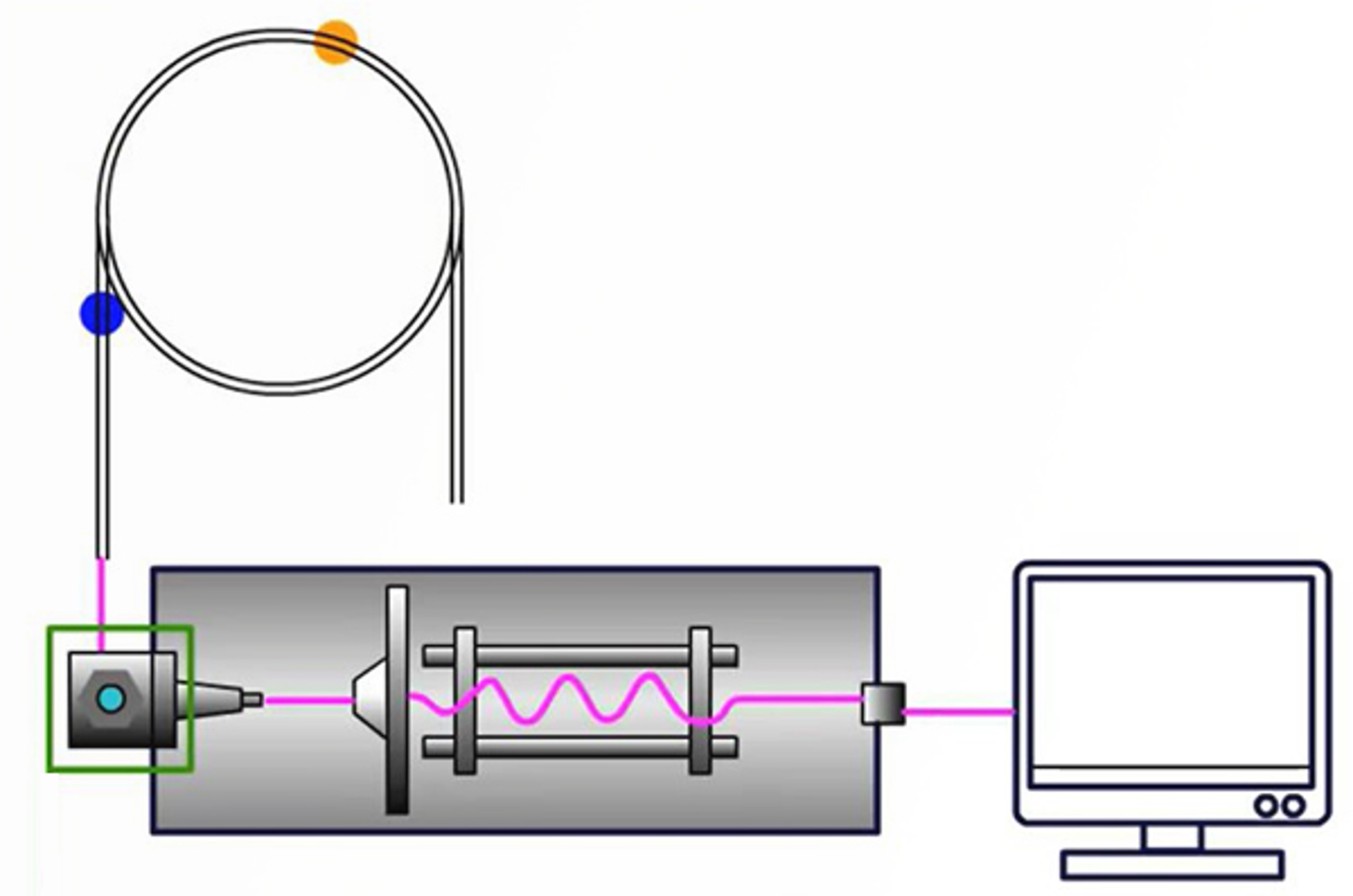
GC-MS Interfaces
After separation in the GC column, analyte species have to be transported to the mass spectrometer to be ionized, mass filtered, and detected. The column outlet needs to be connected to the ion source of the mass spectrometer and this module presents the correct interface types for use with different GC columns and MS instrument types.

