Essentials for New Analytical Scientists
Endorsed by

This learning path covers essential skill sin basic lab skills, HPLC, GC, GC-MS, LC-MS, sample preparation, and data analysis.
76 Modules 1 Webcast
77 Items

HPLC Introduction
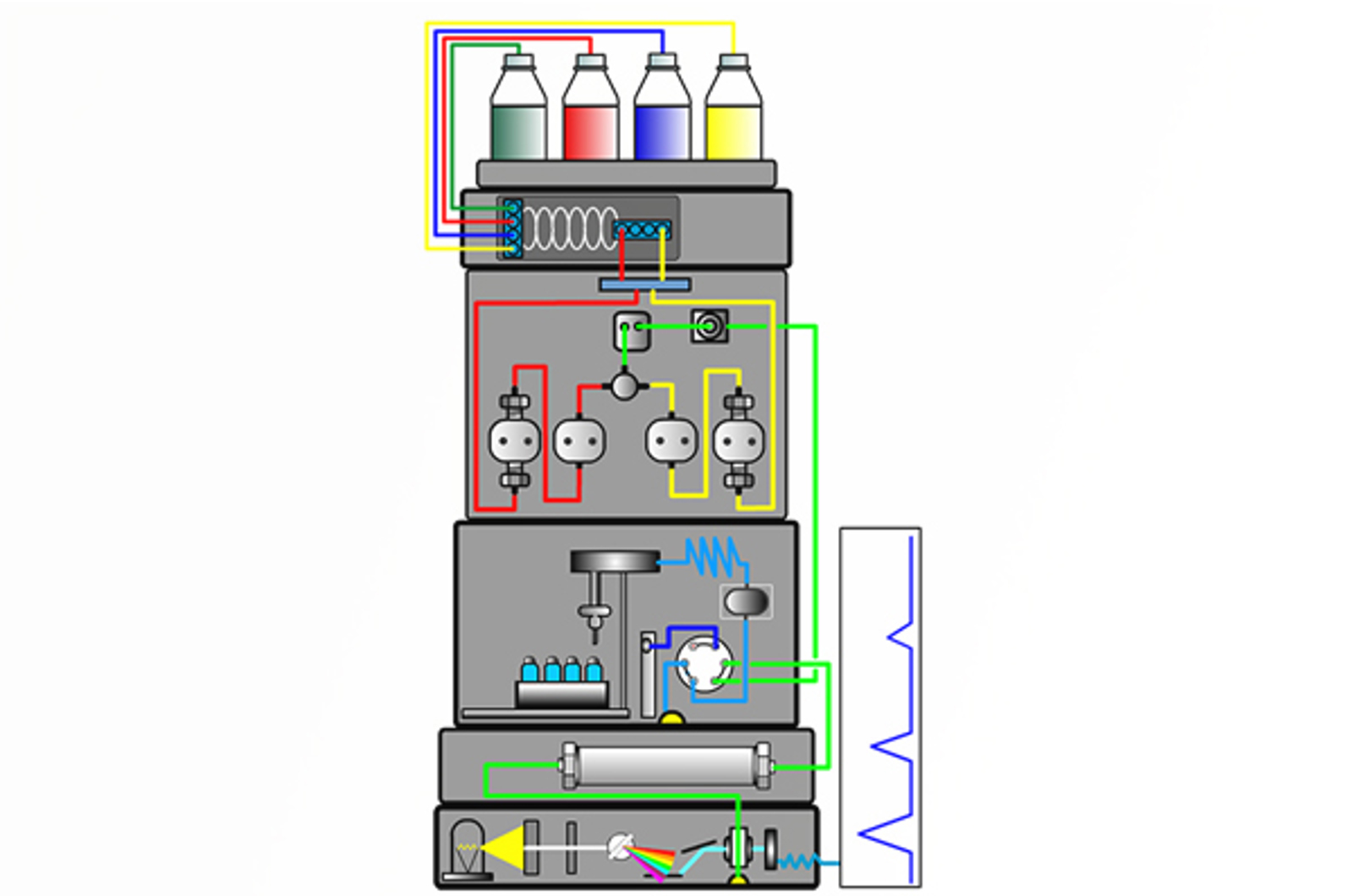
The aim of this module is to give a brief history of liquid chromatography and compare and contrast high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with gas chromatography (GC). Liquid chromatography (LC) is explained, and the function of each component of the HPLC system discussed. The chromatogram is also introduced.
Endorsed by 

HPLC Chromatographic Parameters
The aim of this module is to introduce and explain the concept of chromatographic resolution. The resolution equation will be defined and its dependence on the chromatographic parameters retention factor, selectivity, and efficiency illustrated.
Endorsed by 
Mobile Phase Considerations
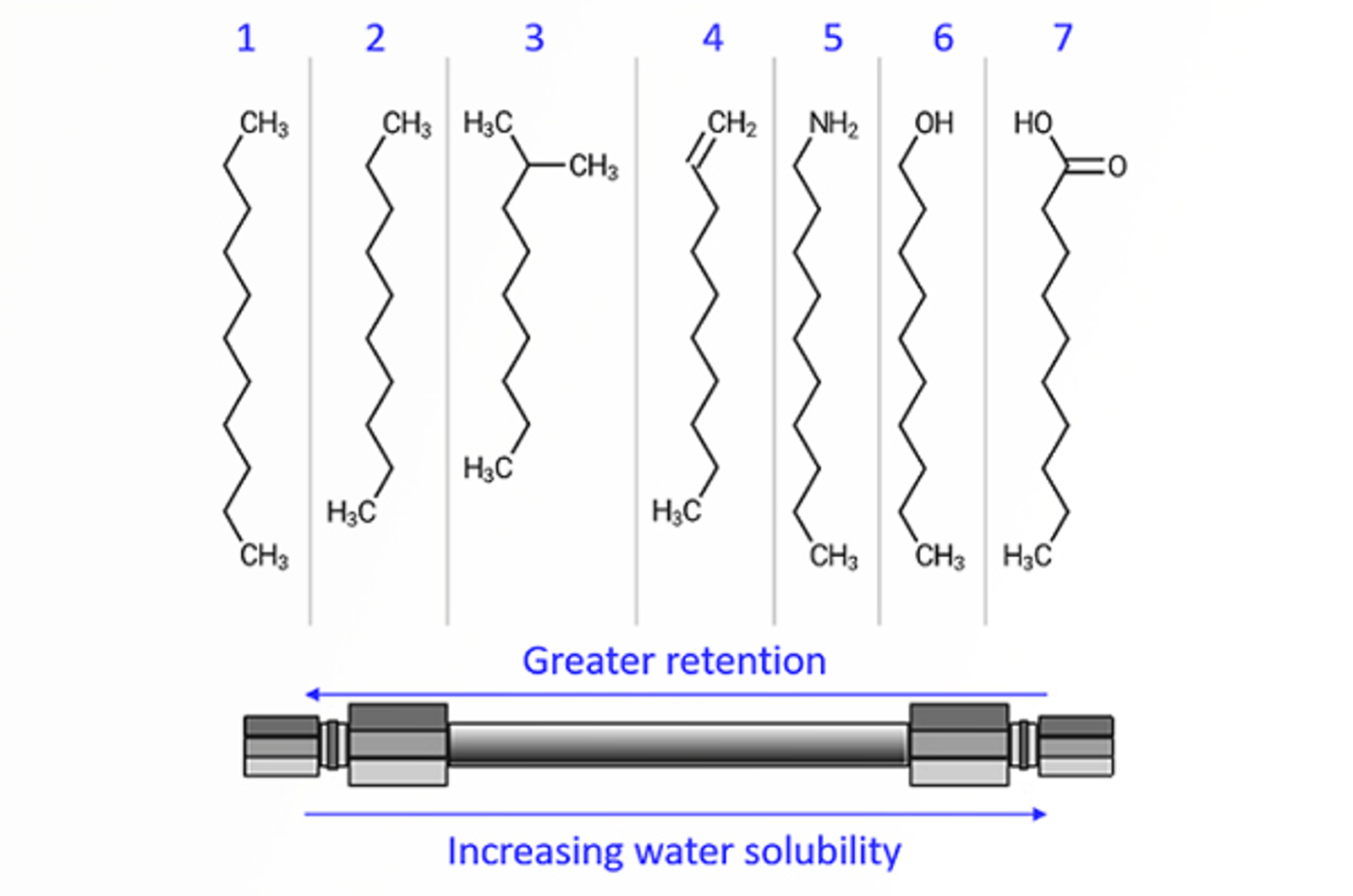
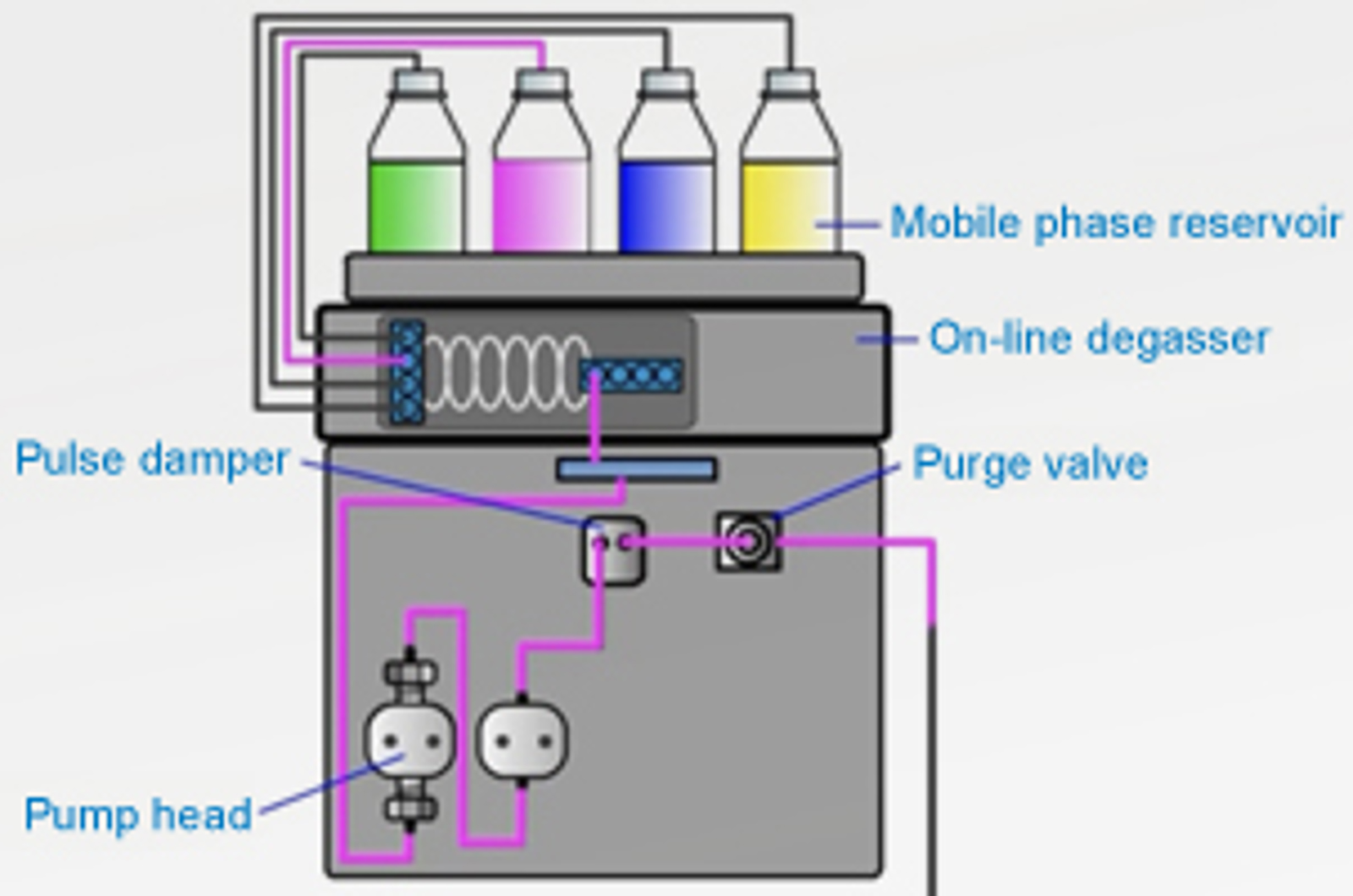
The aim of this module is to explain the purpose of the mobile phase in HPLC. Topics include the best way to prepare mobile phase, potential problems caused by improper preparation and use of mobile phases, and the way that mobile phase composition effects retention and selectivity in reverse phase HPLC.
Endorsed by 
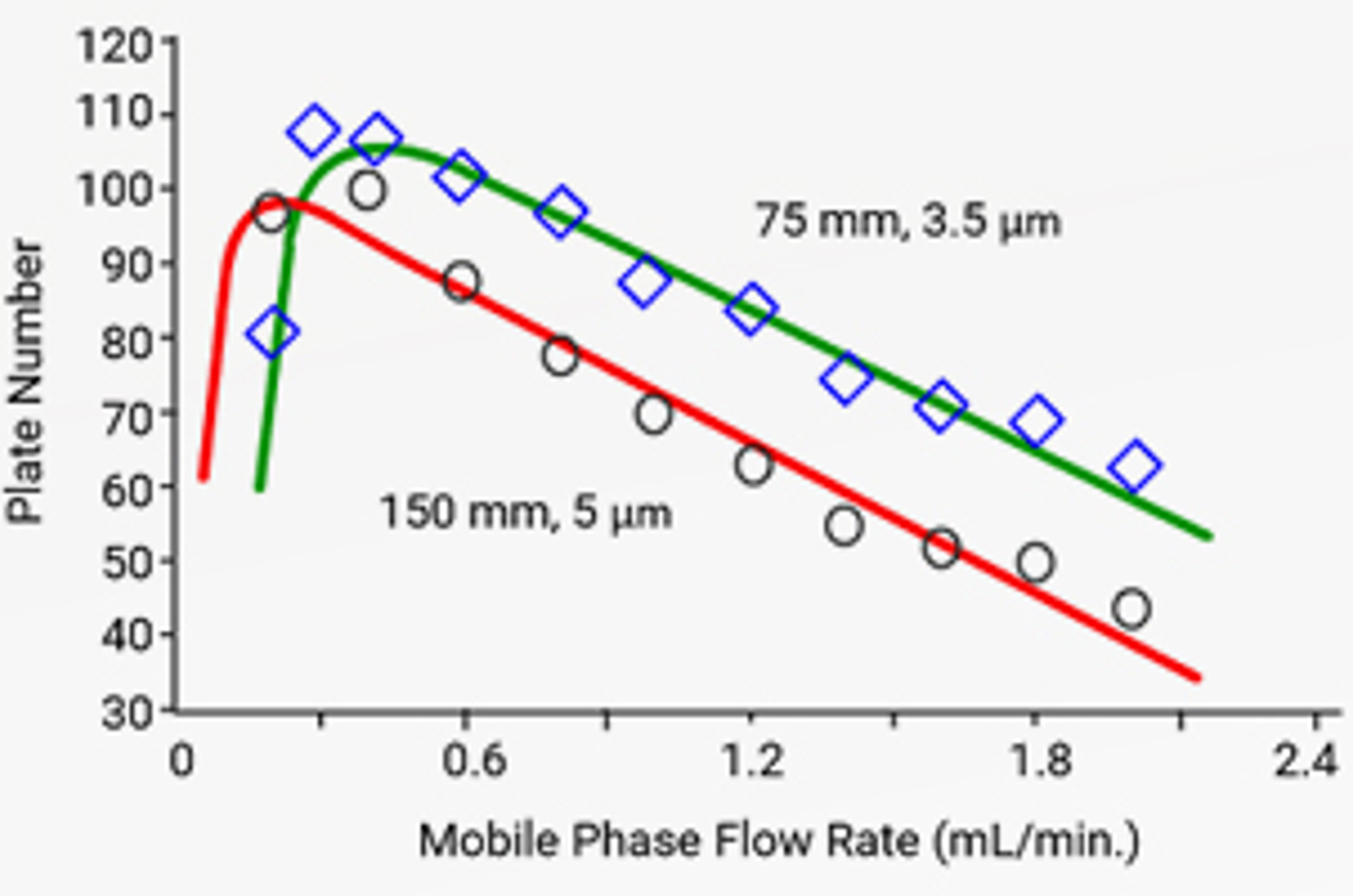
HPLC Column Chemistry
The aim of this module is to introduce silica as a major stationary phase support for reversed phase HPLC separations and for normal phase applications. The use of bonded phases in various chromatographic applications, and the influence of surface silica silanol groups on chromatographic separations is illustrated. Modern bonded phases that give an advantage to today’s chromatographer are introduced.
Endorsed by 

HPLC Band Broadening
The aim of this module is to illustrate the principle of band broadening in HPLC. The van Deemter equation and the terms of the equation will be defined and explained. The effects of eddy diffusion, longitudinal diffusion, and mass transfer on the efficiency of chromatographic peaks will be explored.
Endorsed by 
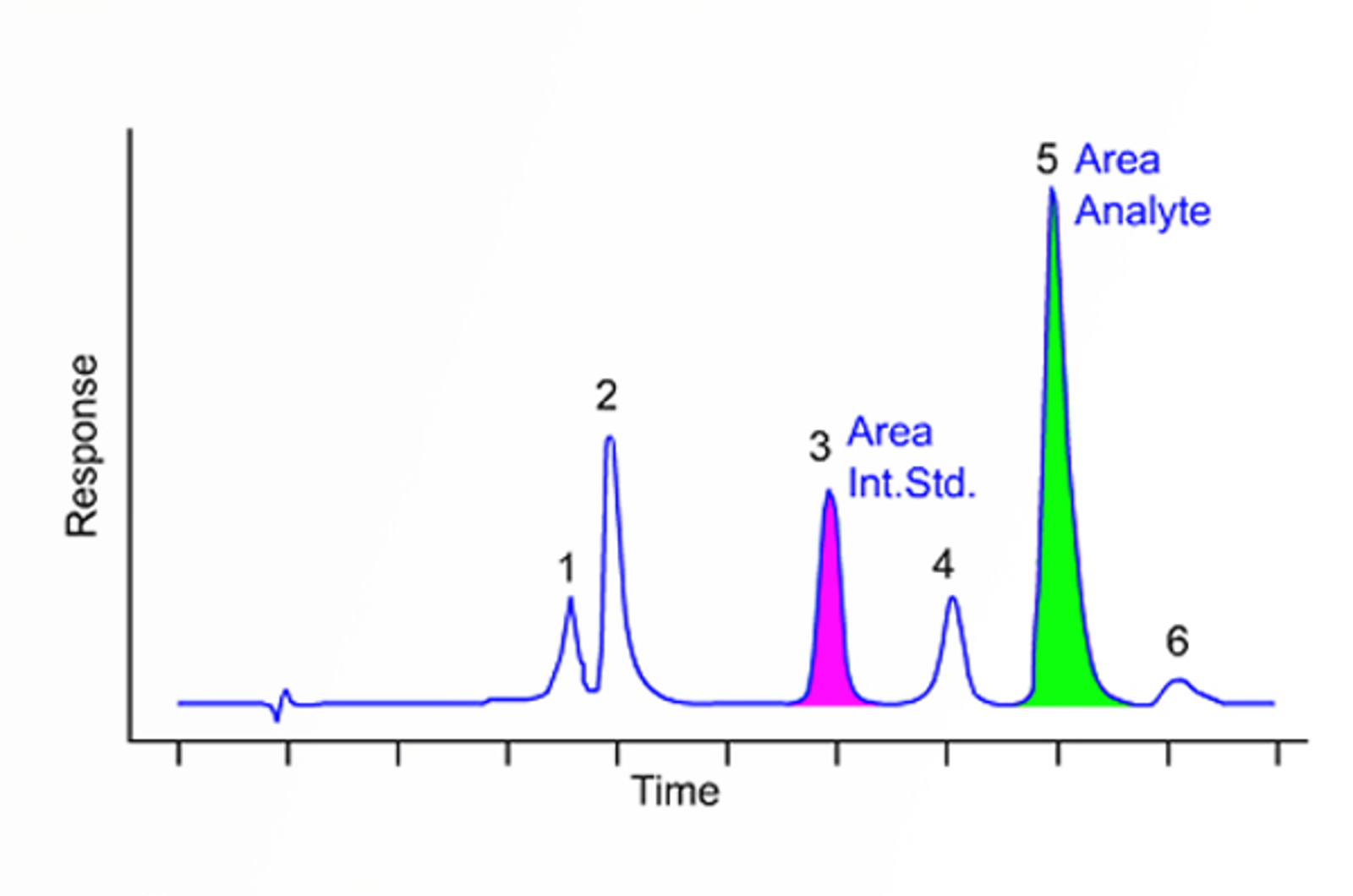
Quantitative and Qualitative HPLC
The aim of this module is to define quantitative HPLC and explain the information that can be derived from this type of HPLC analysis. We highlight the principles of peak identification and analyte characterization from a practical perspective.
Endorsed by 
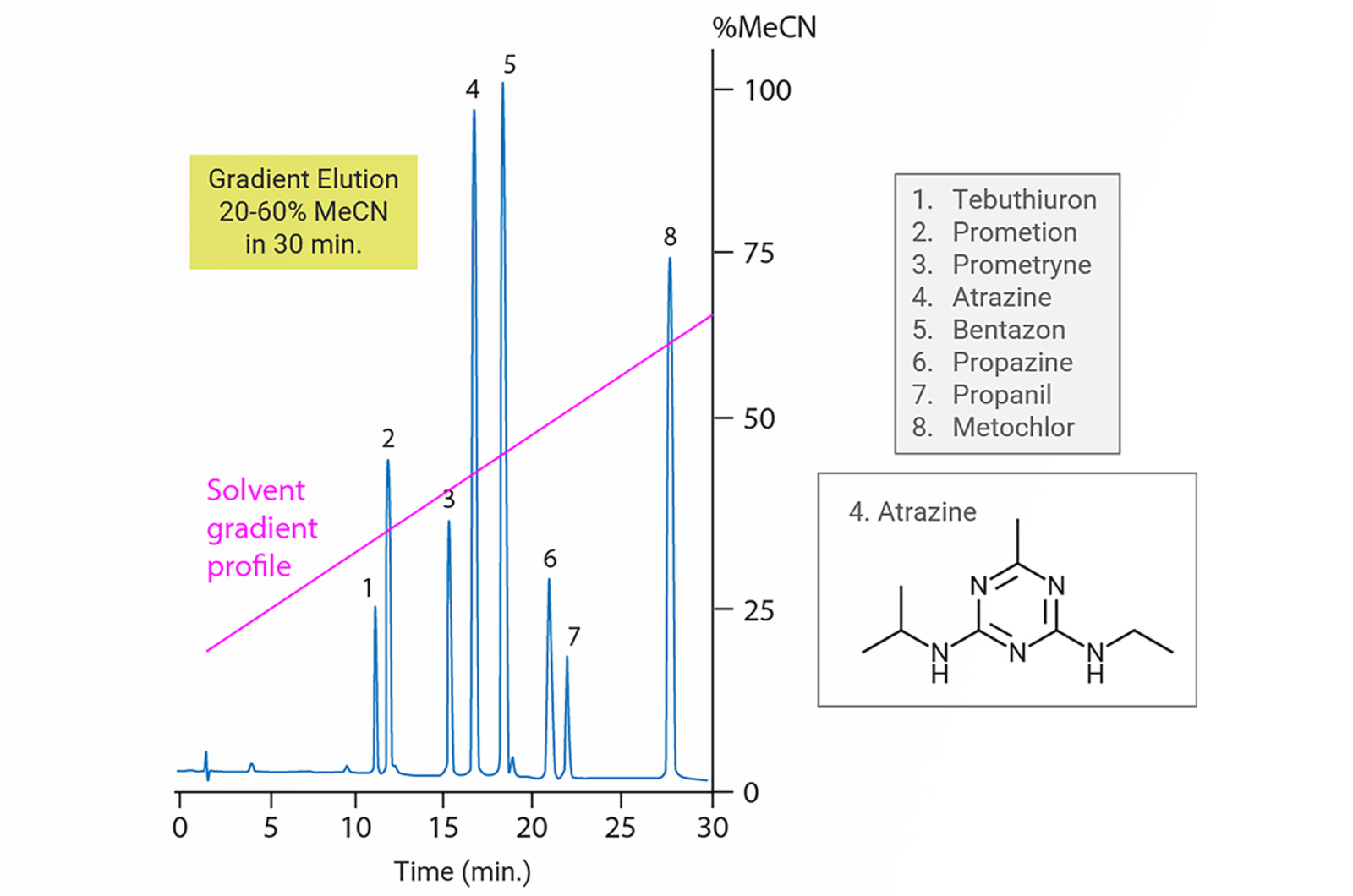
Gradient HPLC
The aim of this module is to explain the problems that can be encountered when using isocratic HPLC.
Endorsed by 
Practical HPLC Video Bootcamp
Join us for a little over an hour on this step-by-step guide through setting up an HPLC instrument. Avoid common errors and pitfalls and understand every step of the process to get your instrument set up correctly every time, decrease down-time, and reduce the risk of re-analysis.
Endorsed by 

