Food and Beverage in Chromatography
In the food and beverage industry, chromatography techniques play a crucial role in analyzing, monitoring, and ensuring the quality, safety, and authenticity of products. CHROMacademy offers comprehensive chromatography training that is applicable to food and beverage professionals. Our courses cover essential techniques, including sample preparation, essential chromatography and mass spectrometry knowledge, practical instrument setup and maintenance, and advanced method development. Whether you're looking to improve quality control, ensure regulatory compliance, or enhance product testing, CHROMacademy provides expert designed training to boost your expertise in chromatography.

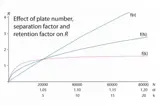
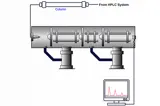
HPLC
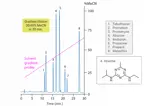
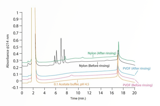
HPLC offers high sensitivity and precision, making it ideal for testing complex mixtures in liquid food and beverage products.
Applications:
- Identifying and quantifying ingredients, preservatives, and additives.
- Detecting contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals, and antibiotics.
- Analyzing sugars, amino acids, vitamins, and flavor compounds.
GC
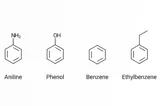
GC is highly effective in analyzing volatile compounds and can separate complex mixtures of gases or liquids with high accuracy.
Applications:
- Analysis of volatile compounds like flavor, aroma, and essential oils.
- Detection of solvents, residual pesticides, and environmental contaminants.
- Testing for alcohol content and preservatives in beverages.
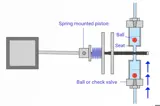
Sample Preparation
Sample preparation is a crucial step in chromatographic analysis in the food and beverage industry, and its importance cannot be overstated.

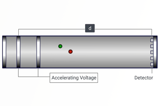
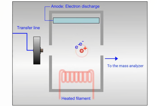
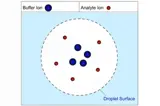
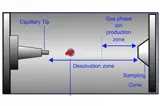
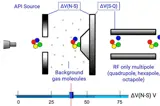
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical tool used extensively in the food and beverage industry to identify and quantify compounds, detect contaminants, and ensure the quality and safety of products. MS provides detailed molecular information, making it indispensable for food quality control, flavor analysis, traceability, and regulatory compliance. CHROMacademy offers MS training that covers key mass spectrometric techniques used in food and beverage analysis.
GC-MS
GC-MS is a highly sensitive and widely used technique for analyzing volatile and semi-volatile compounds in food and beverages.
Applications:
- Flavor and fragrance analysis: Identifying and quantifying volatile compounds responsible for taste and aroma.
- Pesticide residue analysis: Detecting trace levels of pesticides in food products.
- Essential oil analysis: Analyzing components in plant-based products (e.g., in herbs or spices).
- Contaminant detection: Identifying contaminants such as solvents or adulterants in food.
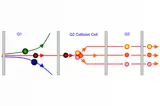
LC-MS
LC-MS is ideal for analyzing non-volatile, thermally labile, and polar compounds that are not amenable to GC analysis.
Applications:
- Foodborne pathogen detection: Identifying and quantifying microorganisms or toxins, such as mycotoxins (e.g., aflatoxins), in food.
- Additives and preservatives analysis: Detecting food additives, preservatives, artificial sweeteners, and colorants in beverages or processed foods.
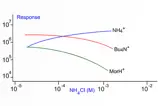
- Nutrient profiling: Measuring essential nutrients such as vitamins, amino acids, and fatty acids in food products.
- Contaminant analysis: Quantifying heavy metals or environmental contaminants like polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in food products.