Practical GC-MS Video Bootcamp
The definitive guide to setting up a GC-MS instrument. Working on a real GC-MS instrument we provide you with the fundamental knowledge on the science, working principles, and correct setup of this powerful piece of equipment. An in-depth tour of how to dismantle and clean the ion source will give you confidence to perform preventative maintenance on your instrument.
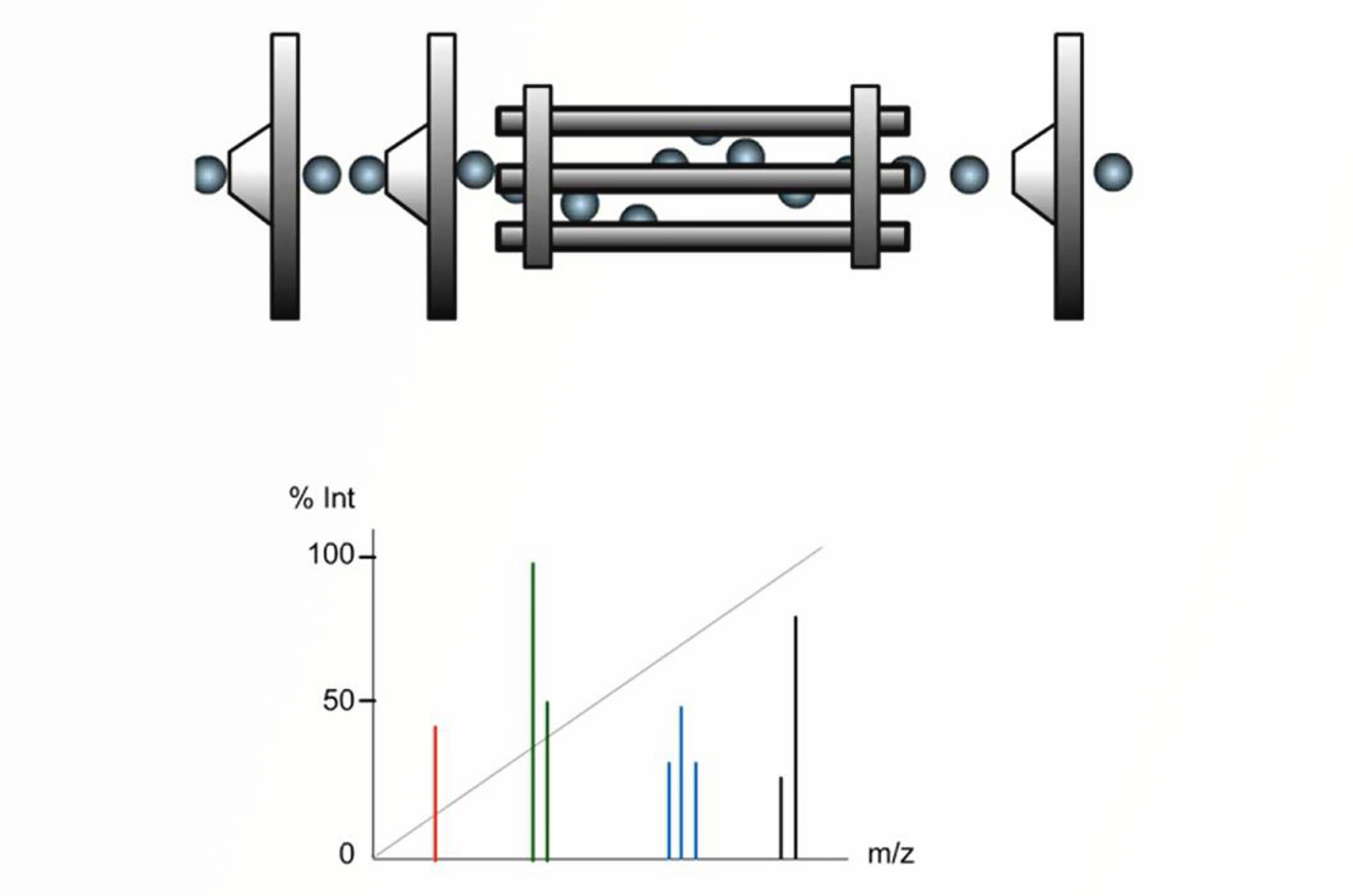
GC-MS Acquisition Modes
GC-MS data acquisition is carried out using full scan or selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode. Scan mode is used to cover a wide range of m/z ratios, whereas, SIM is used to gather data for specific masses of interest. This module will explain the differences between the data generated, provide you with details on the parameters which can be set to acquire the data, and the impact of the acquisition mode and parameters on the sensitivity of that data.