HPLC Method Review and Workload Planning
In this module an experienced analyst takes you step-by-step through the process of how we do this. We'll look in detail at every part of what appears to be a straightforward HPLC method, paying particular attention to the many areas which carry a high risk of error and how we can plan our work to minimize many of these common errors.
Endorsed by 
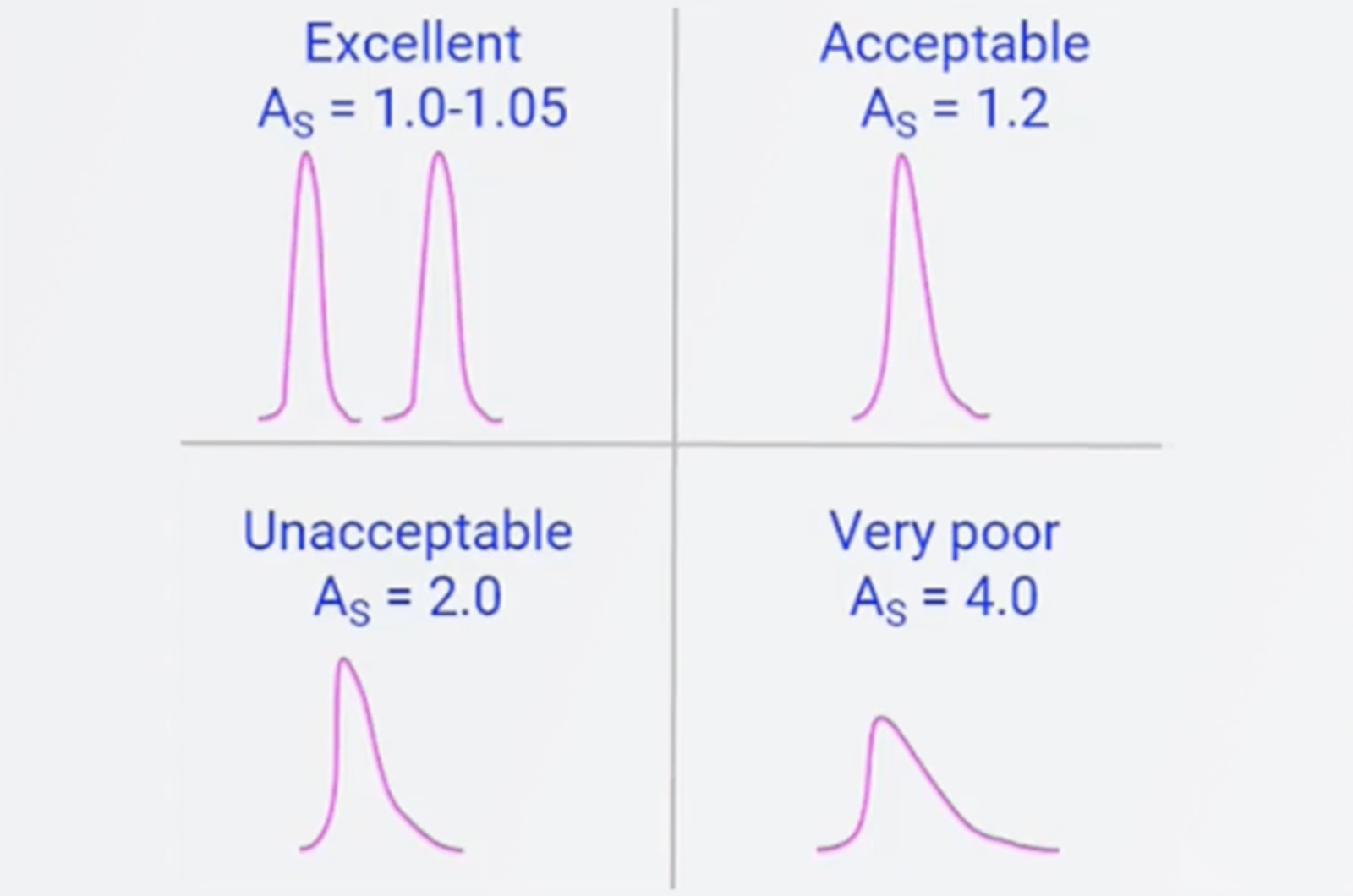
System Suitability for HPLC
System suitability is a series of checks built in to a sequence to ensure all sample data is correct and valid. This webcast will describe how we design and perform system suitability and which chromatographic parameters we should be assessing during the process.
Endorsed by 
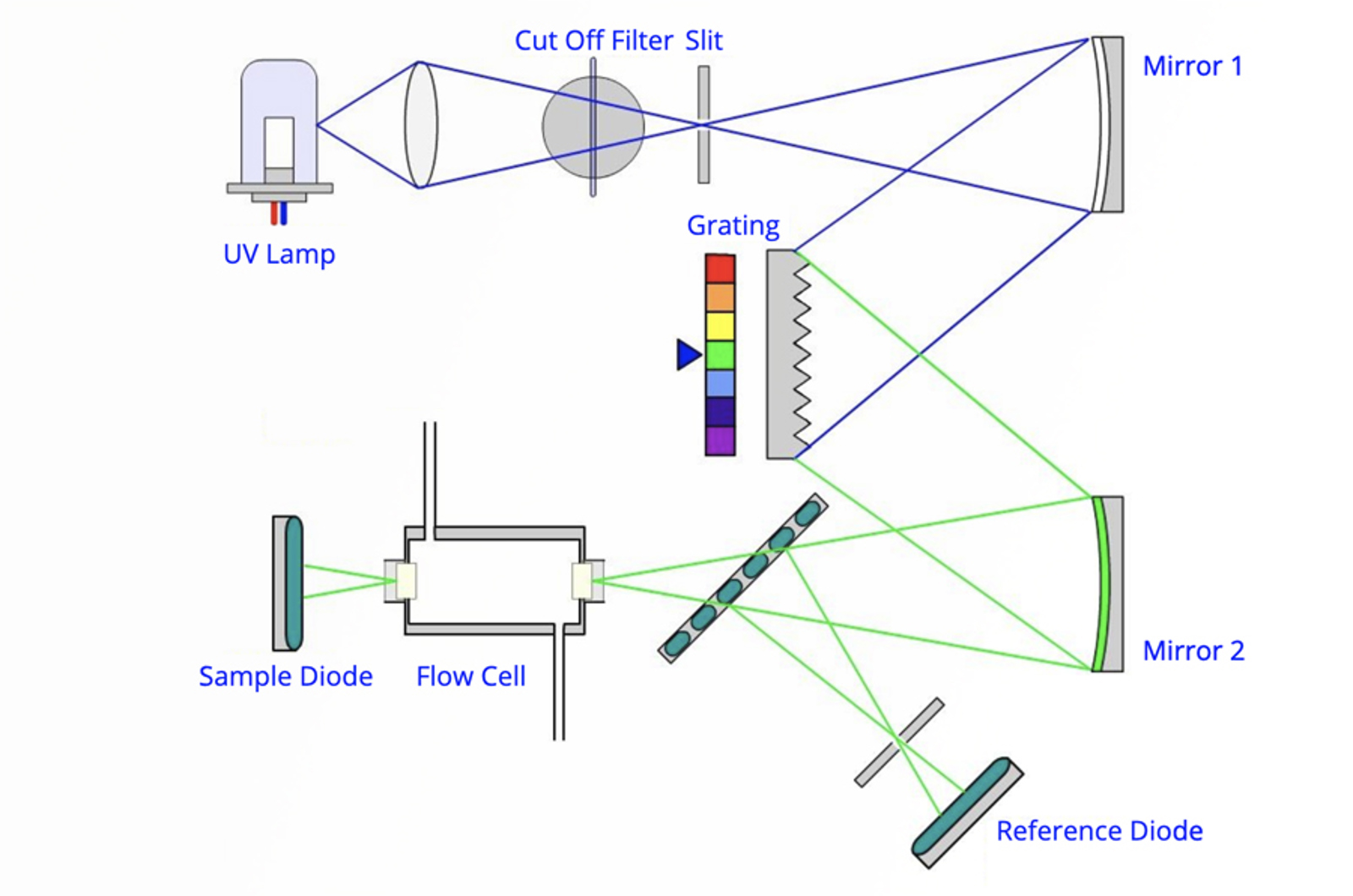
HPLC Detectors
The aim of this module is to describe the purpose and general operating principles of detectors for HPLC. The general terms and concepts by which detector operation and performance are outlined. Specific operating principles of a range detectors for HPLC are covered, including UV-visible, refractive index, and fluorescence detectors.
Endorsed by 

Practical HPLC Video Maintenance
This practical user maintenance module covers common HPLC maintenance operations. The video content demonstrated in this module will allow you to better care for and set up your instruments, which ensures they function correctly and produce the best possible data.
Endorsed by 
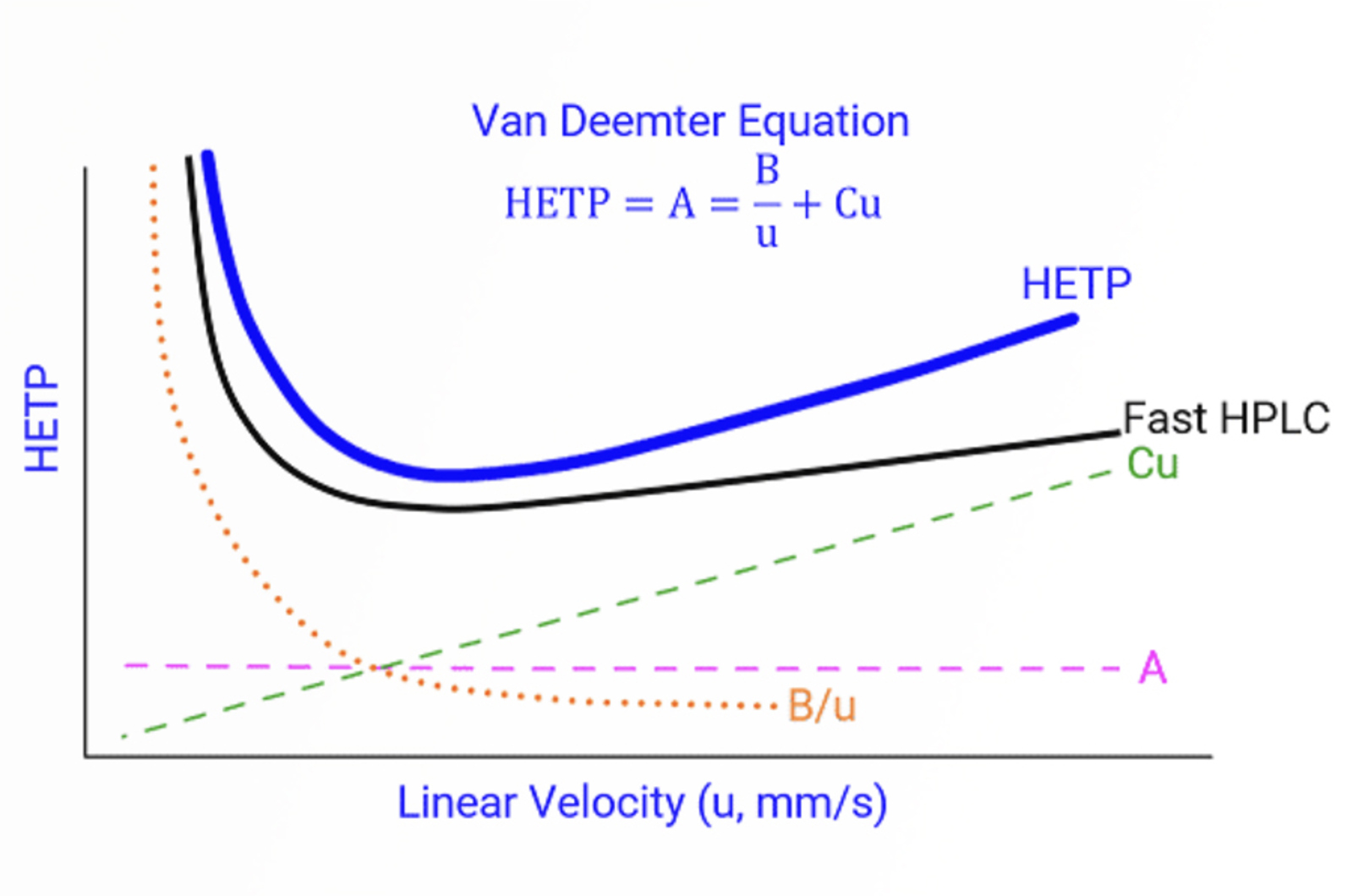
Fast HPLC
The aim of this module is to introduce a variety of methods to speed up HPLC separations, and highlight the limitations of these methods. The fundamental approaches of speeding up HPLC will be explained. We will also investigate the balance between speed and resolution.
Endorsed by 

HPLC Interactive Tools
Our interactive HPLC tools all in one place. The calculators included in this section allow you to quickly transfer gradient and fast HPLC methods. Calculate new injection volume, gradient segment times, flow rates, and more to ensure method transfer success.
Endorsed by 
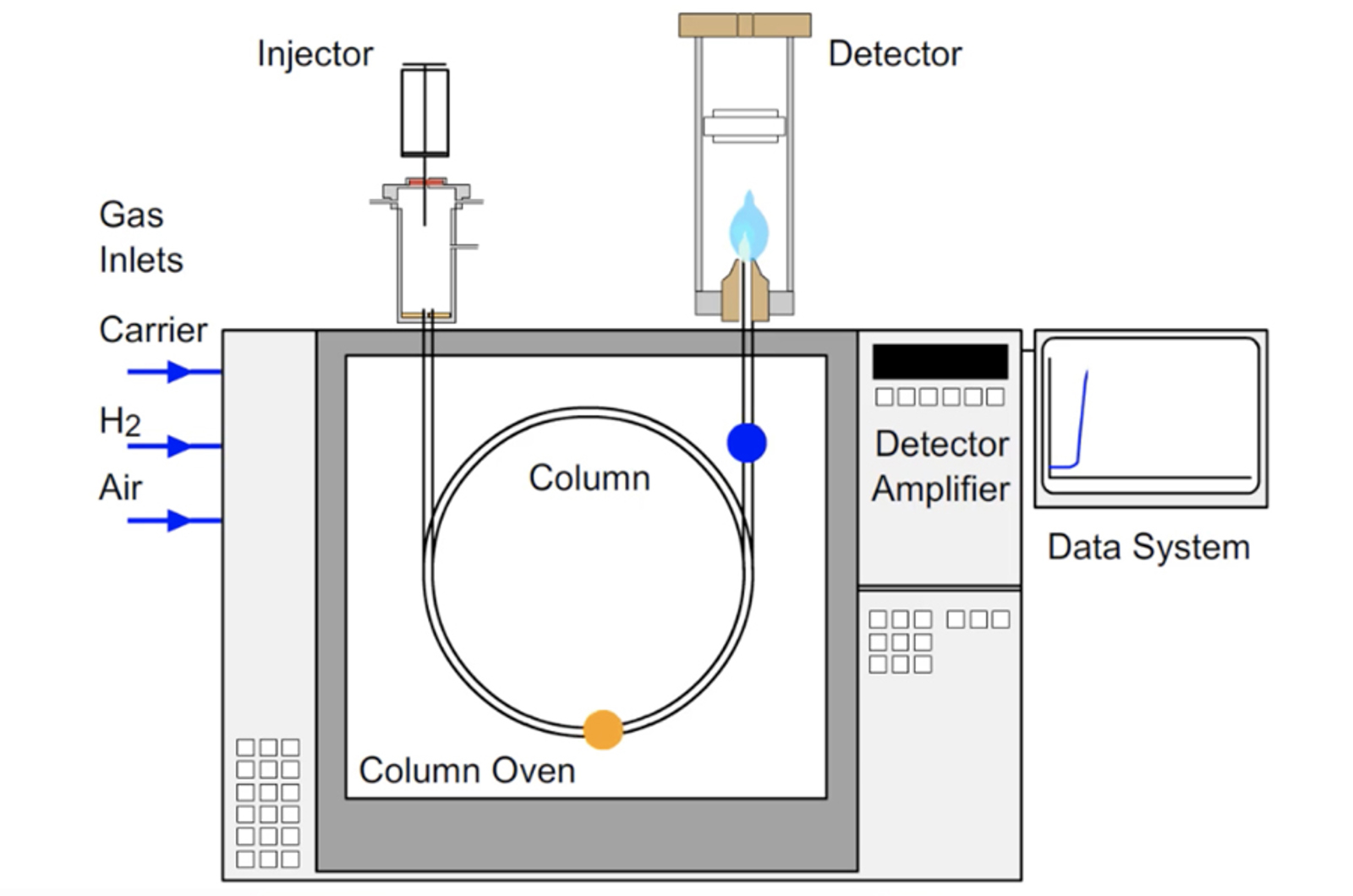
GC Introduction
This short module covers the history of gas chromatography (GC) and introduces the chromatographic process and the major components of a GC instrument. The technique is compared and contrasted with other analytical techniques such as high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The terms and appearance of a typical chromatogram are also explained. We will outline the fundamental basis for separation in GC, and indicate the major advantages of GC and the application areas in which it is used.
Endorsed by 
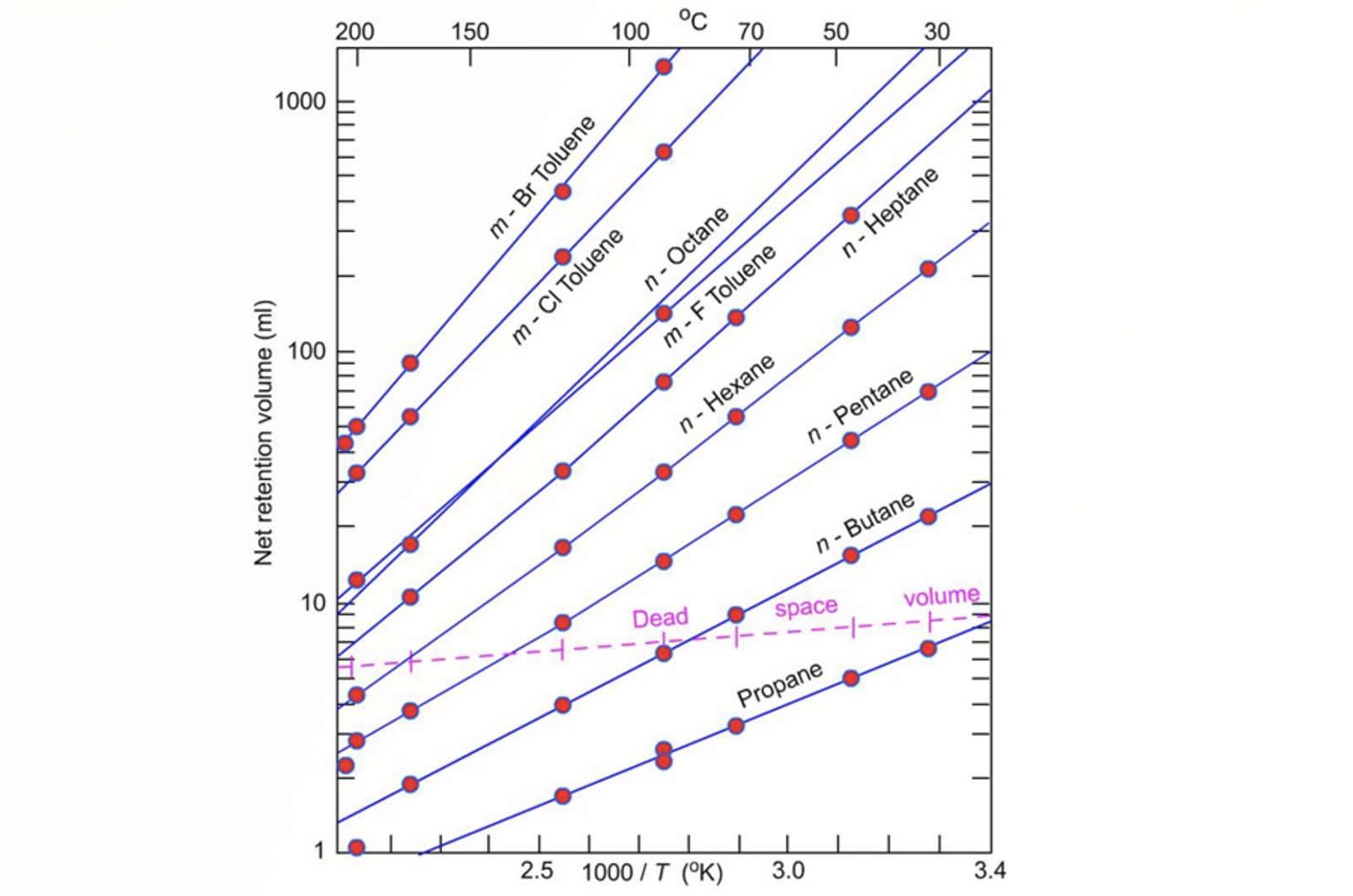
GC Chromatographic Parameters
The most important thing in GC is to obtain the optimum resolution in the minimum time. Each of the important chromatographic parameters (resolution, retention factor, selectivity, efficiency, and asymmetry) are explained and illustrated with real life examples in this module.
Endorsed by 
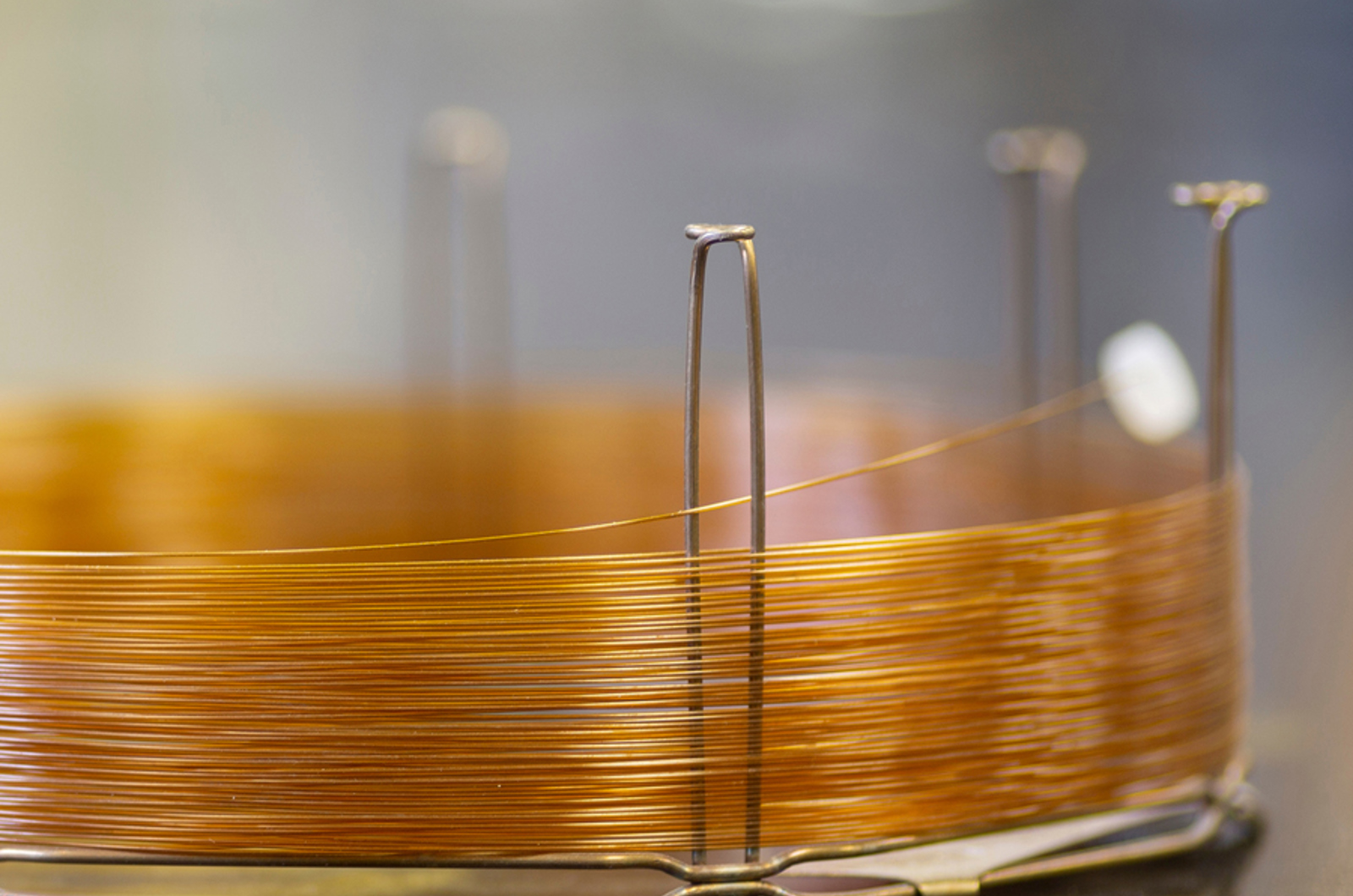
Introduction to GC Columns
The analytical column is where the separation is actually performed. This module will introduce capillary GC columns, the most common type used for GC applications. Providing guidelines on how to prepare, install, and condition a GC column for analysis.
Endorsed by 

GC Columns
The aims of this module include the comparison and contrast of packed and capillary columns. A revision session of of fundamental intermolecular interactions is included in order to relate the various types of interaction to retention in GC. We will explore various stationary phase types and explain the critical factors in choosing a phase. The important physical parameters of capillary GC columns and their relationship with retention, resolution and efficiency in GC separations is investigated.
Endorsed by 
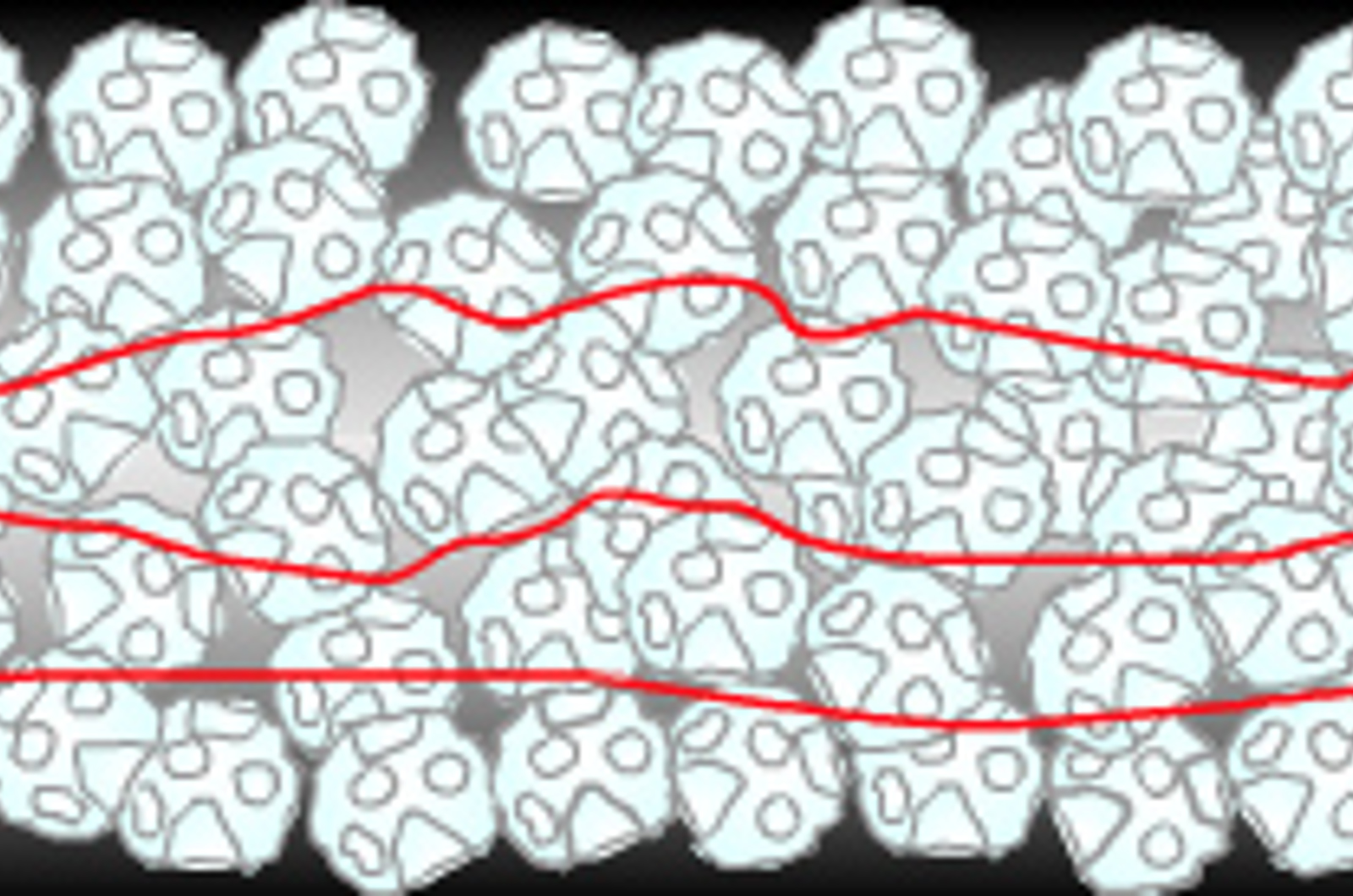
GC Band Broadening
The aims of this module are to illustrate and explain the principles of band broadening in GC, as well as the van Deemter and Golay equations. The effects of eddy diffusion, longitudinal diffusion, and mass transfer on the efficiency of chromatographic peaks will be explained. It will be shown how to use the van Deemter coefficients to illustrate how to optimize the efficiency of chromatographic separations and to reduce band broadening.
Endorsed by 

Practical GC Video Bootcamp
A step by step guide to setting up a GC instrument. From checking the cylinders, dismantling the inlet, to correctly installing a column and lighting an FID. All before shutting the instrument down correctly. This practical module uses video filmed on a GC instrument in the lab to ensure that you get the most realistic walk through of the instrument; allowing you to correctly setup your instrument every time to get the most from it and decrease down-time by avoiding common mistakes.
Endorsed by 

GC Temperature Programming
The aims of this module include illustrating the relationship between temperature and retention in GC.