GC-MS Library Searching
This module will detail the process of obtaining and extracting spectra for library matching, what is involved in the matching process, and interpreting match results. As well as providing learning on troubleshooting poor library matching.
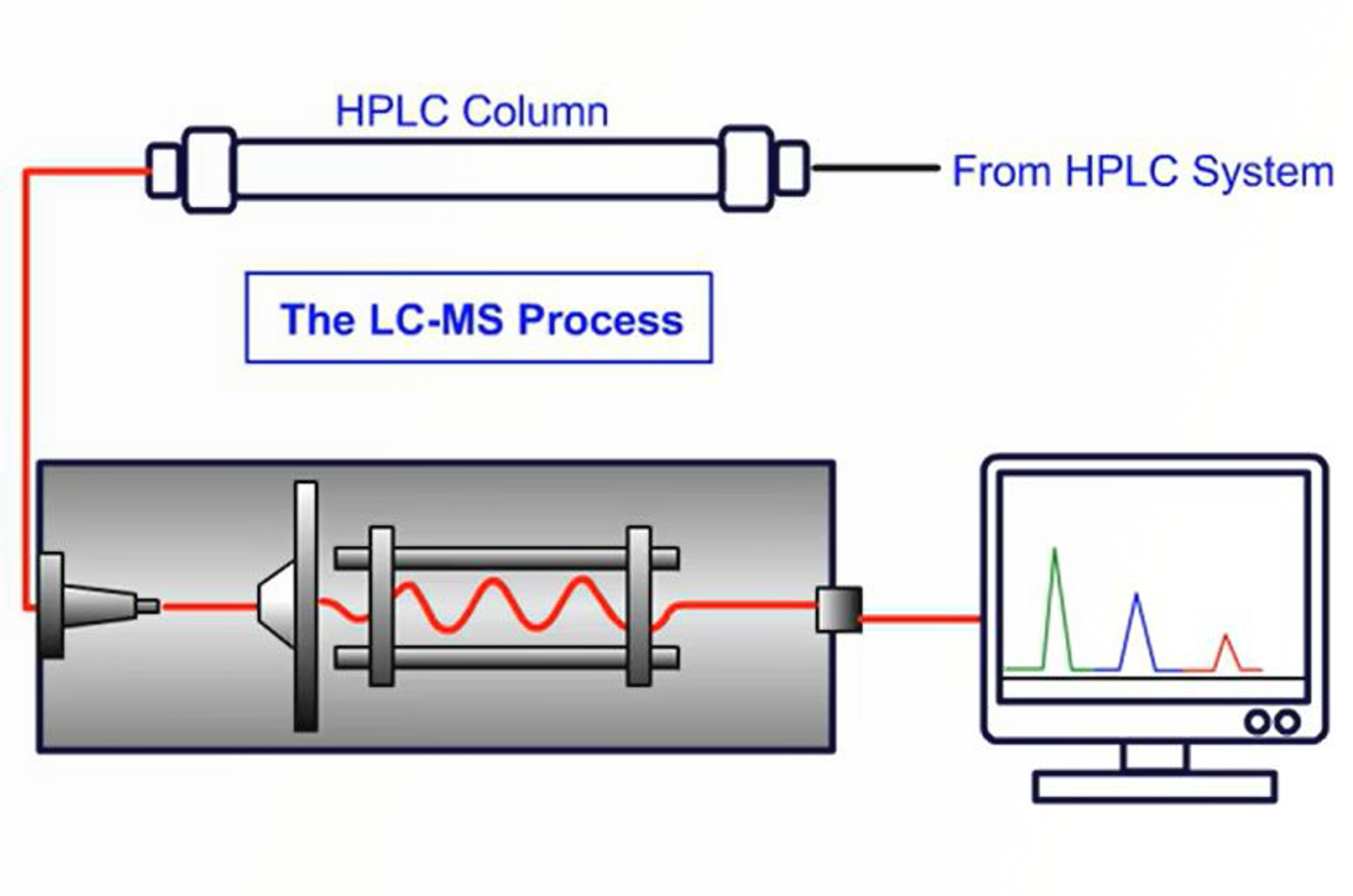
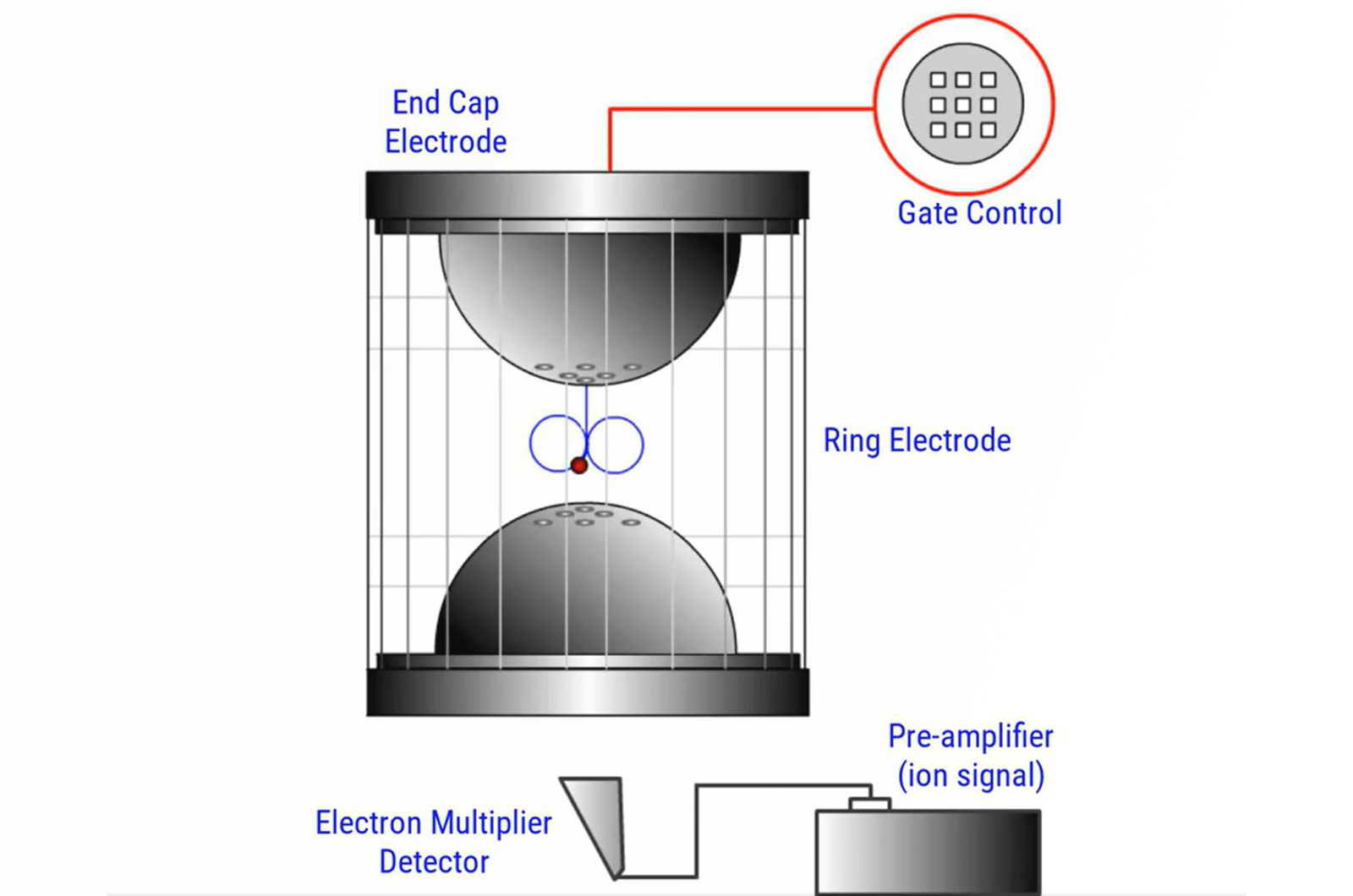
Introduction to Mass Analyzers
In its simplest form the process of mass analysis in GC-MS involves the separation or filtration of analyte ions or fragments of analyte ions created in the ion source. There are several very popular types of mass analyzer associated with routine GC-MS analysis; all of which differ in the fundamental way in which they separate species on a mass-to-charge basis. This module gives an overview of mass analyzers.
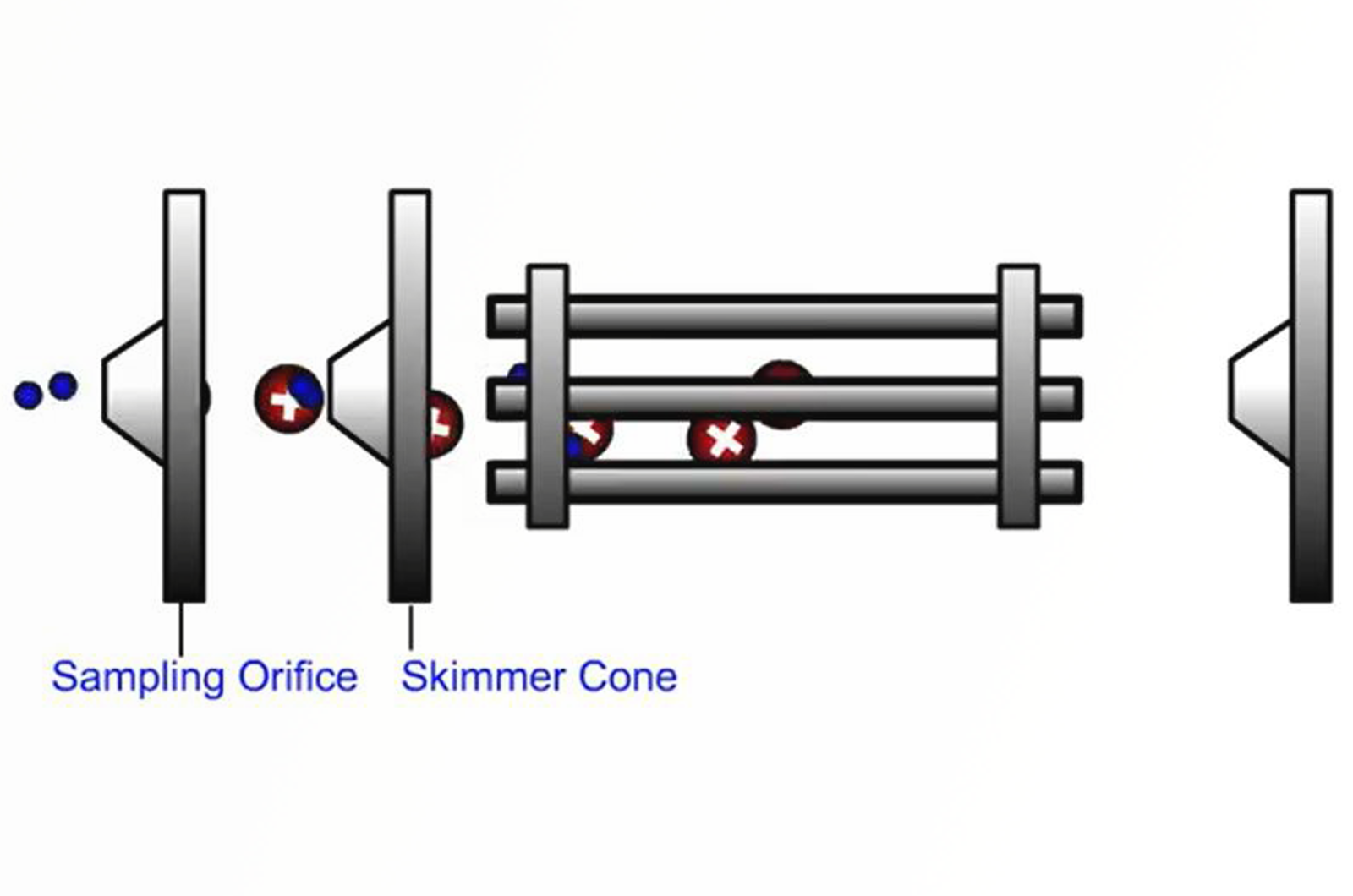
Quadrupole Mass Analyzers
In quadrupole mass analyzing devices, electric fields are used to separate ions according to their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) as they pass along the central axis of four parallel equidistant rods (or poles) that have fixed (DC) and alternating (RF) voltages applied to them.