GC Method Review
When performing an analysis, we follow a written method. This contains all the instructions and settings by which the analysis is performed. For even a simple method, this requires a lot of knowledge and experience. In this module an experienced analyst walks you through all parts of a typical method, explaining all the important areas that require understanding and planning.
Endorsed by 
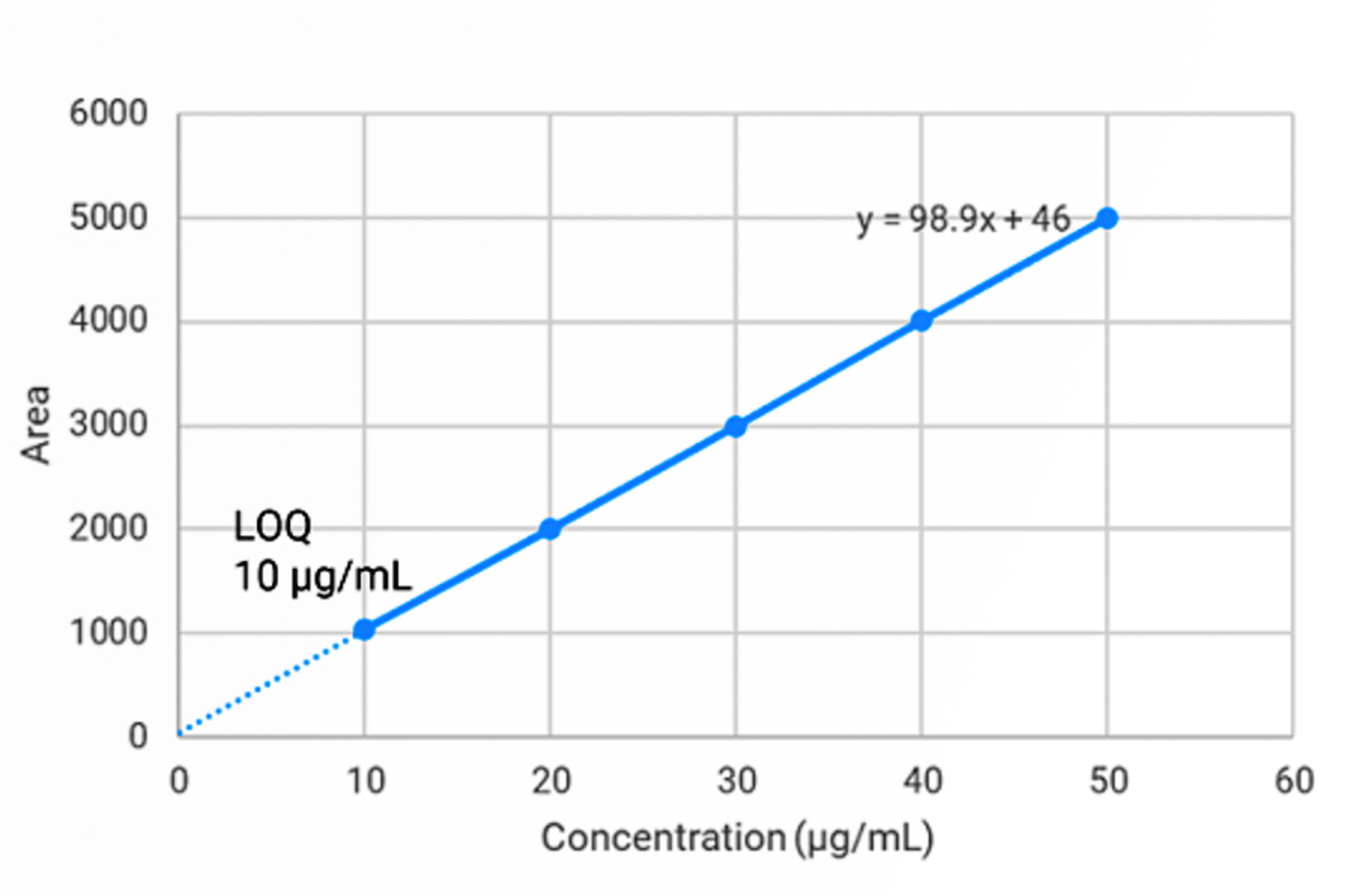
Introduction to System Suitability for Gas Chromatography
As part of that sequence, we perform additional injections which allow us to verify that the entire GC system is working correctly, this is system suitability. The actual parameters assessed during system suitability vary between companies, the type of analysis we are performing, and the method/compounds being used. This module outlines some of the common system suitability tests we see in GC analyses.
Endorsed by 
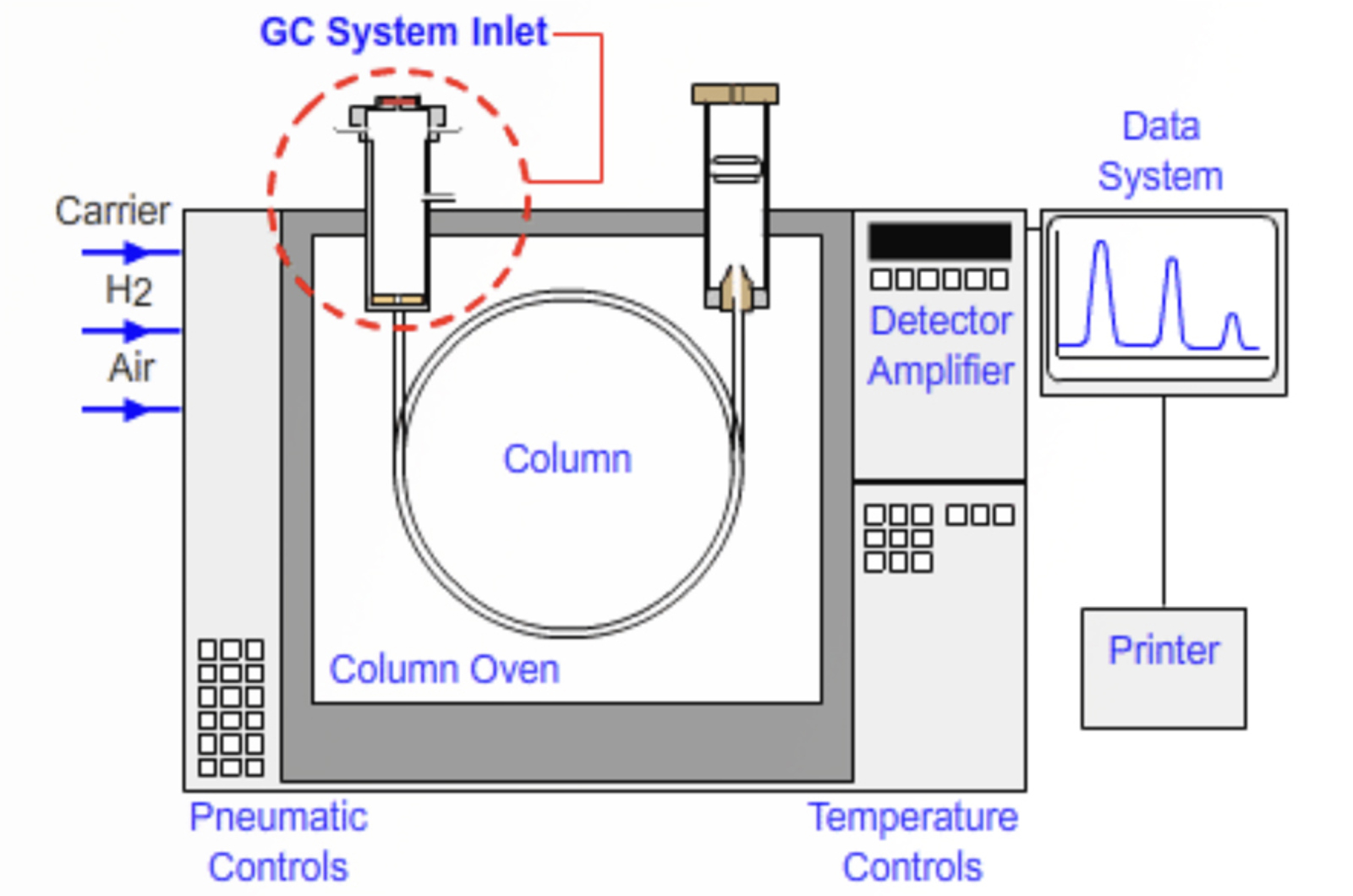
GC Sample Introduction
The aims of this module are to outline the various injector categories for GC as well as describe the components and working principle of split and splitless injectors. We will look at problems associated with each of these injection types and explain how they are overcome practically and give examples of optimizing inlet parameters. The working principles, components, and optimization for a series of common GC inlets are explained, and choices for inlet consumables are also discussed.
Endorsed by 

GC Detectors
The aim of this module is to highlight the various detector types available for GC and describe the performance characteristics associated with these detectors. The working principles behind flame ionization, electron capture, nitrogen phosphorous, thermal conductivity, and flame photometric detectors (FID, ECD, NPD, TCD, and FPD, respectively) are explained, as well as the optimization process for each of the detector types.
Endorsed by 
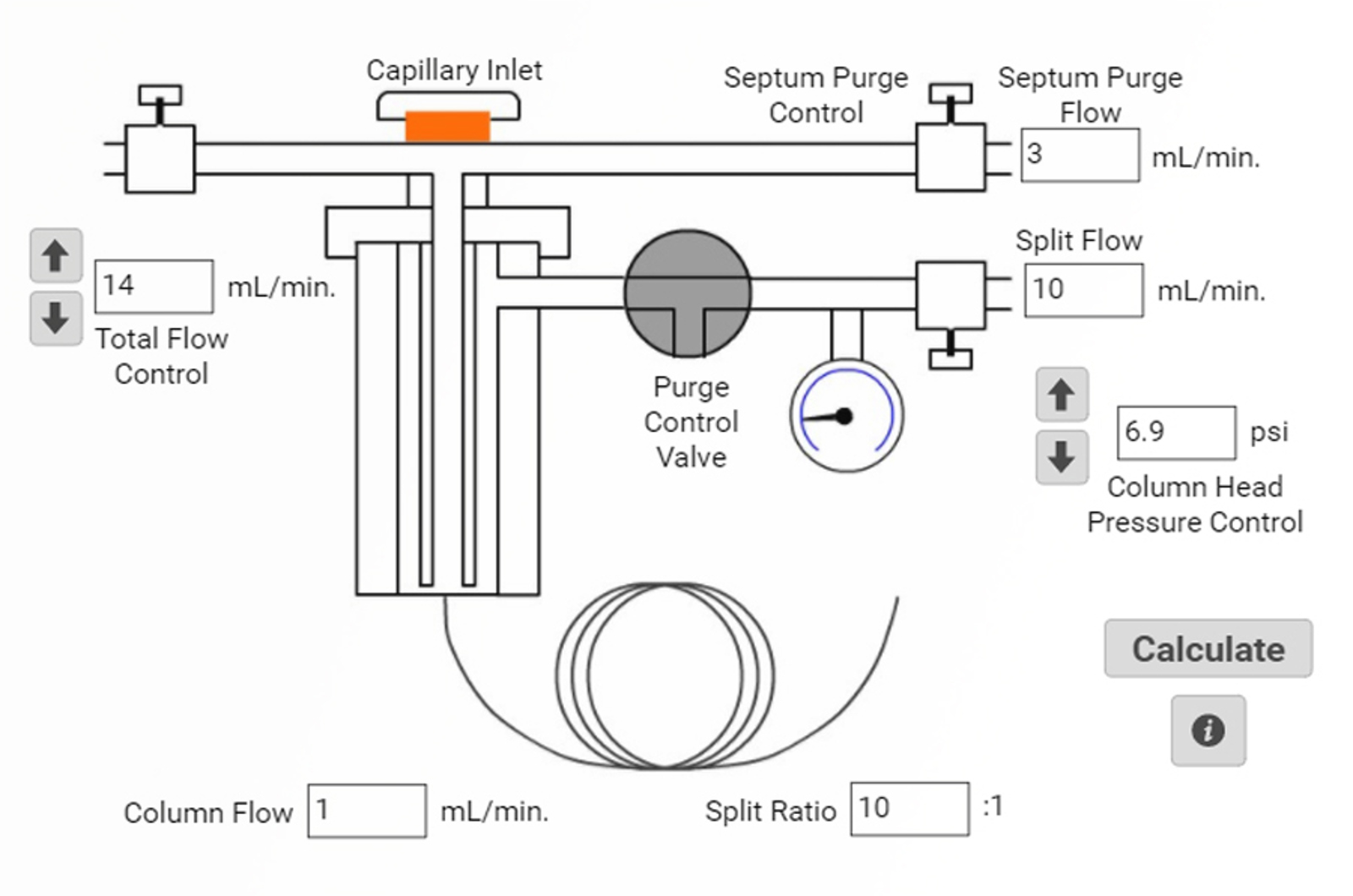
GC Interactive Tools
All of our interactive GC tools in one place. The GC backflash calculator is an invaluable tool to ensure that you can optimize your GC injection volume avoiding problems such as contamination due to backflash. Calculate the split ratio and the flows and pressures using our other interactive tools; providing understanding of how the GC inlet and gas supply function.
Endorsed by 
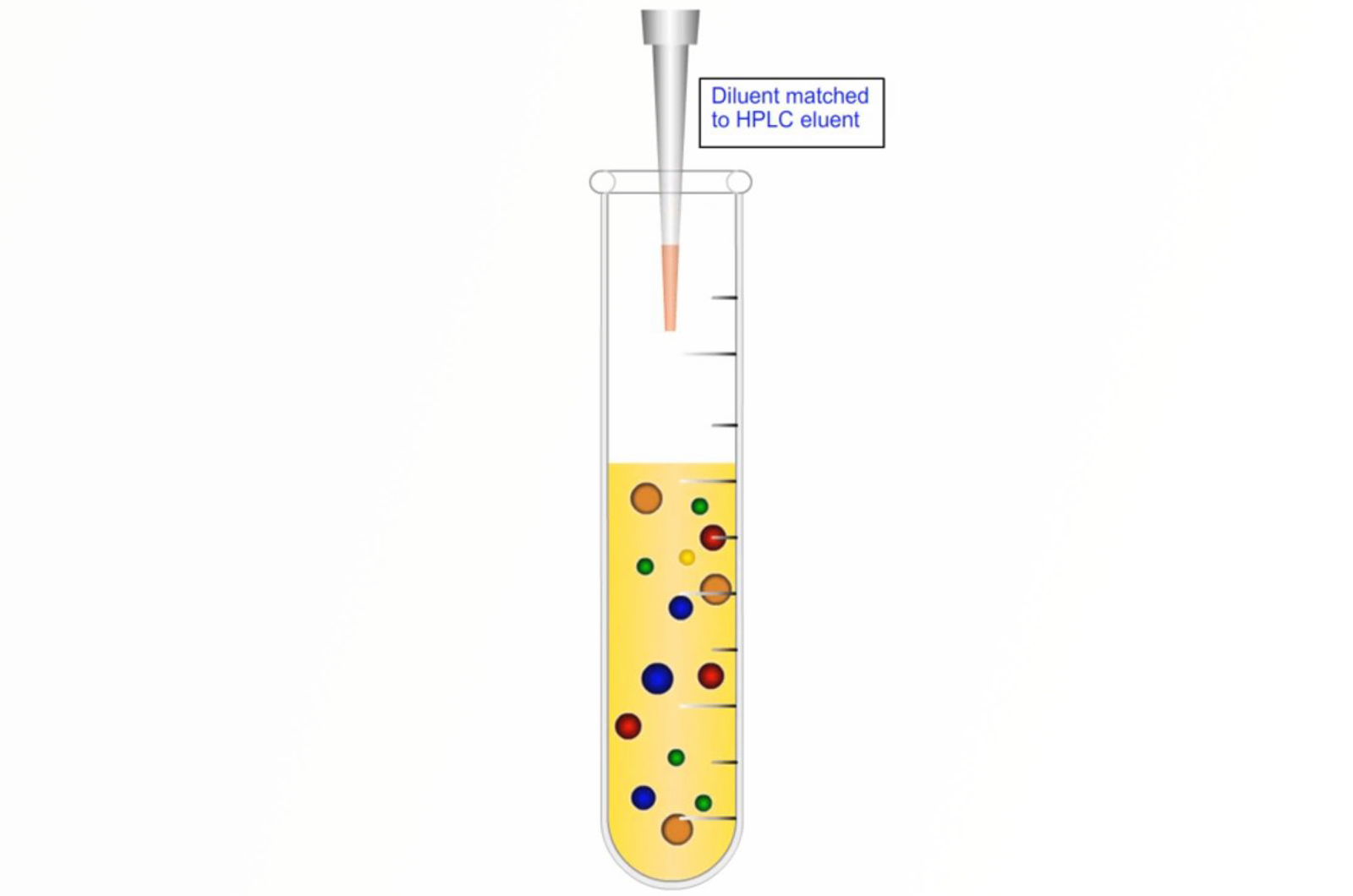

Primary Sample Preparation Techniques
This module takes an initial look at the science behind the most commonly used sample preparation techniques.
Endorsed by 
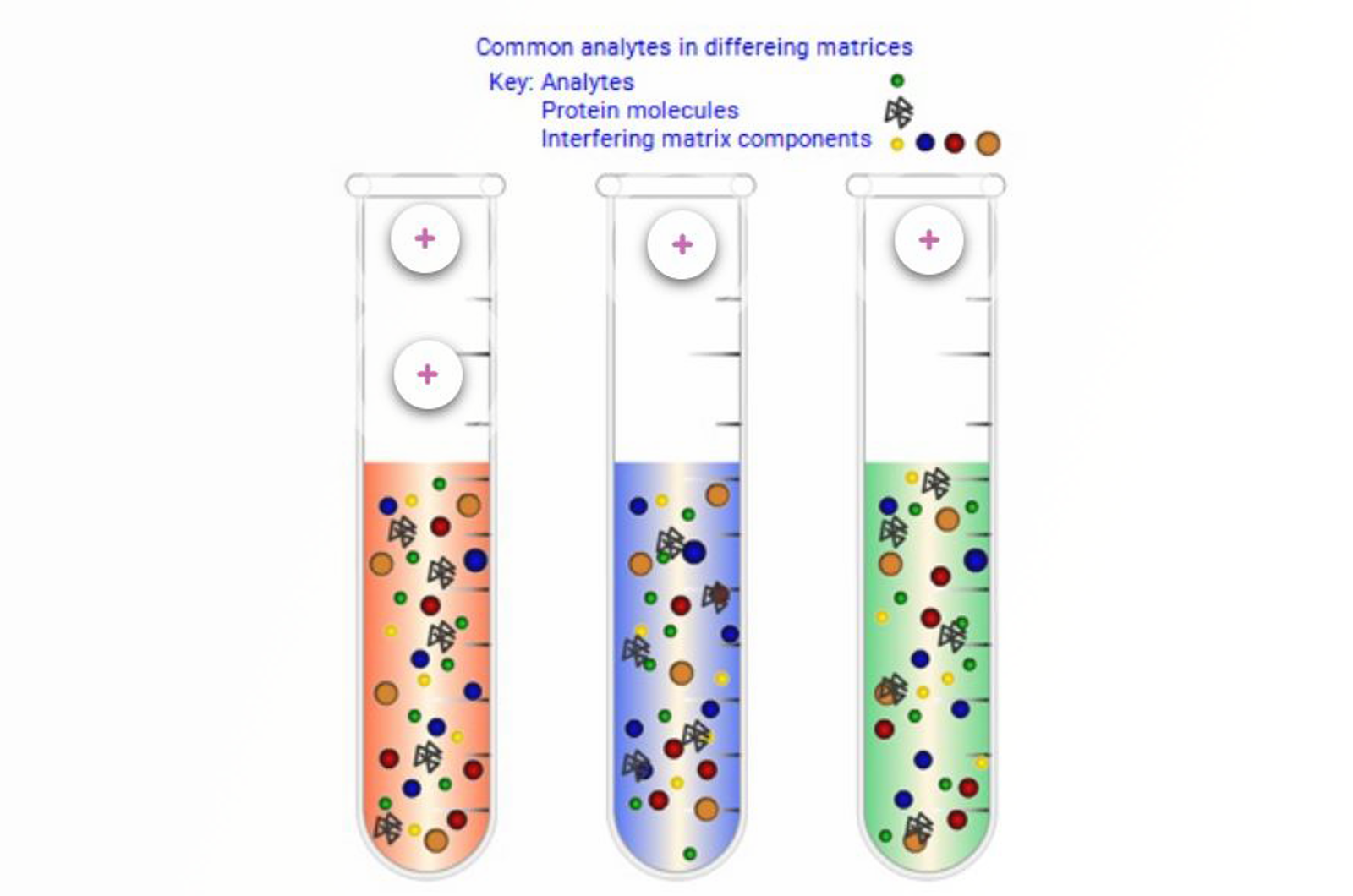