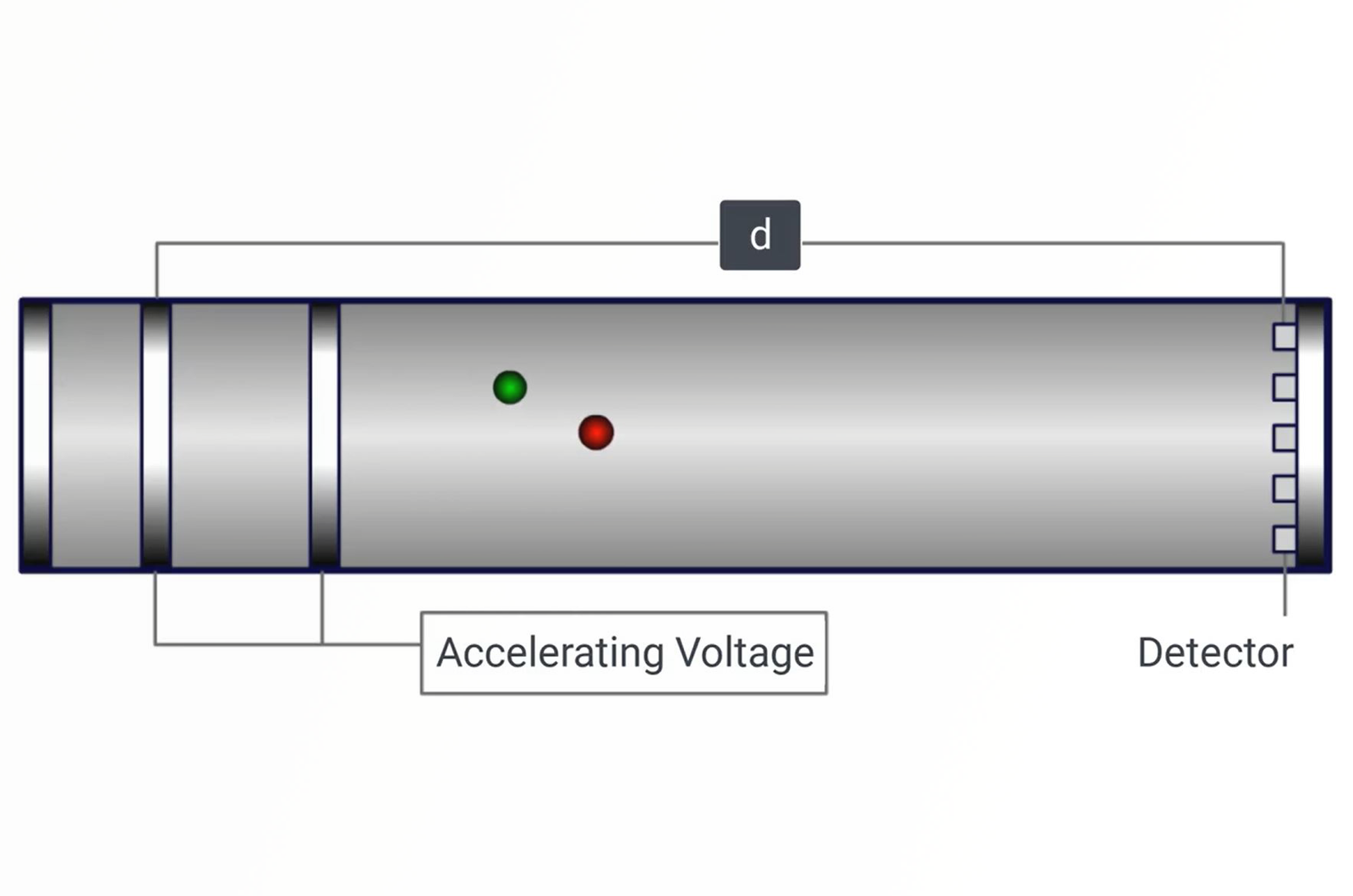
Time-of-Flight (ToF) Mass Analyzers
The basic principles of mass analysis using time-of-flight mass analyzers are relatively straightforward in comparison to many of the other typical mass analyzing devices. Ions are extracted (or produced) in short bursts or packets within the ion source and subjected to an accelerating voltage. The ions then drift or fly down an evacuated tube of set length.