Molecular Properties
This module introduces the concept of functional group chemistry as a means of targeting separation mechanisms in liquid and solid phase extraction (SPE).
Sponsored by 
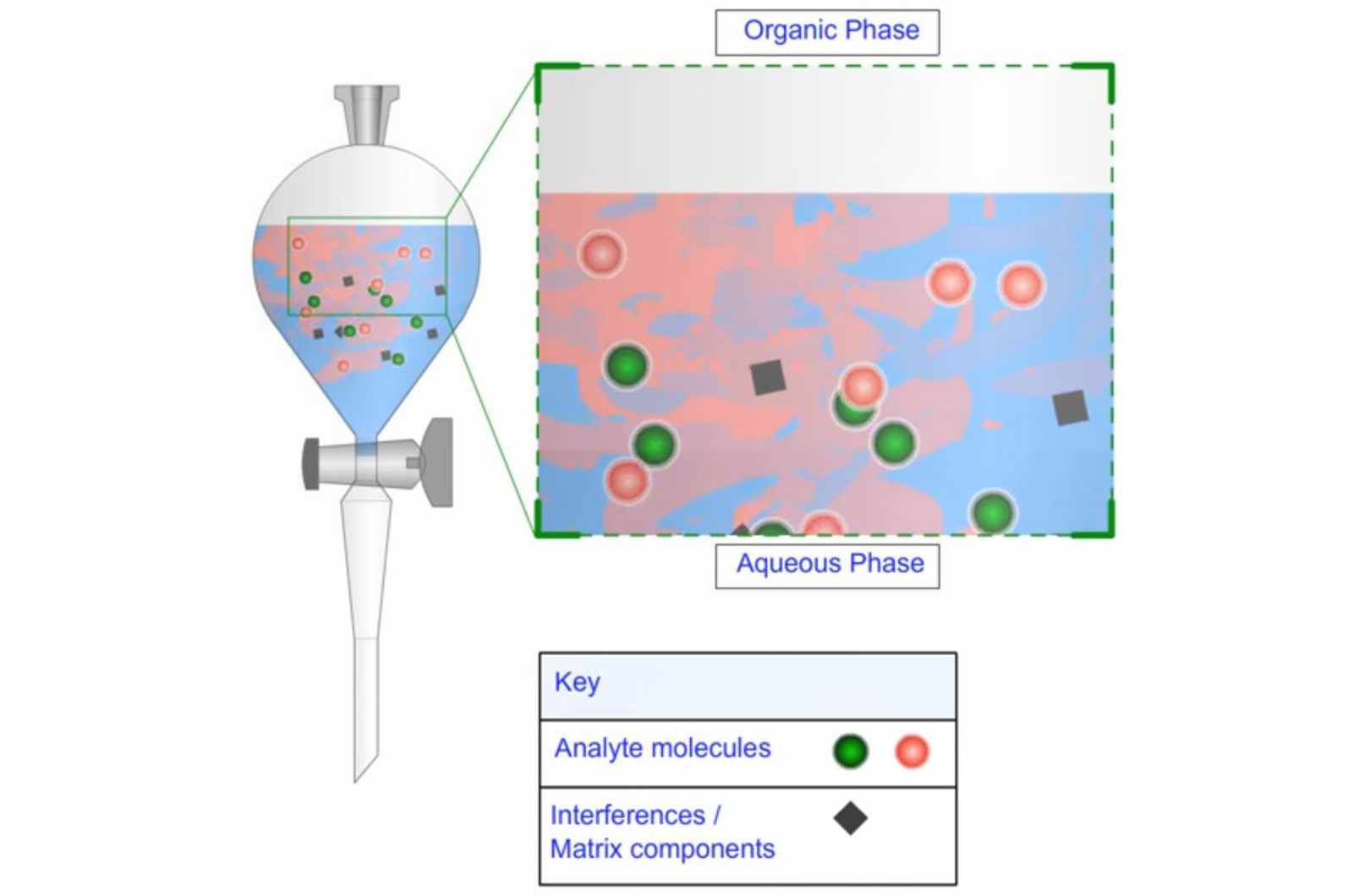
Liquid/Liquid Extraction Techniques
In this module, the basic principles of liquid/liquid extraction (LLE) are described, as well as an overview of limitations and drawbacks of LLE protocols. Specific advice is given for various problems that are routinely encountered. Emulsions and how to deal with them is discussed, and support-assisted liquid/liquid extraction (SALLE) is presented as a useful variation on standard liquid/liquid extraction.
Endorsed by 
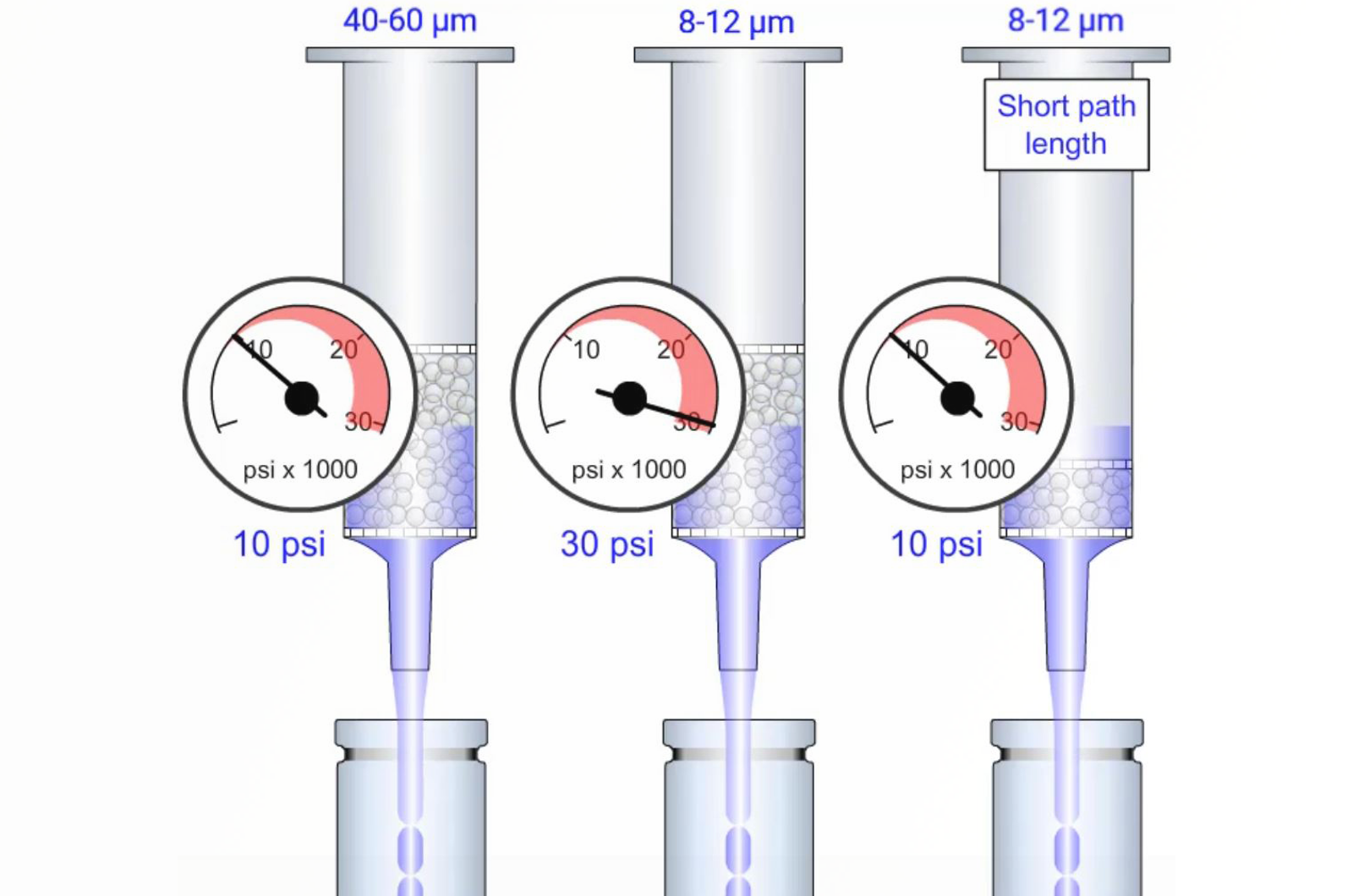
SPE Overview
This module introduces the terminology associated with solid phase extraction (SPE). It explains the chemistry and physical properties associated with SPE sorbents and substrates, the different steps in a solid phase extraction protocol, sorbent selection, eluent solvent strength optimization, and the use of pH and ionic additives to control selectivity in SPE.
Endorsed by 
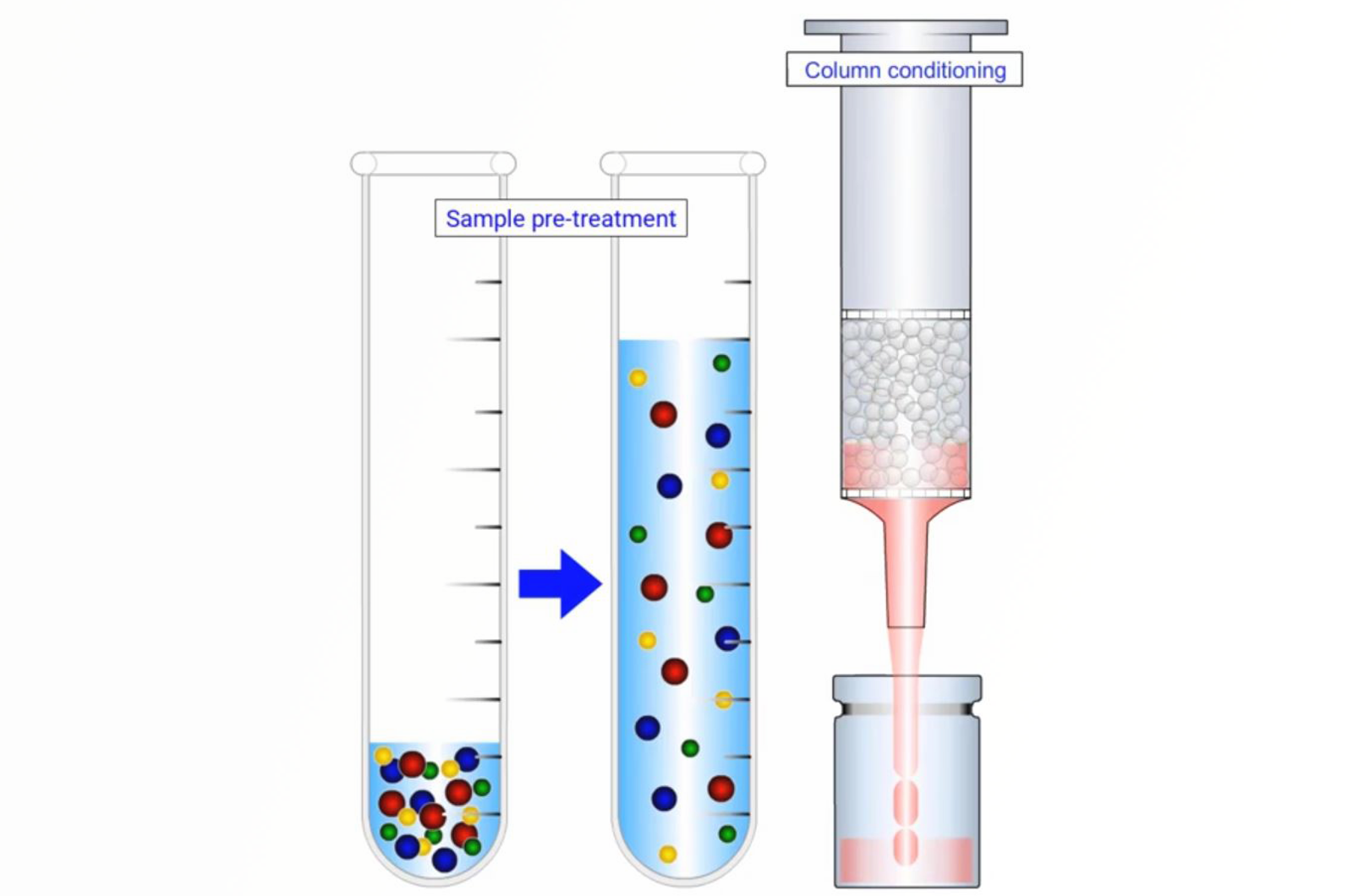
SPE Mechanisms
The purpose of this module is to highlight the various steps in the protocol for various modes (sorbents) for conventional solid phase extraction procedures including: non-polar SPE, polar SPE, cation exchange SPE, anion exchange SPE, and mixed-mode SPE. For each mode the various portocol steps are examined in terms of the solvents and solutions used, sorbents used, solvent additives, pH, and ionic strength manipulation.
Endorsed by 
SPE Method Development
This module fully investigates the various aspects of practical SPE, as well as describing the basic principles and stages of method development in SPE.
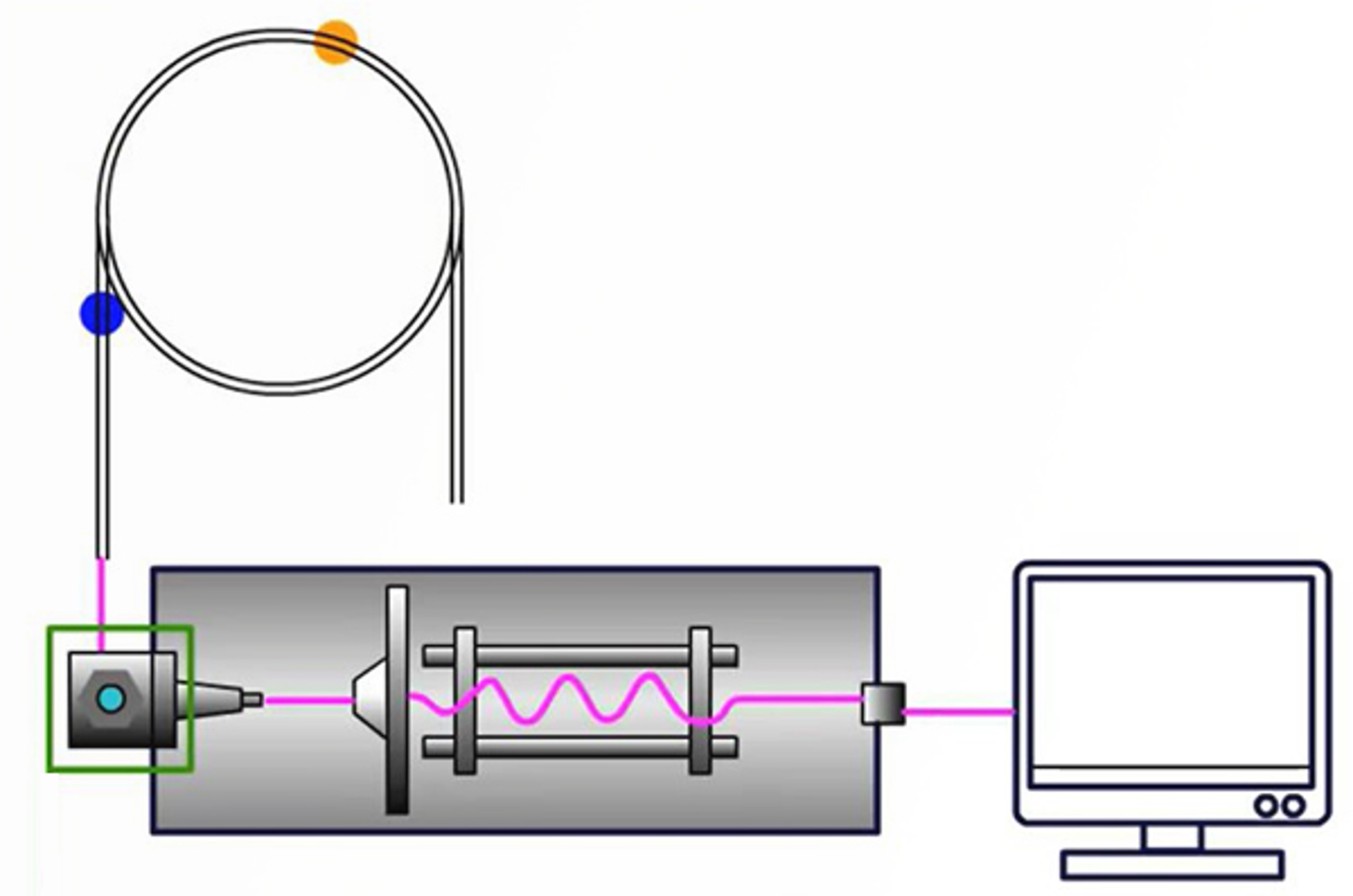
GC-MS Introduction
Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is a hyphenated technique which combines the separating power of gas chromatography (GC) with the detection power of mass spectrometry (MS). This module will explore the instrument acquisition methods used and examine the type of data that can be produced from such systems.
Endorsed by 

GC-MS Ionization
An introduction to the ionization processes which occur in GC-MS. Ionization is the process whereby electrons are either removed or added to atoms or molecules to produce ions.
Endorsed by 

GC Considerations
This module explores the main GC considerations when using MS detectors. The choice of column phase and dimensions are considered, as well as the effects of carrier gas flows on the MS vacuum system.
Endorsed by 
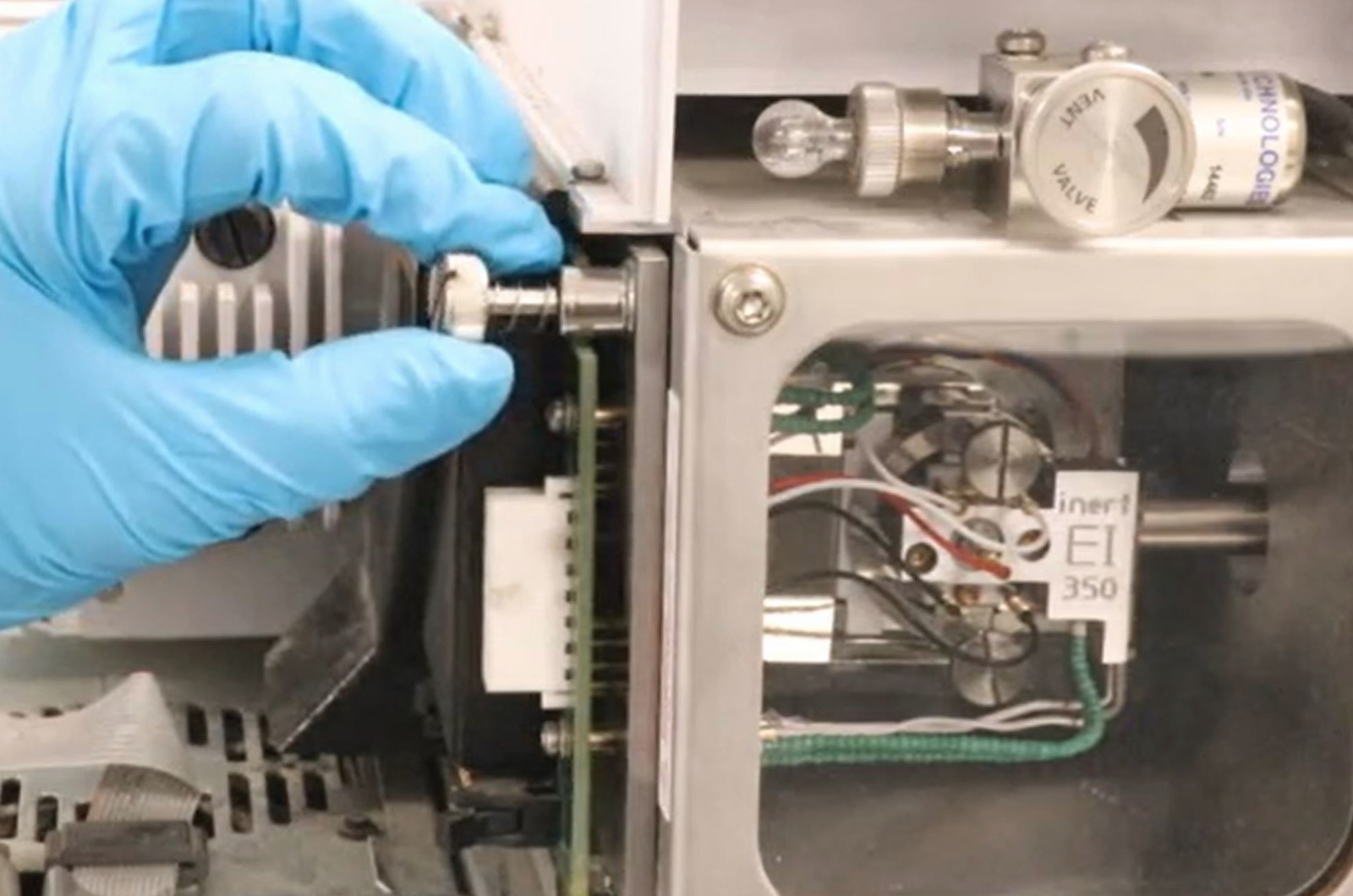
Practical GC-MS Video Bootcamp
The definitive guide to setting up a GC-MS instrument. Working on a real GC-MS instrument we provide you with the fundamental knowledge on the science, working principles, and correct setup of this powerful piece of equipment. An in-depth tour of how to dismantle and clean the ion source will give you confidence to perform preventative maintenance on your instrument.
Endorsed by 
GC-MS Acquisition Modes
GC-MS data acquisition is carried out using full scan or selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode. Scan mode is used to cover a wide range of m/z ratios, whereas, SIM is used to gather data for specific masses of interest. This module will explain the differences between the data generated, provide you with details on the parameters which can be set to acquire the data, and the impact of the acquisition mode and parameters on the sensitivity of that data.
Endorsed by 
GC-MS Library Searching
This module will detail the process of obtaining and extracting spectra for library matching, what is involved in the matching process, and interpreting match results. As well as providing learning on troubleshooting poor library matching.
Endorsed by 
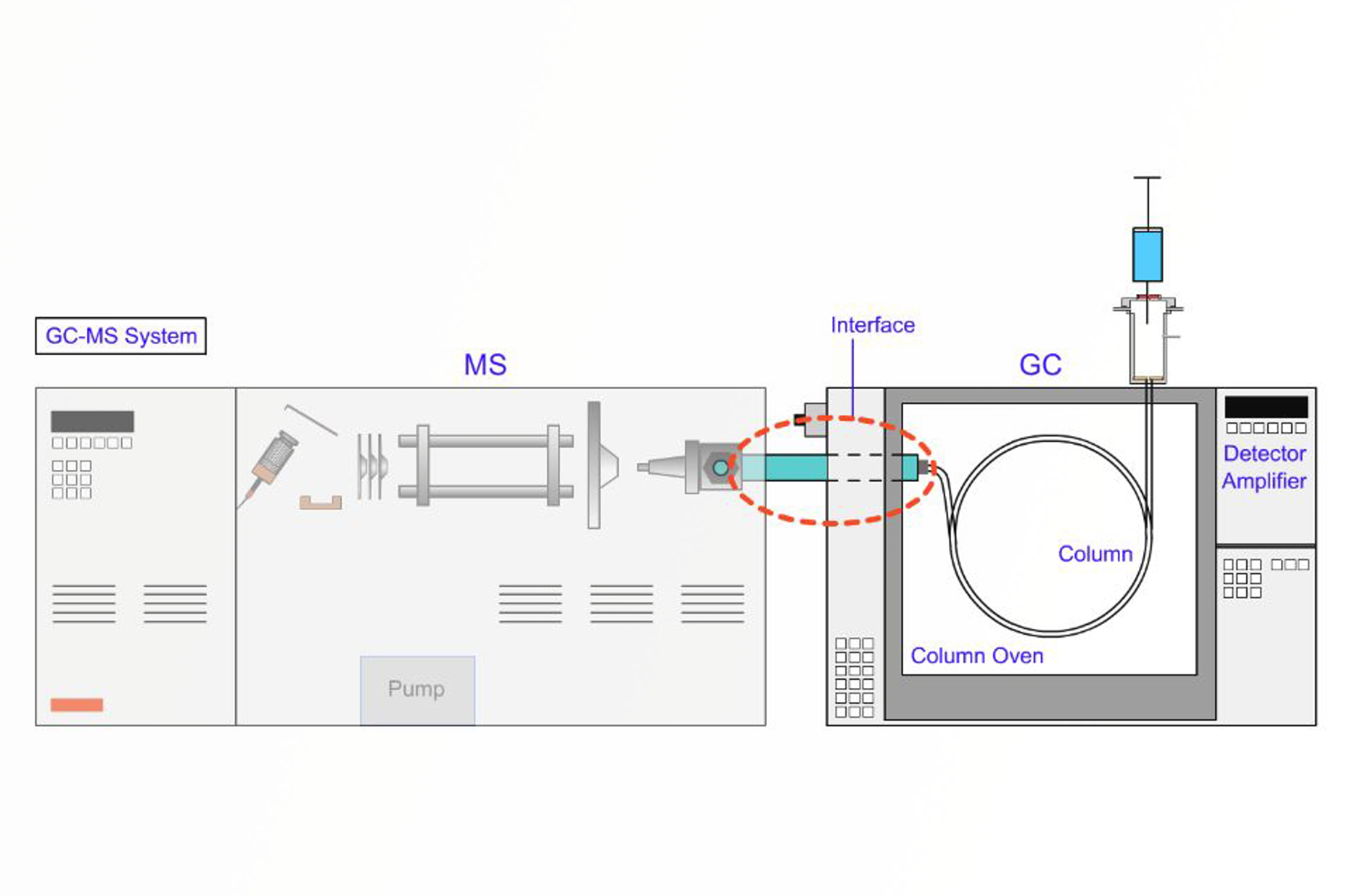
GC-MS Interfaces
After separation in the GC column, analyte species have to be transported to the mass spectrometer to be ionized, mass filtered, and detected. The column outlet needs to be connected to the ion source of the mass spectrometer and this module presents the correct interface types for use with different GC columns and MS instrument types.
Endorsed by 
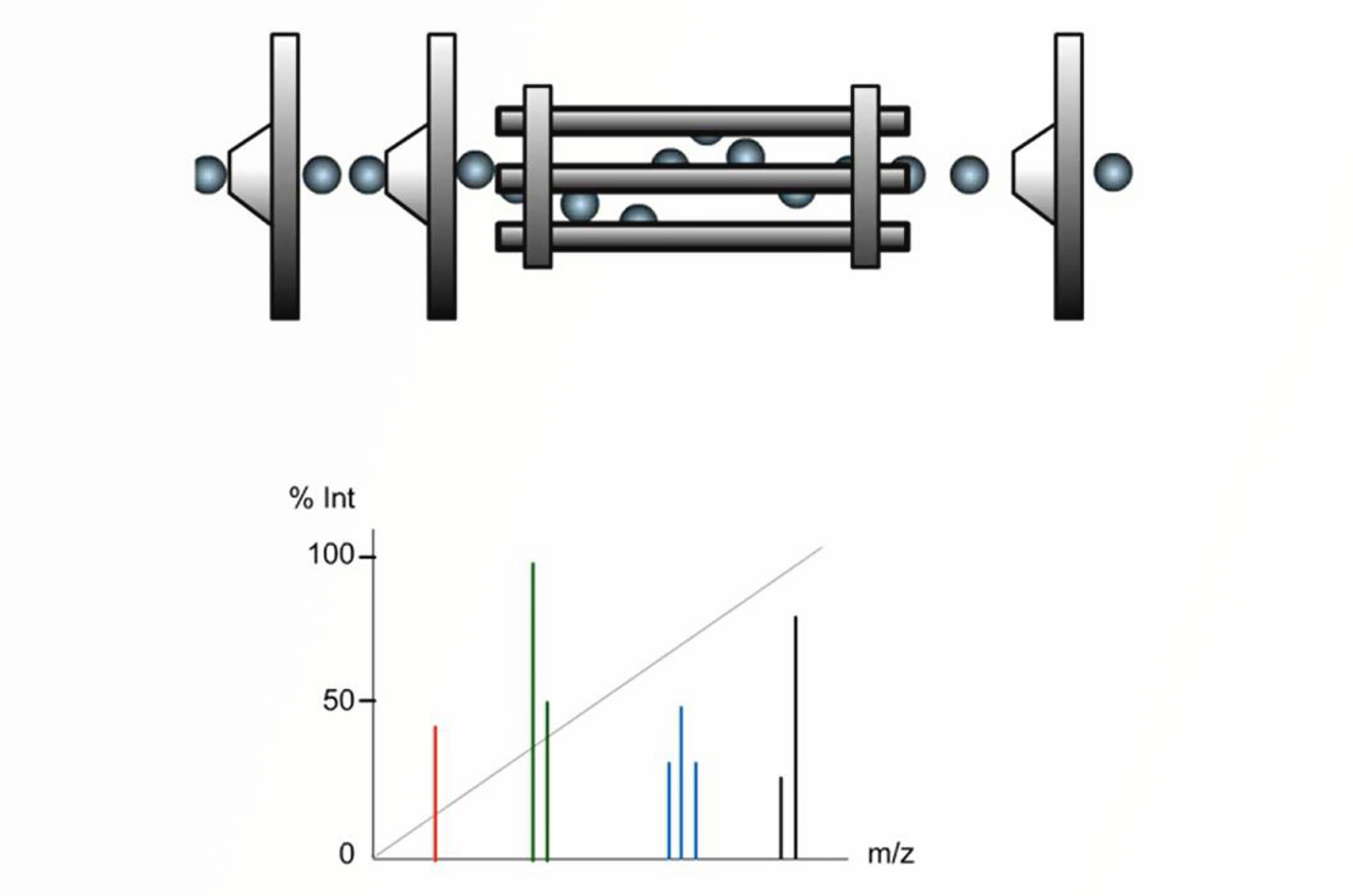
Introduction to Mass Analyzers
In its simplest form the process of mass analysis in GC-MS involves the separation or filtration of analyte ions or fragments of analyte ions created in the ion source. There are several very popular types of mass analyzer associated with routine GC-MS analysis; all of which differ in the fundamental way in which they separate species on a mass-to-charge basis. This module gives an overview of mass analyzers.
Endorsed by 
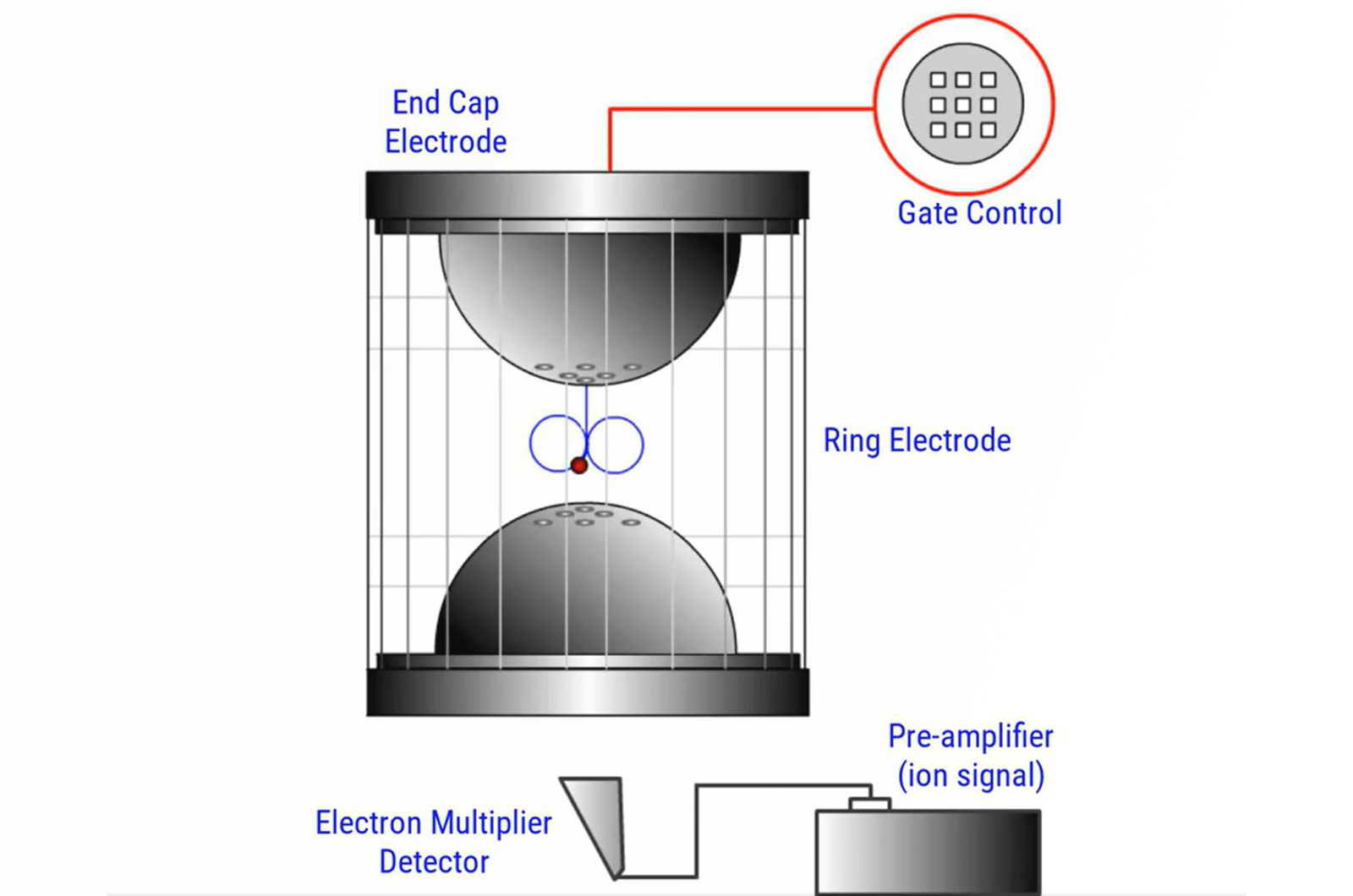
Ion Trap Mass Analyzers
Ion trap mass analyzers use oscillating electric fields (RF) to trap ions in a controlled manner. This module explores the principles of operation of ion trap mass analyzers.
Endorsed by 
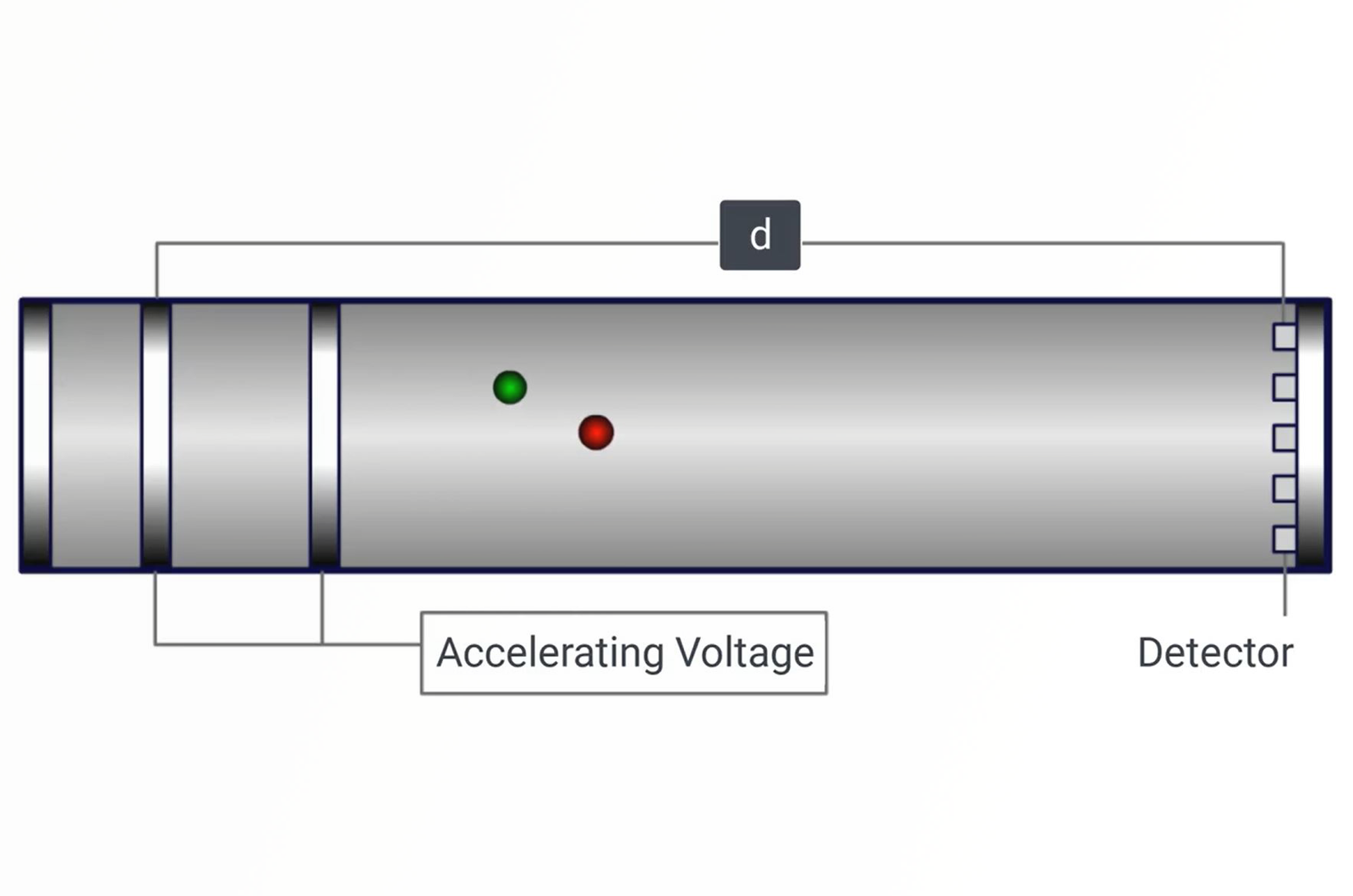
Time-of-Flight (ToF) Mass Analyzers
The basic principles of mass analysis using time-of-flight mass analyzers are relatively straightforward in comparison to many of the other typical mass analyzing devices. Ions are extracted (or produced) in short bursts or packets within the ion source and subjected to an accelerating voltage. The ions then drift or fly down an evacuated tube of set length.
Endorsed by 
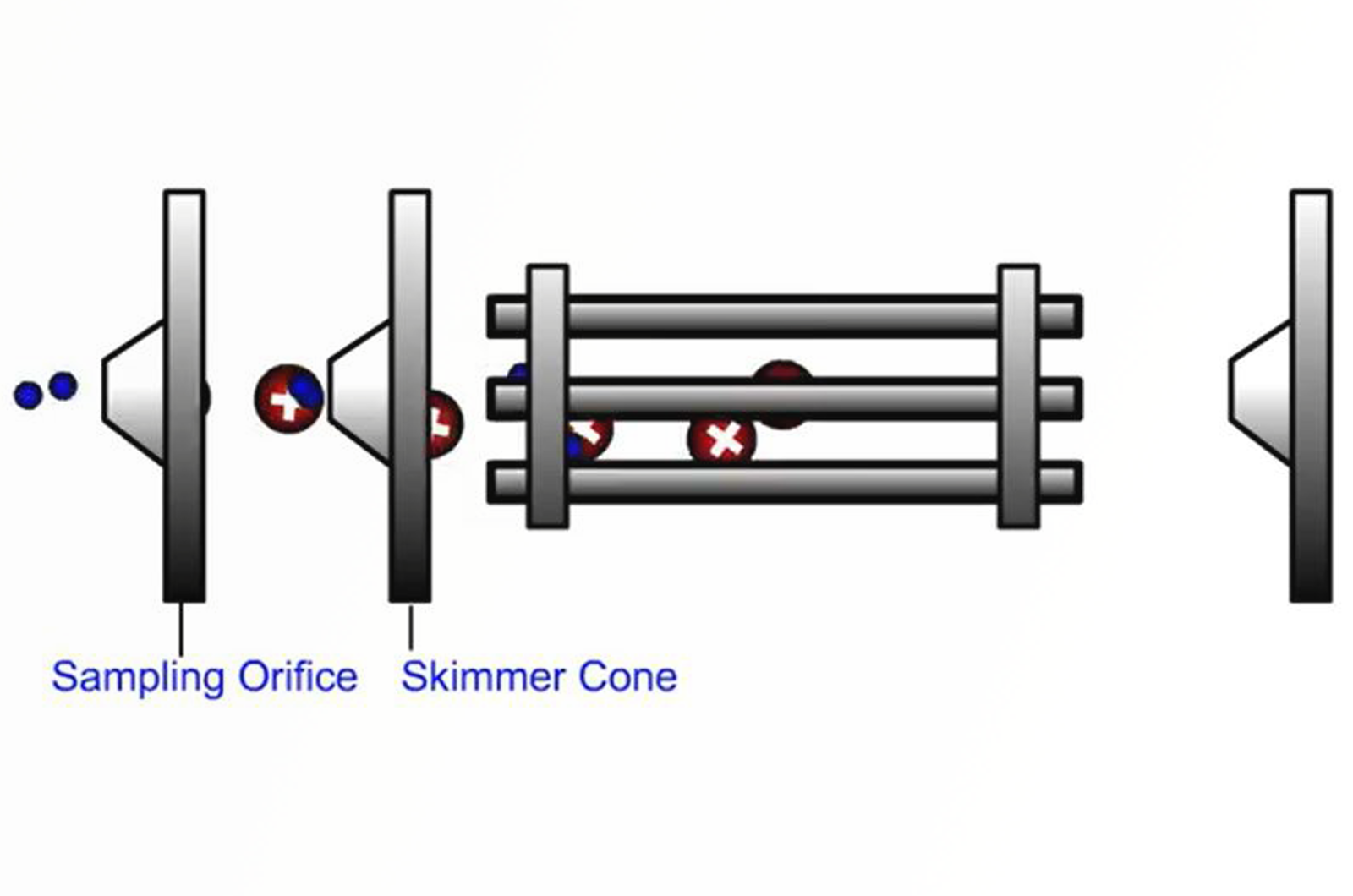
Quadrupole Mass Analyzers
In quadrupole mass analyzing devices, electric fields are used to separate ions according to their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) as they pass along the central axis of four parallel equidistant rods (or poles) that have fixed (DC) and alternating (RF) voltages applied to them.
Endorsed by 
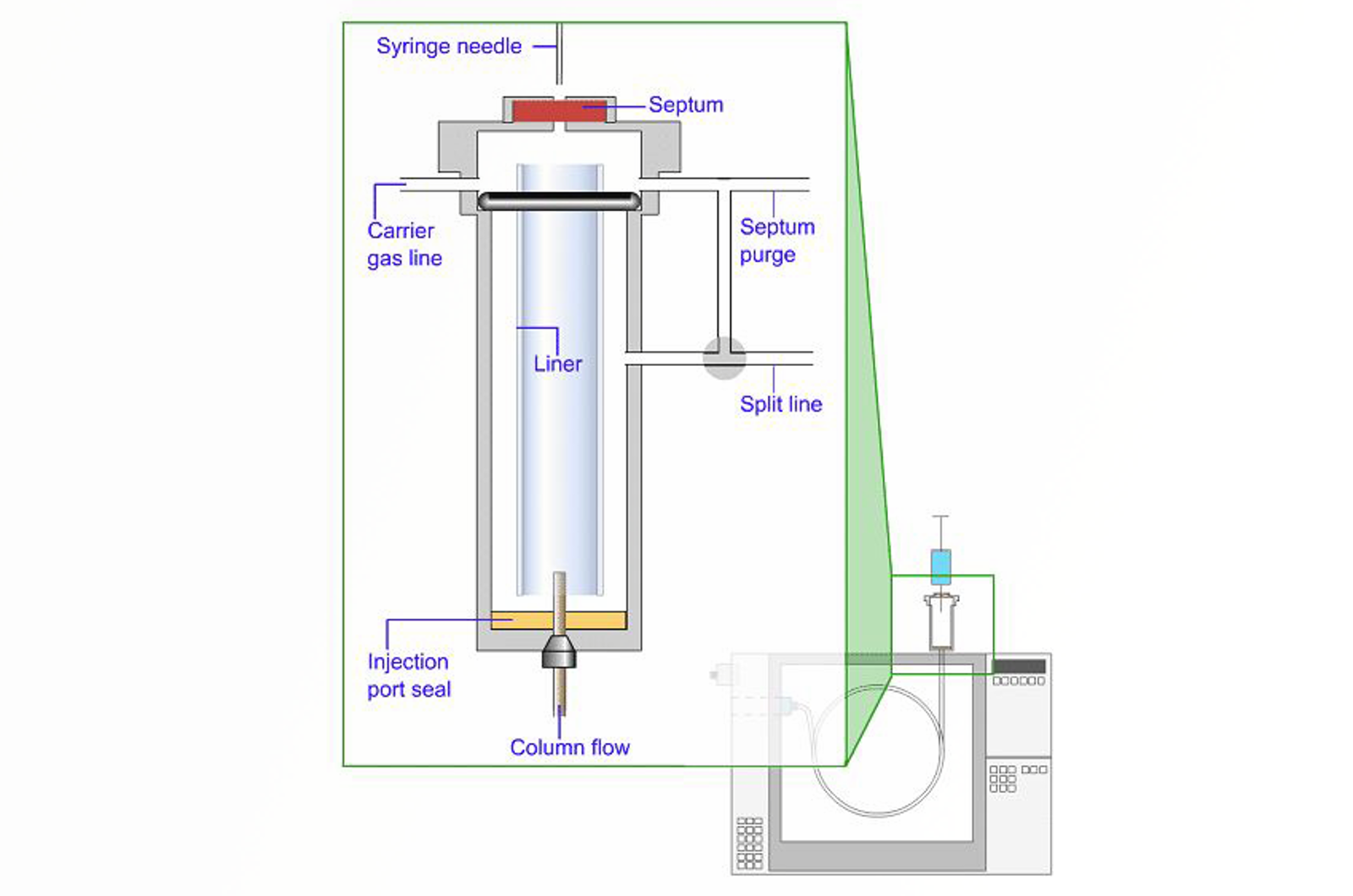
GC-MS Sample Introduction
Perhaps the most difficult step in any GC-MS analysis is the sample introduction. Solid or liquid samples need to be converted to the gas phase and then efficiently transported onto the GC column. The primary aim with all sampling techniques is to ensure a representative and homogeneous gaseous aliquot of the sample under investigation is delivered to the GC column. This module will explore the main GC considerations when using MS detectors.
Endorsed by 
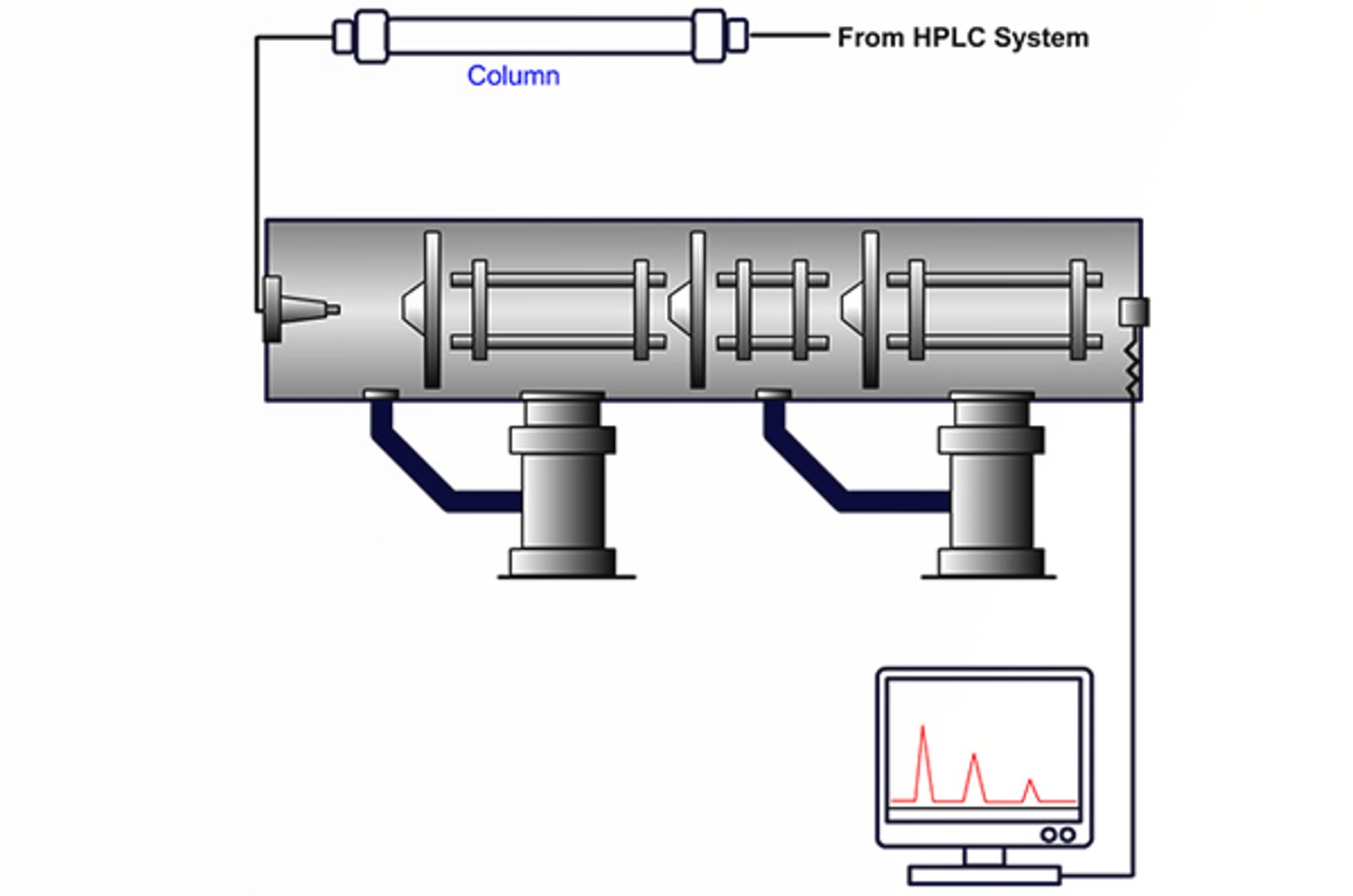
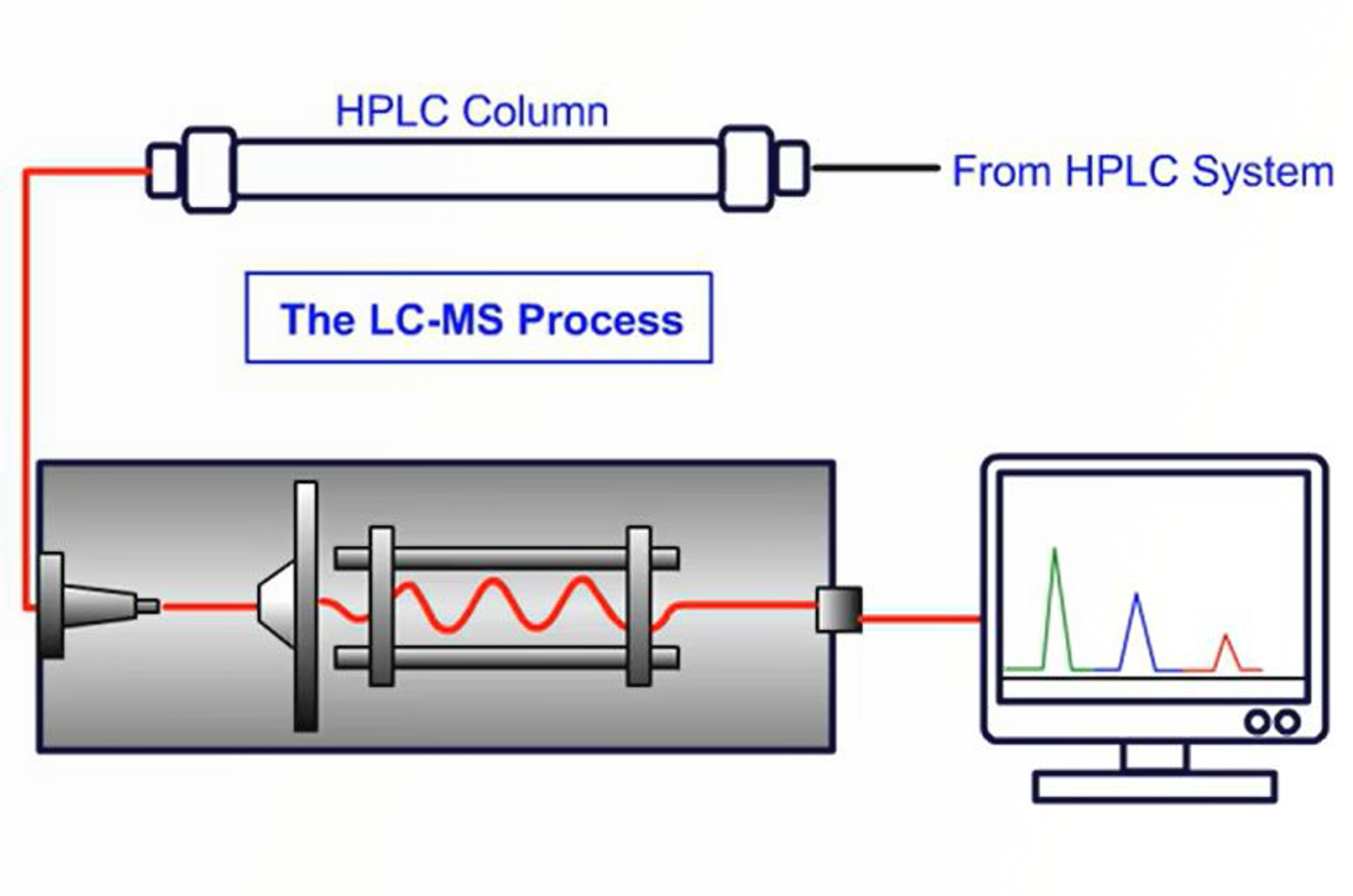
LC-MS Introduction
LC-MS is a hyphenated technique, which combines the separating power of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), with the detection power of mass spectrometry (MS). LC-MS covers a broad range of application areas. This module explores the instrument acquisition methods used and examines the type of data that can be produced from such systems.
Endorsed by 
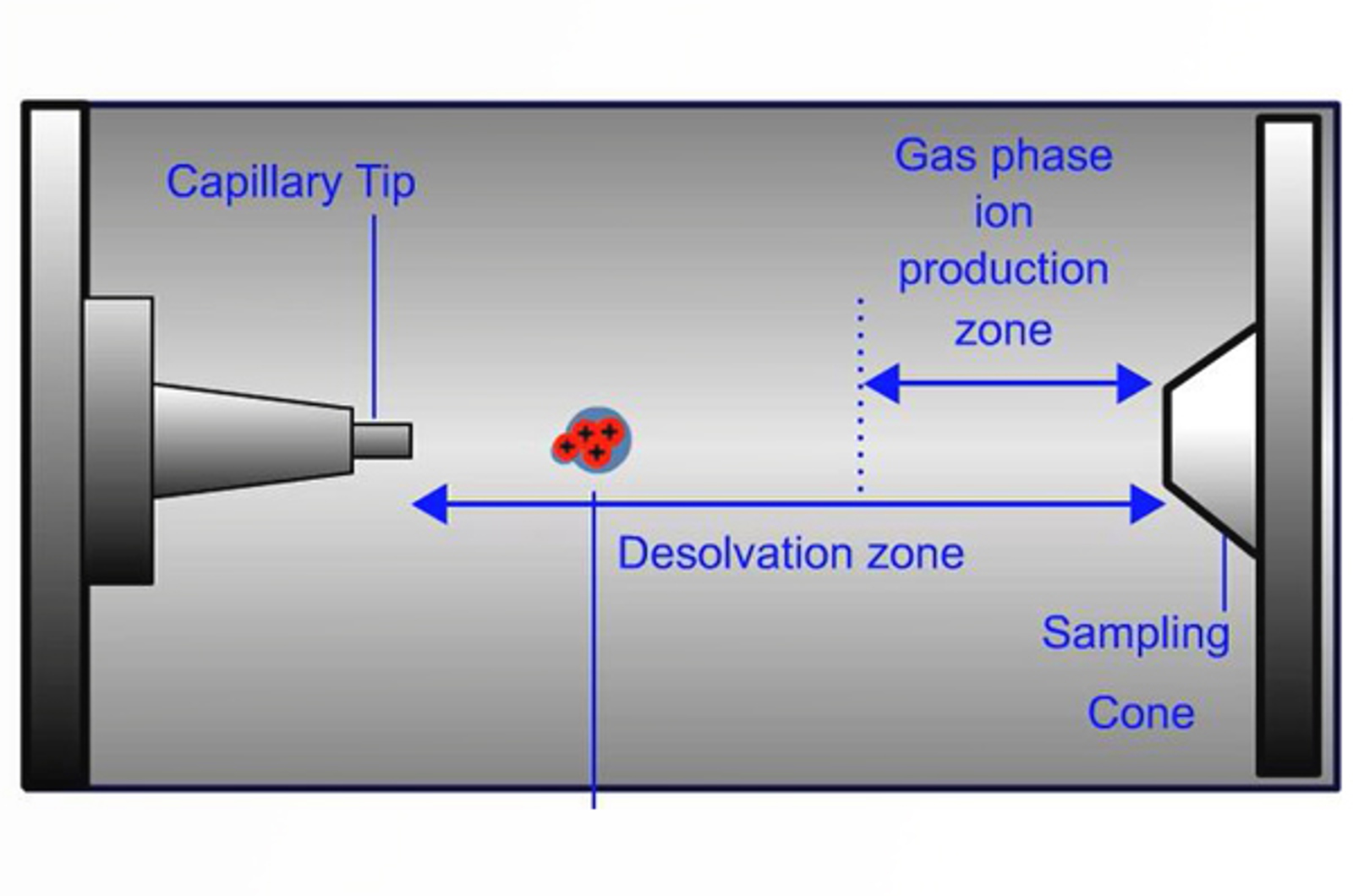
Electrospray Ionization (ESI) Theory
Electrospray is the dispersion of a liquid into electrically charged droplets, combining the two processes of droplet formation and droplet charging. The process of droplet charging is affected by eluent flow rate, liquid surface tension, and electrolyte concentration. This module explains the function of the major components of an electrospray interface and discusses ways to optimize signal using electrospray ionization.
Endorsed by 
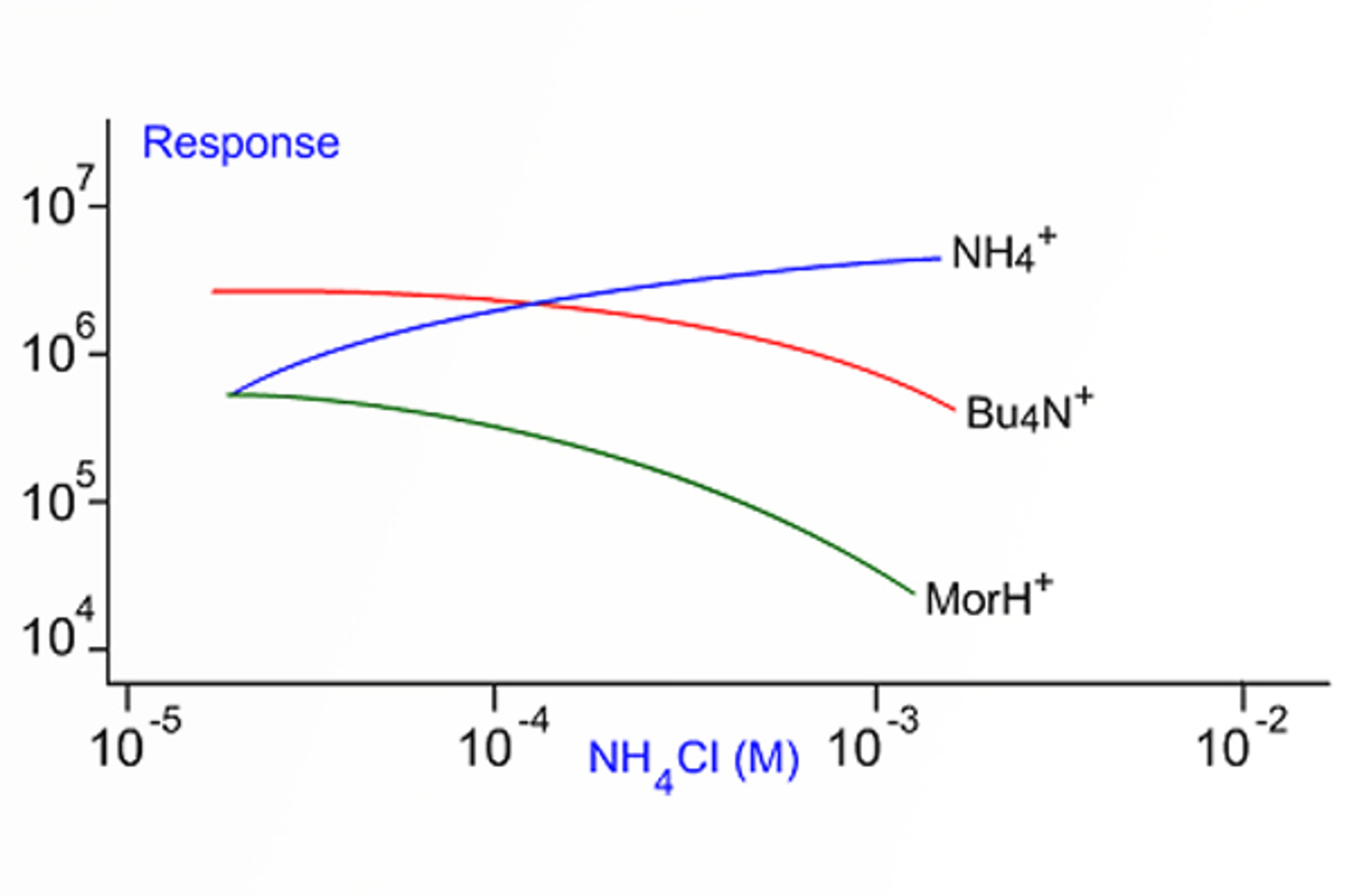
Electrospray Ionization (ESI) Technique
This module discusses important parameters when carrying out electrospray ionization (ESI). Find out practical tips for overcoming ion suppression, optimizing sprayer position, and the role pH plays in signal intensity.
Endorsed by 
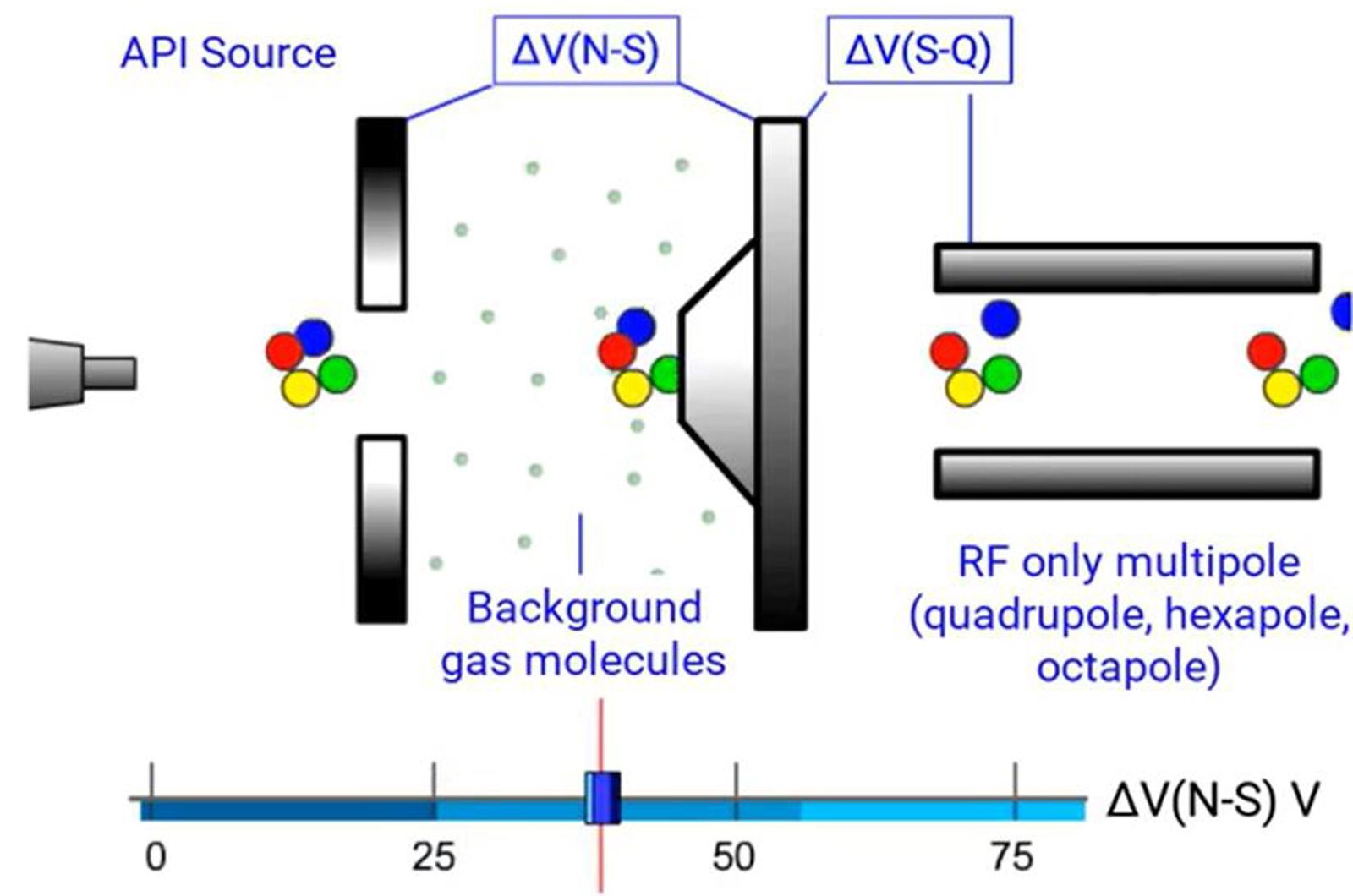
Electrospray Ionization Instrumentation
Electrospray is the dispersion of a liquid into electrically charged droplets, combining the two processes of droplet formation and droplet charging. This module discusses the major components of an electrospray interface and investigates methods for optimizing signal.
Sponsored by 
Practical LC-MS Video Bootcamp
Working at a real LC-MS system and with real data, our technical team methodically take you through the practical process of LC-MS; from basic instrument setup, to mobile phase and signal optimization, and up to complex MS/MS experiments.
Endorsed by 
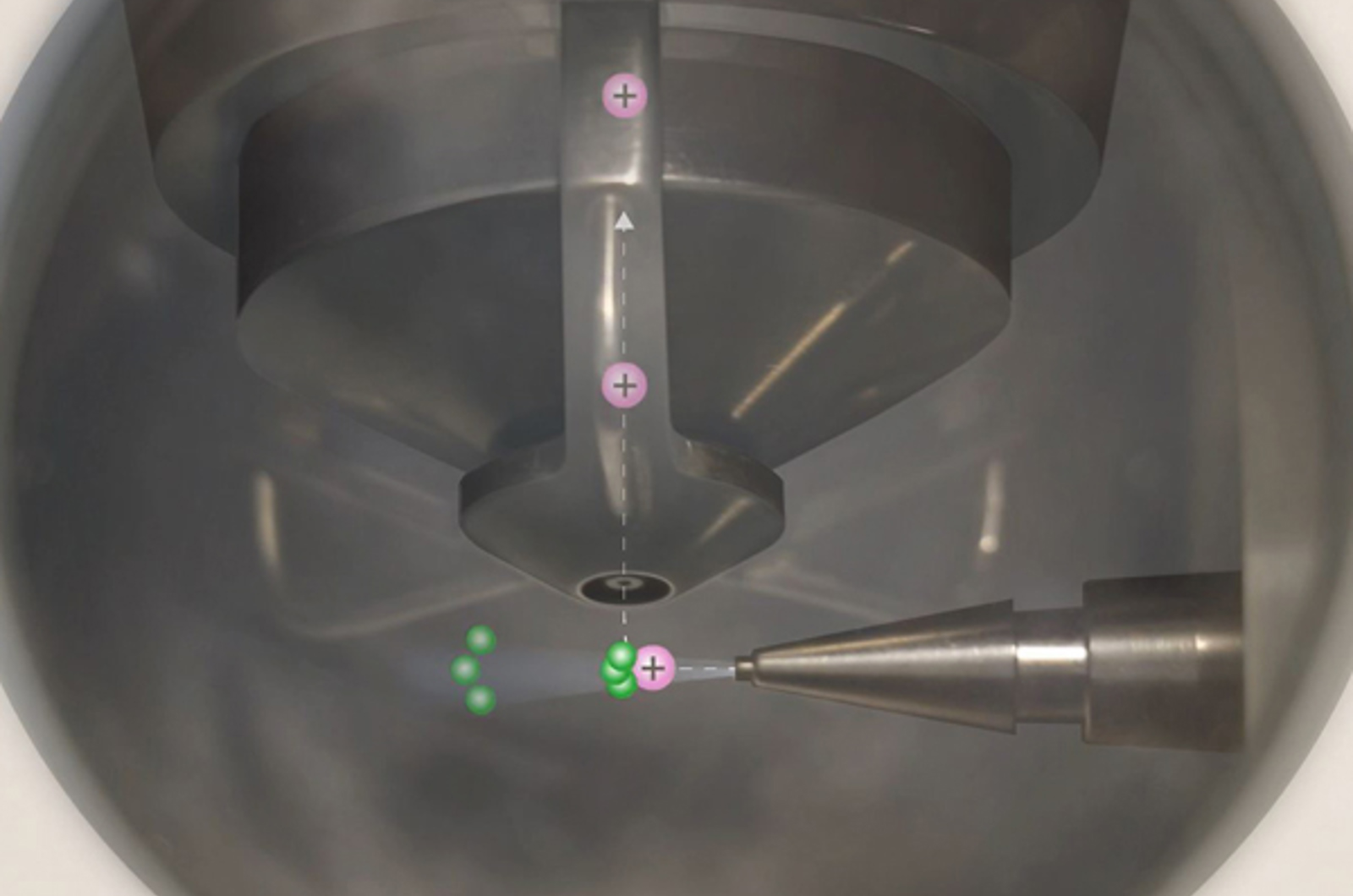
Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization (APCI) Theory
This module introduces atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) concepts, explains the function of each component of the APCI interface, and investigates ways in which to optimize and troubleshoot the technique.
Endorsed by 
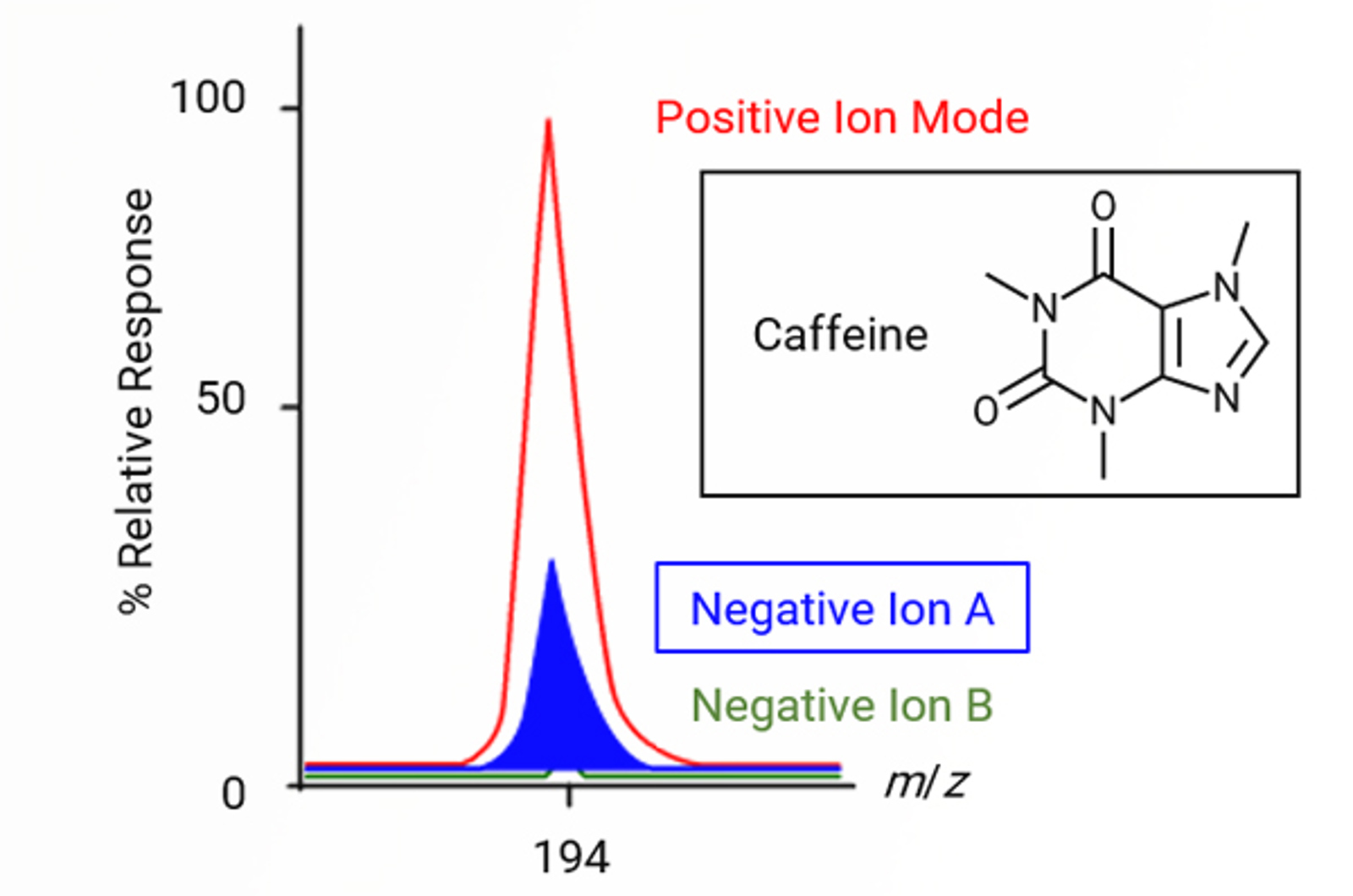
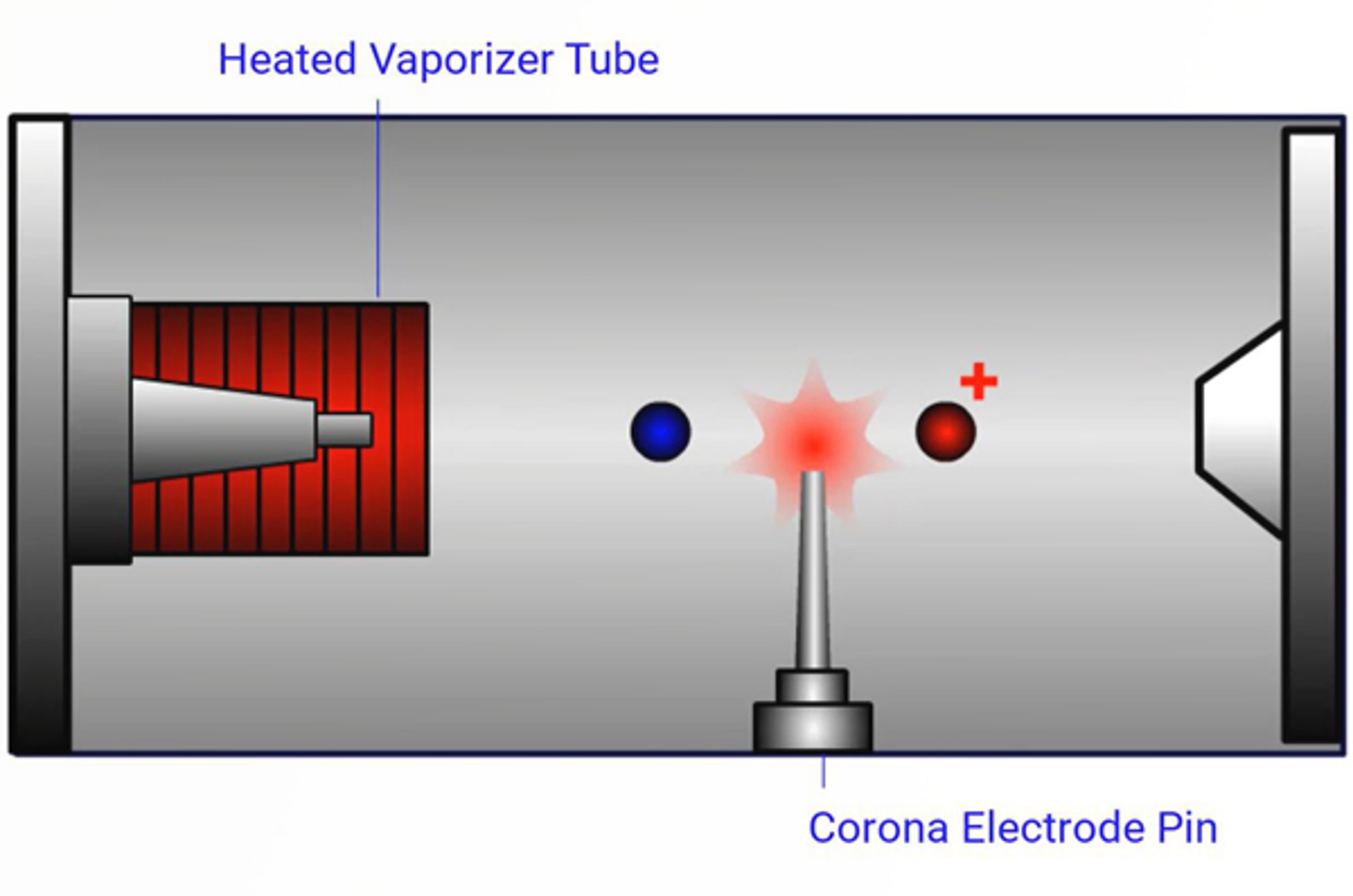
Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization (APCI) Technique
This module explains the important parameters when using atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) and offers practical tips on source parameter optimization.
Endorsed by 
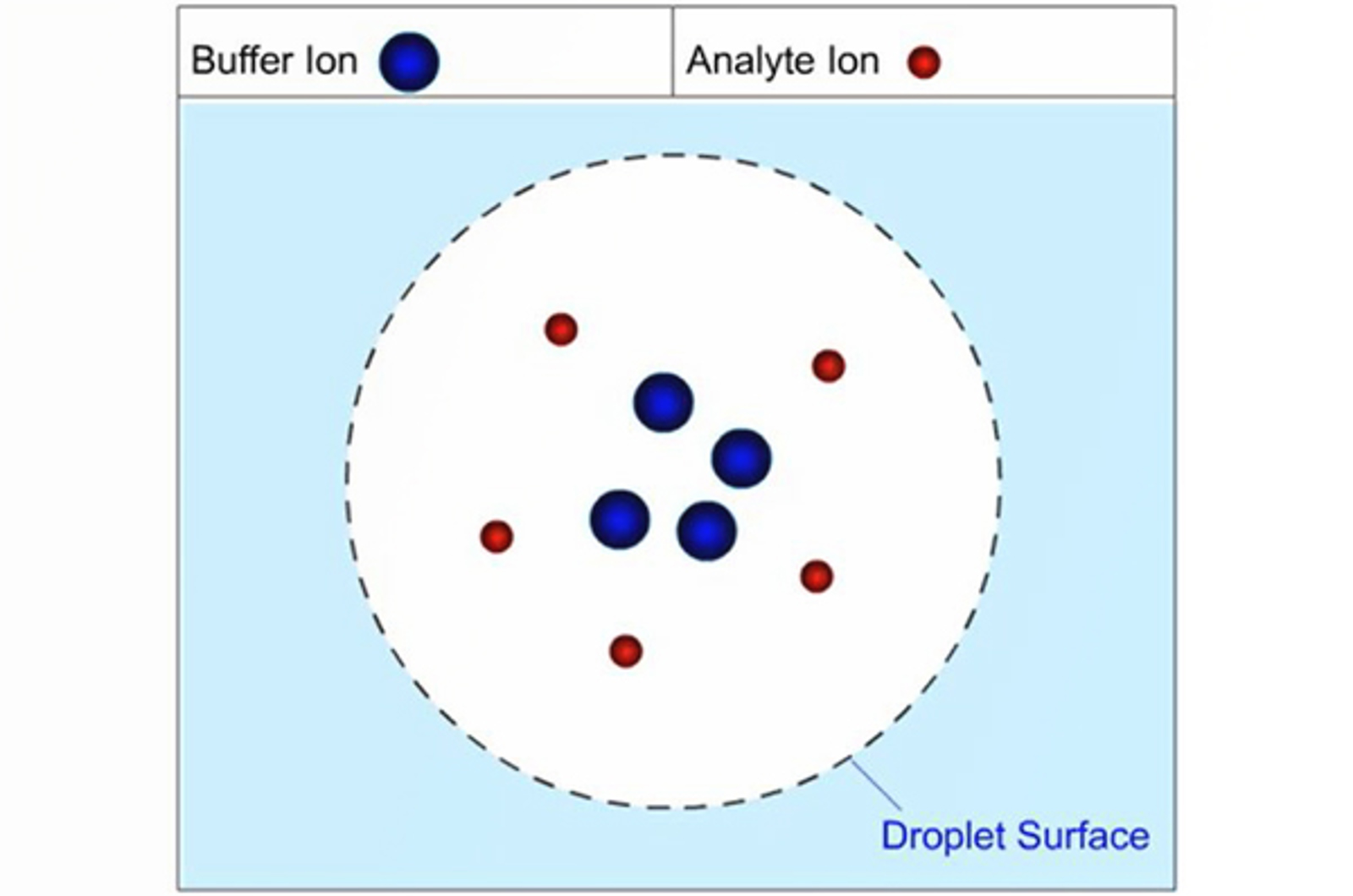
Solvents, Buffers, and Additives
In this module we will examine common additives used in LC-MS and explain the role of solvents, buffers and eluent pH in signal optimization.
Endorsed by 
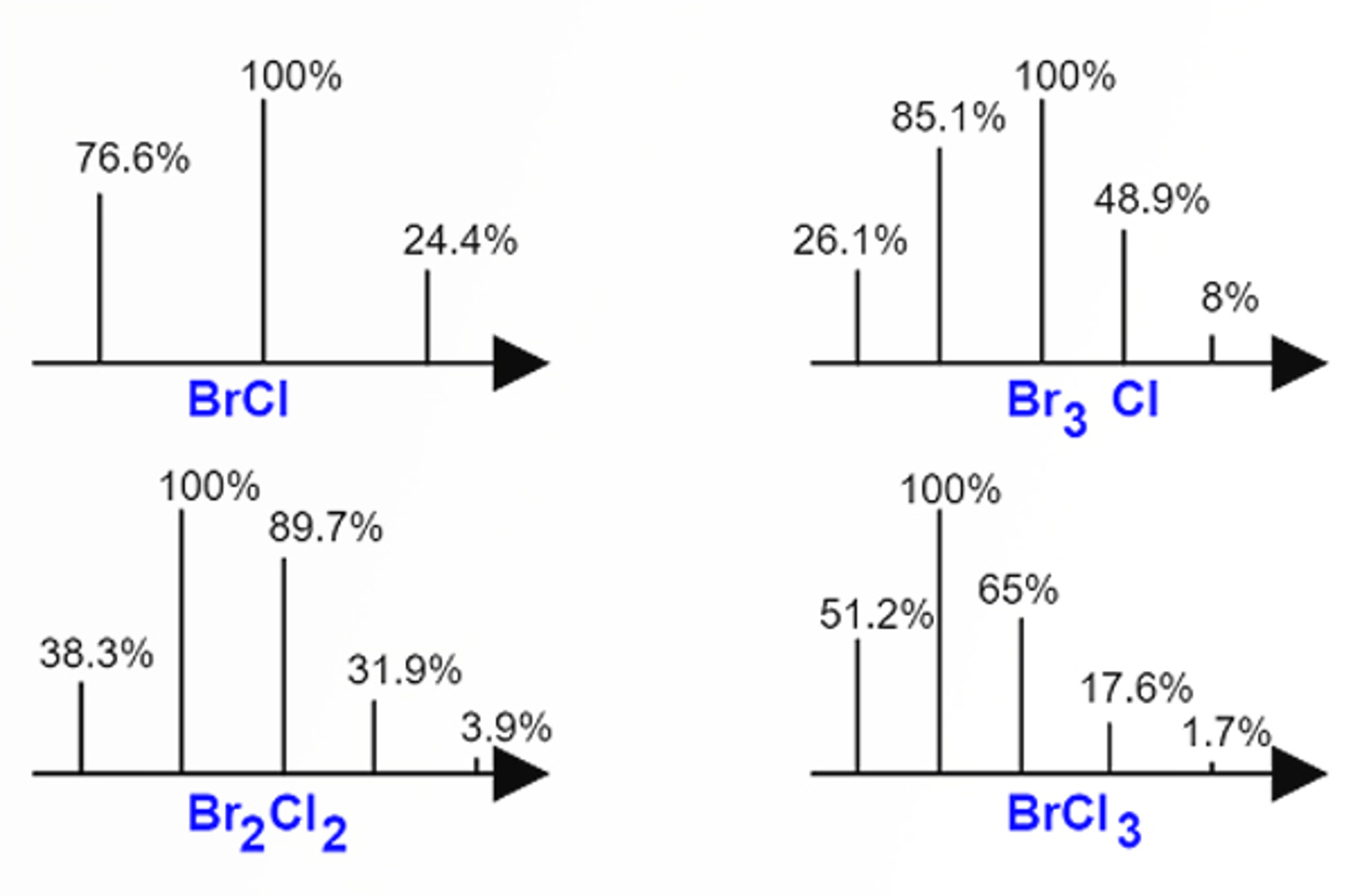
LC-MS Interpretation
This module introduces the principles and fundamental concepts of mass spectral interpretation.
Endorsed by 
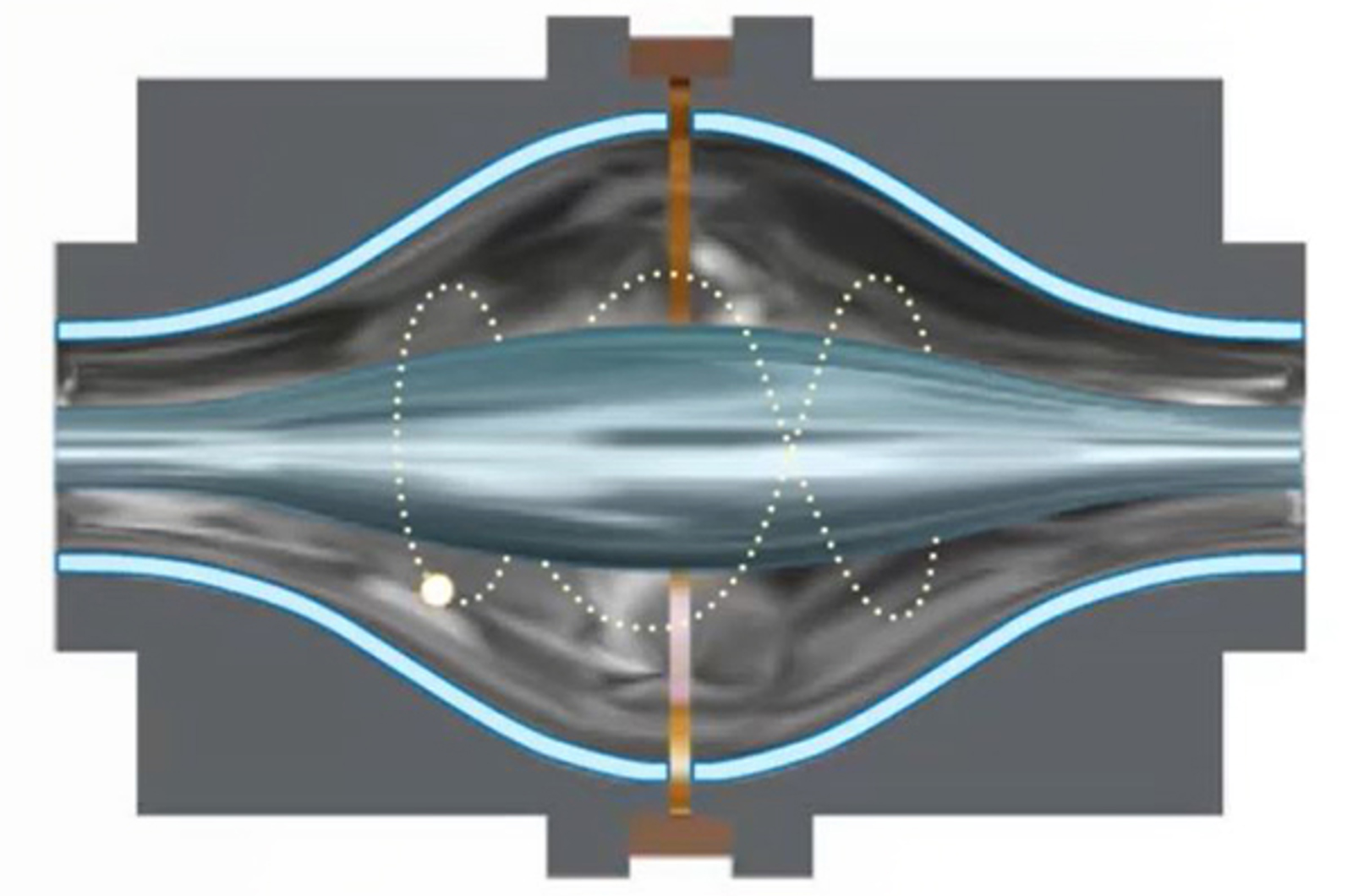
Orbitrap Mass Analyzers
Ion trapping techniques are important tools in mass spectrometry. However, traditional ion trap mass analyzers have disadvantages in either performance or high complexity and cost. This module will explore the theory and working principles of orbitrap mass analyzers.
Endorsed by 
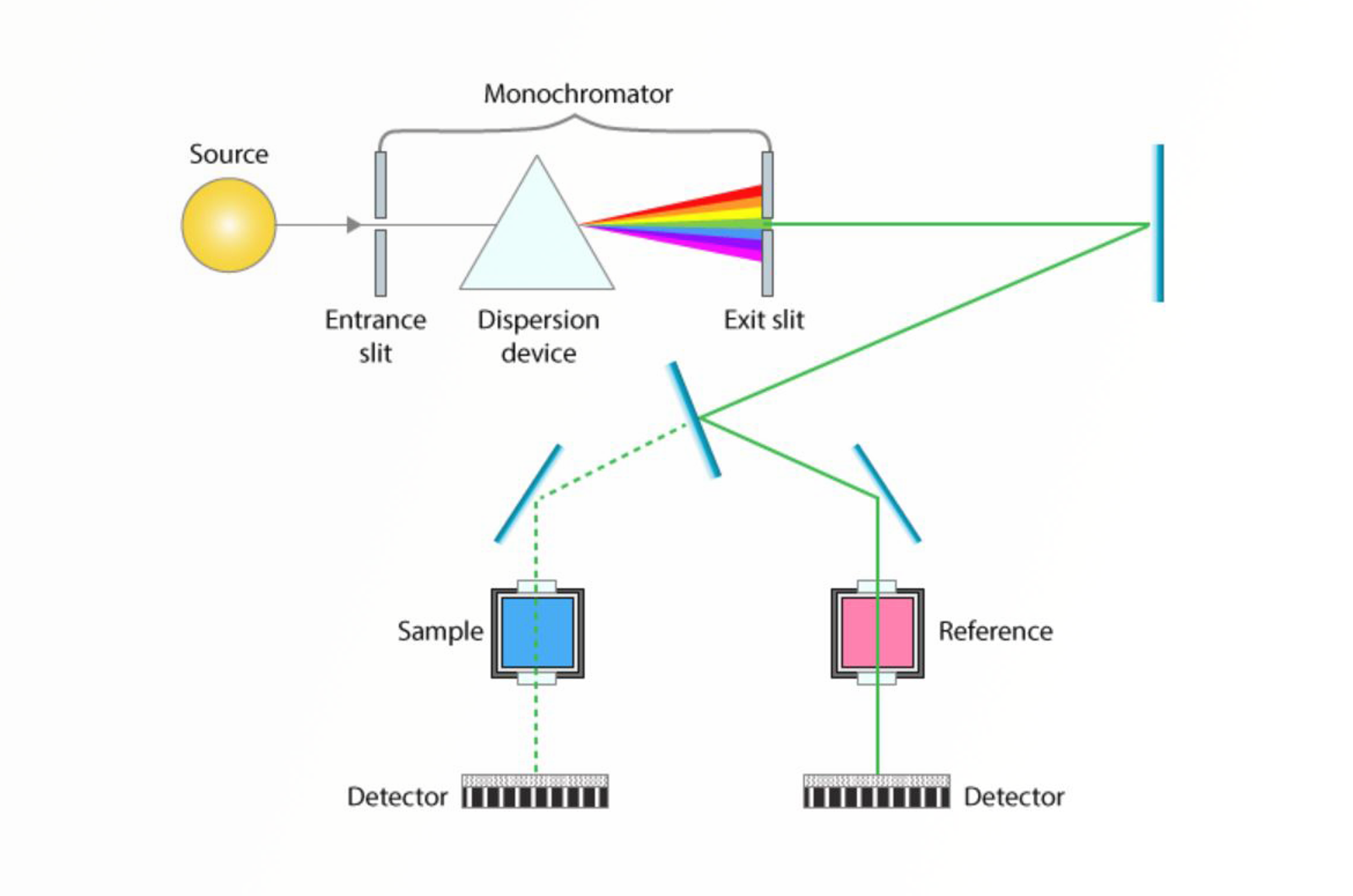
UV-Visible Spectroscopy
This module covers the fundamental scientific principles behind UV-visible spectroscopy, the principles of the instrumentation, and practical tips for optimizing the instrument parameters.
Endorsed by 
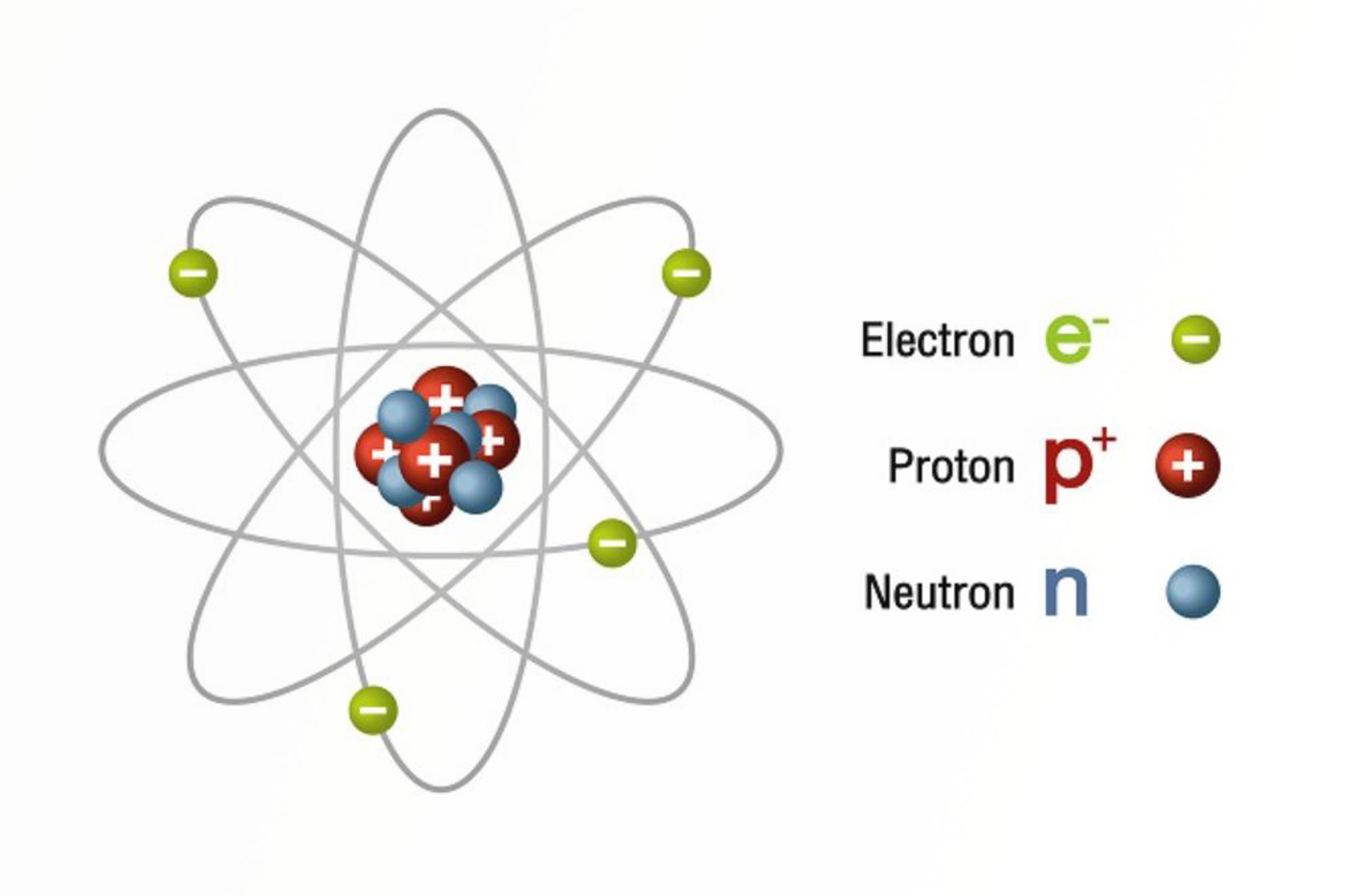
Fundamental Chemistry
This module provides a fundamental understanding of chemistry to give chromatographers better insight into the chemical process which occur during sample preparation and chromatographic separation.
Endorsed by 

Transferable Skills in the Chemical Industry
In this module, we will explore key transferable skills that will enhance your effectiveness and efficiency as an analytical chemist.
Endorsed by 
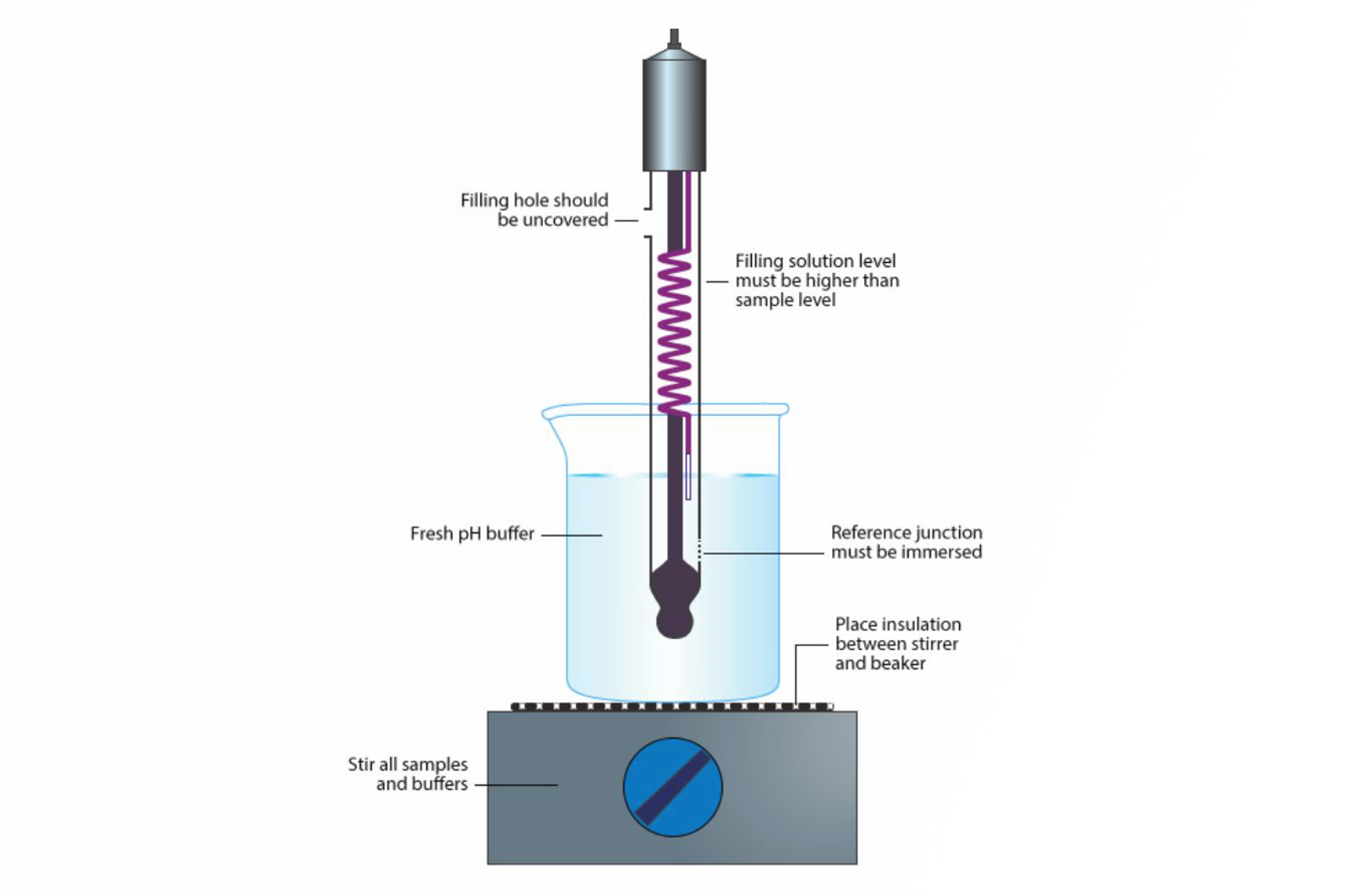
Measuring pH
This module will discuss the equipment used to measure pH and how to use it.
Endorsed by 
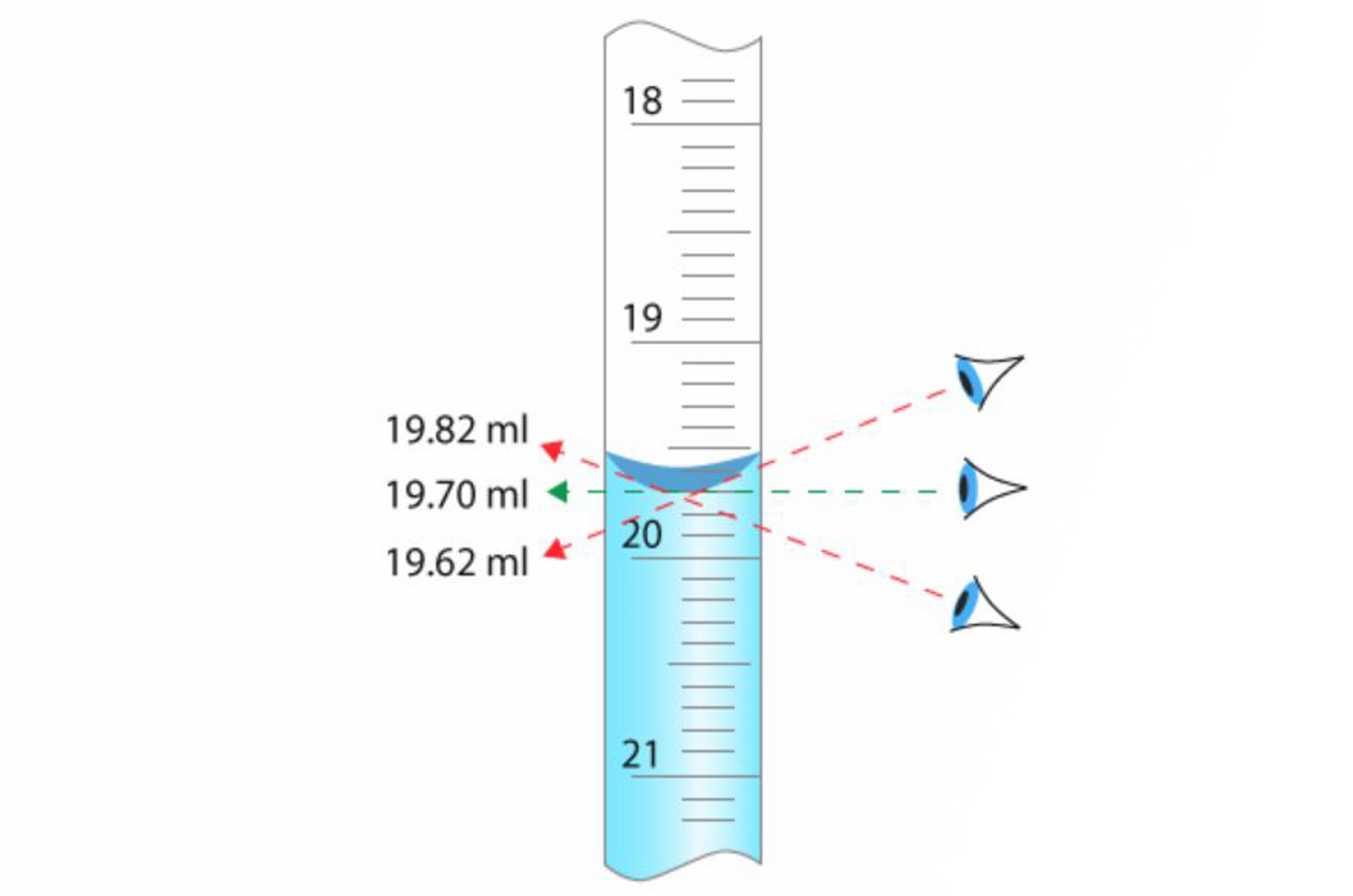
Volumetric Lab Equipment
This module will discuss the different types of volumetric lab equipment and how each piece should be used correctly.
Endorsed by 
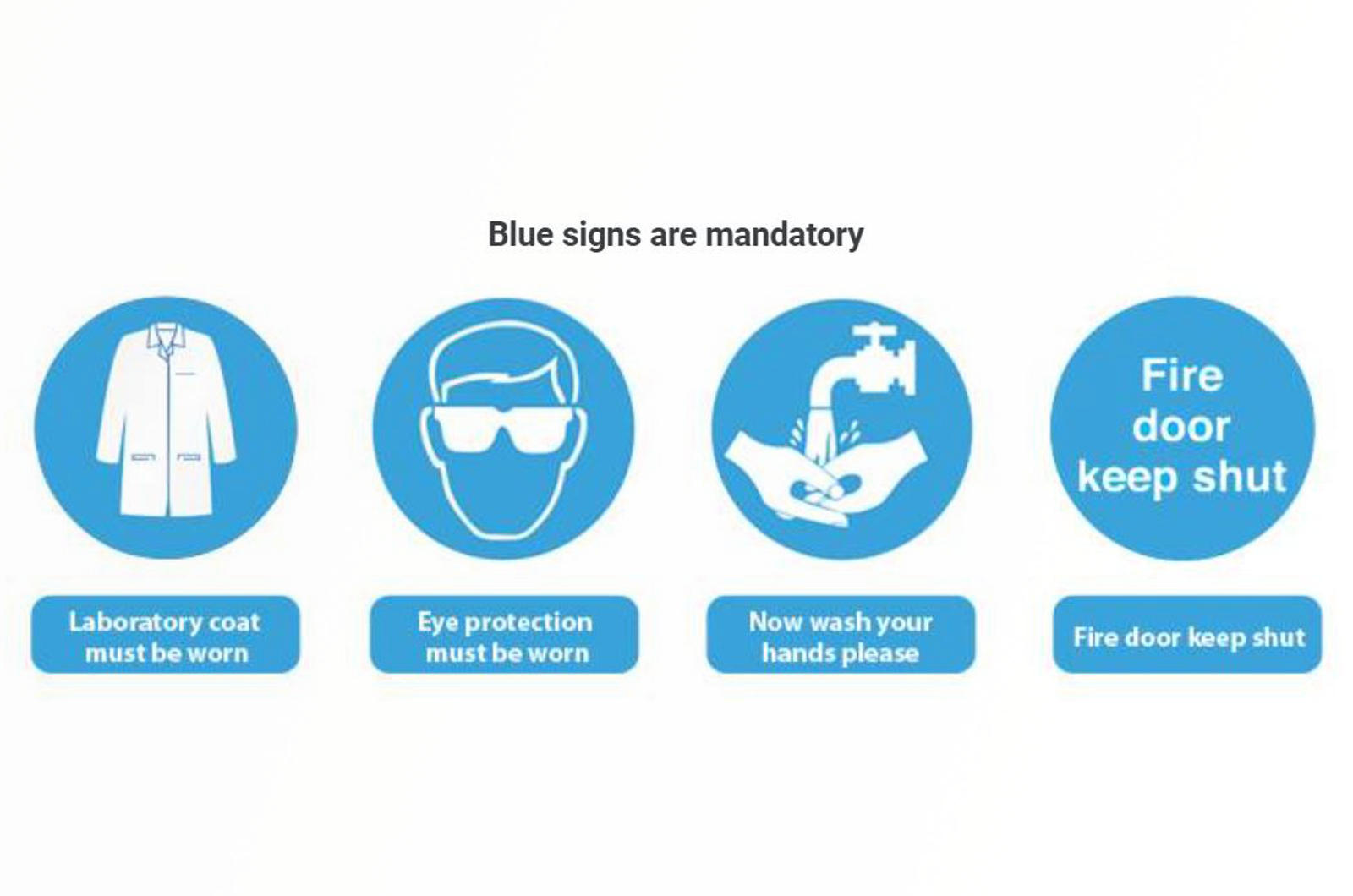
Laboratory Safety
This module will detail some common safety measures that relate to all laboratories.
Endorsed by 

Balances
This module focuses on the use of balances in the lab and discusses best practice on their use.
Endorsed by 
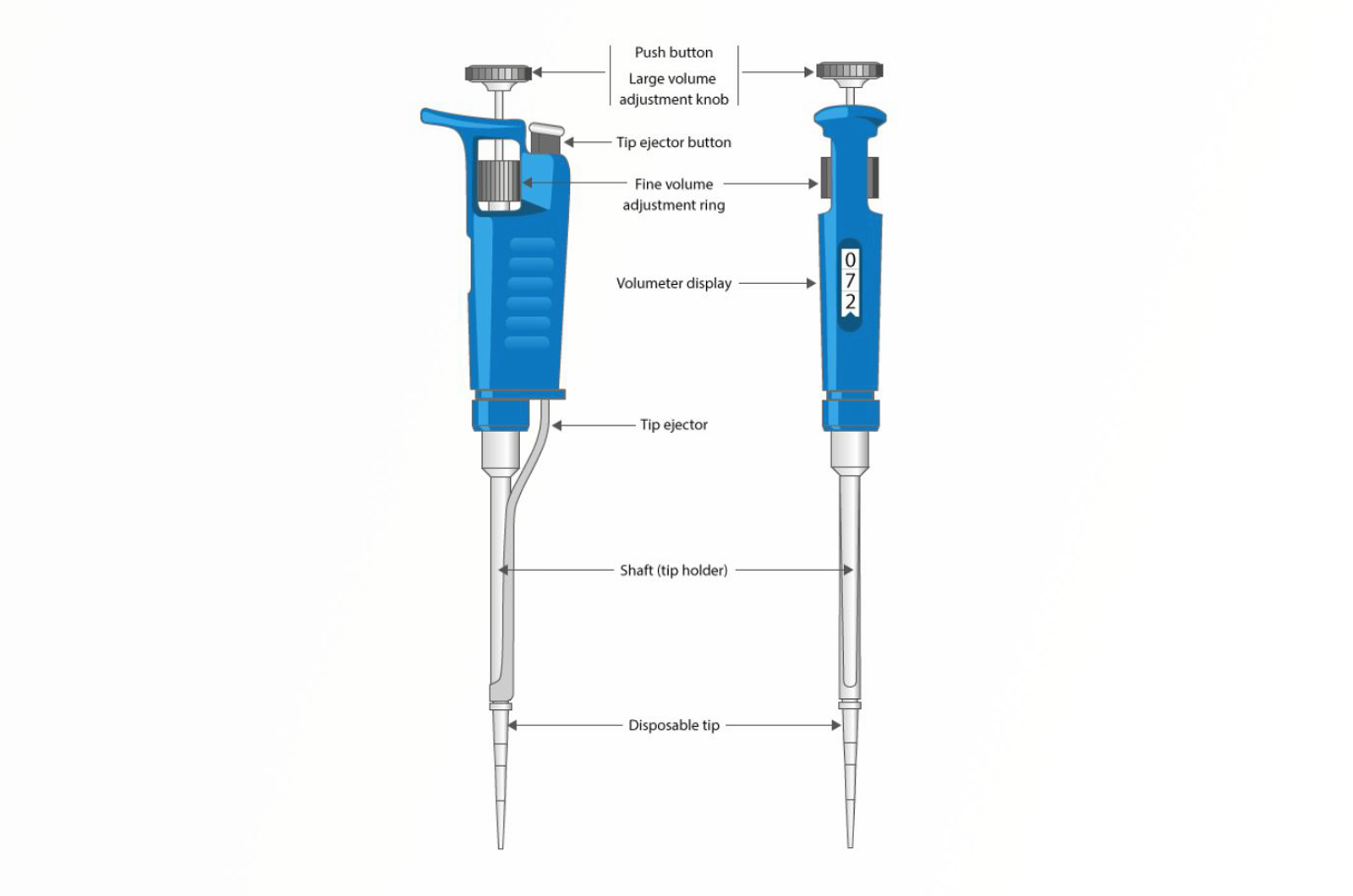
Automatic Pipettes
The focus of this module is to provide you with practical information to improve your pipetting technique - this encompasses the use of pipettes, how to select the correct pipette and tip, how to and why we calibrate pipettes, as well as how to maintain them in order to have confidence that they are functioning reliably.
Endorsed by 

Glass Pipettes
This module teaches you the main aspects of the essential skill of using glass pipettes.
Endorsed by 
Eliminating Error During Preparation of Samples
In this module we will follow two very experienced analysts as they guide you through the process of managing your workspace an samples in a way that eliminates errors.
Endorsed by 
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
This module introduces the chemistry of amino acids, peptides, and proteins.
Endorsed by 
Mass Spectrometry Basics for Biomolecule Analysis
This module covers the fundamentals of mass spectrometry for the analysis of biomolecules.
Endorsed by 
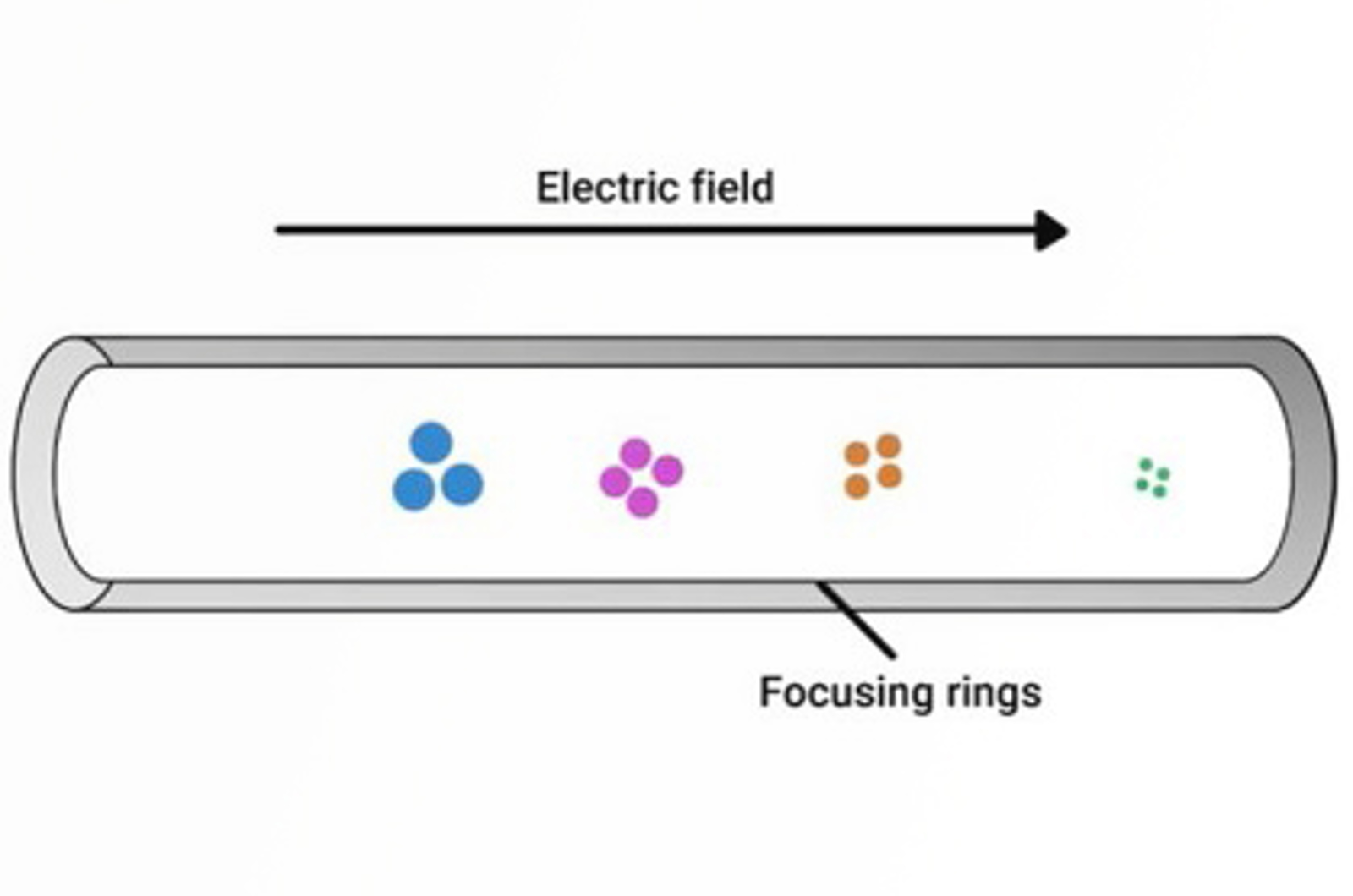
Introduction to Ion Mobility Spectrometry (IMS)
This introductory module will detail IMS instrument components and how separation occurs as well as considering the advantages of hyphenating the technique with chromatography and particularly mass spectrometry to provide two-dimensional separation data which can be particularly useful in the analysis of biomolecules.
Endorsed by 
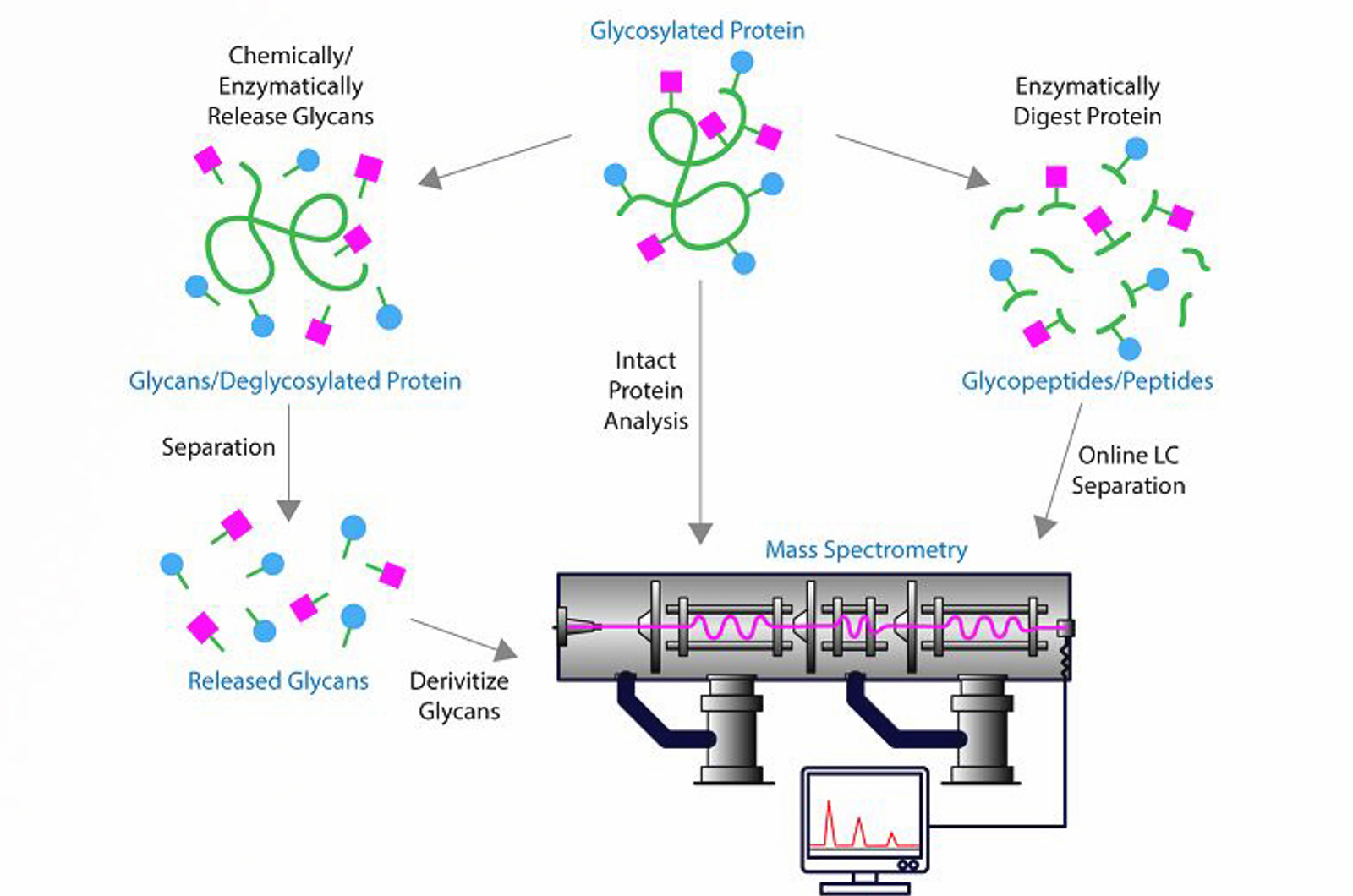
Introduction to Mass Spectrometry for Biomolecules
This module provides an introduction to mass spectrometry for biomolecules.
Endorsed by 
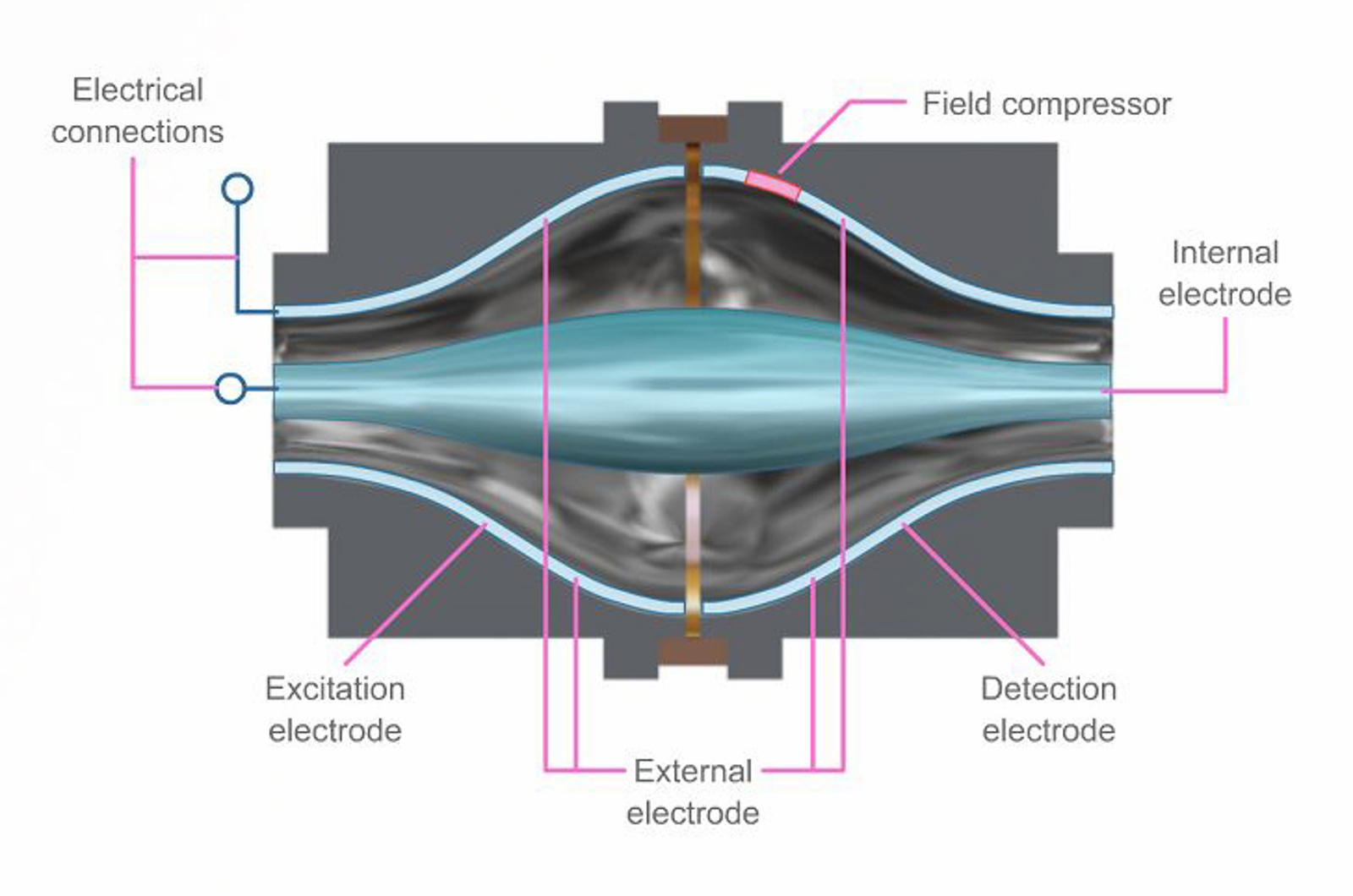
Mass Analyzers Used in Biomolecule Analysis
The working principles of time-of-flight (ToF), orbitrap, and fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR) mass analyzer will be discussed in this module.
Endorsed by 
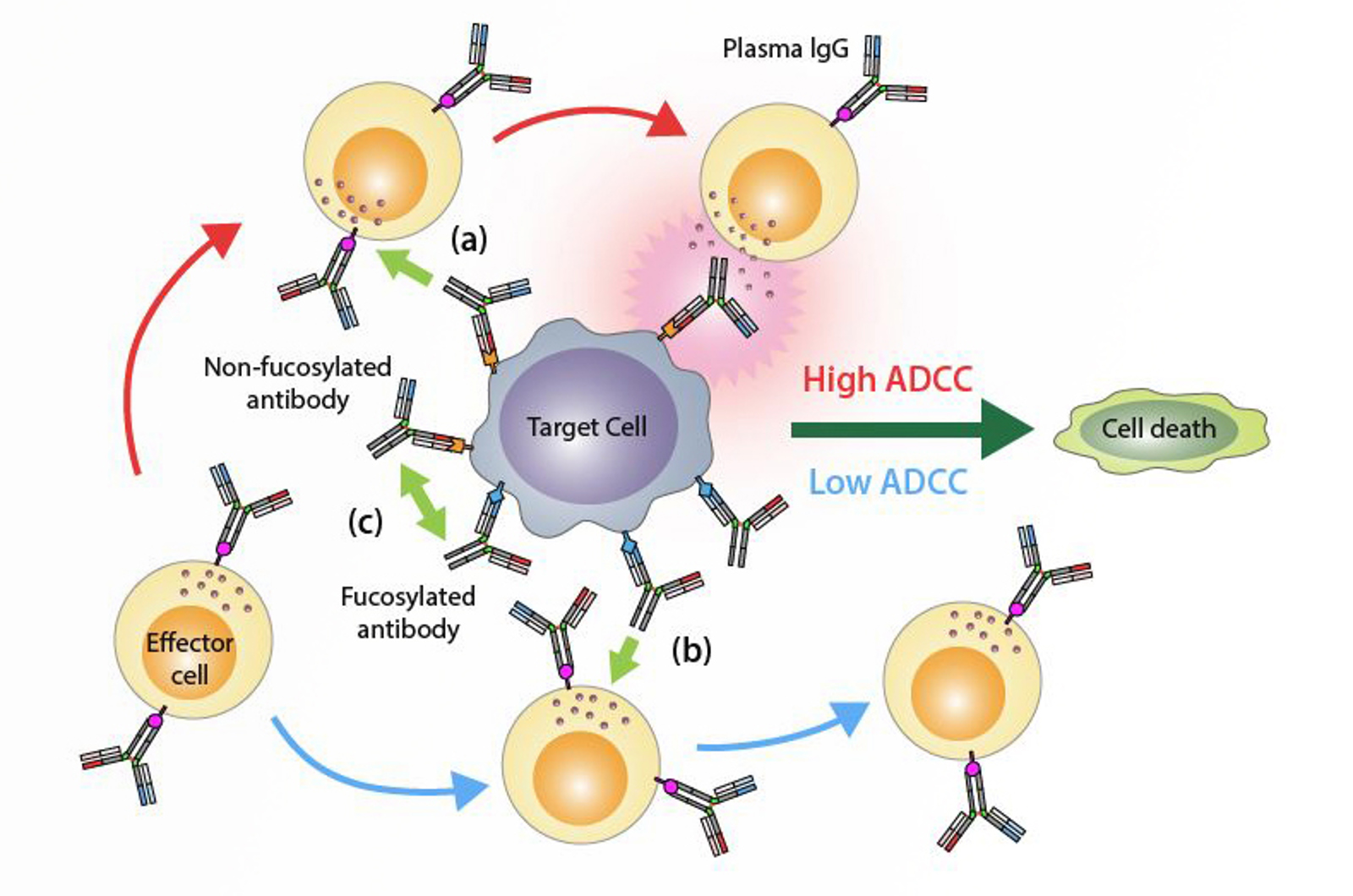
Biopharmaceuticals
This module will consider the fundamental structural characteristics of biopharmaceuticals.
Endorsed by 
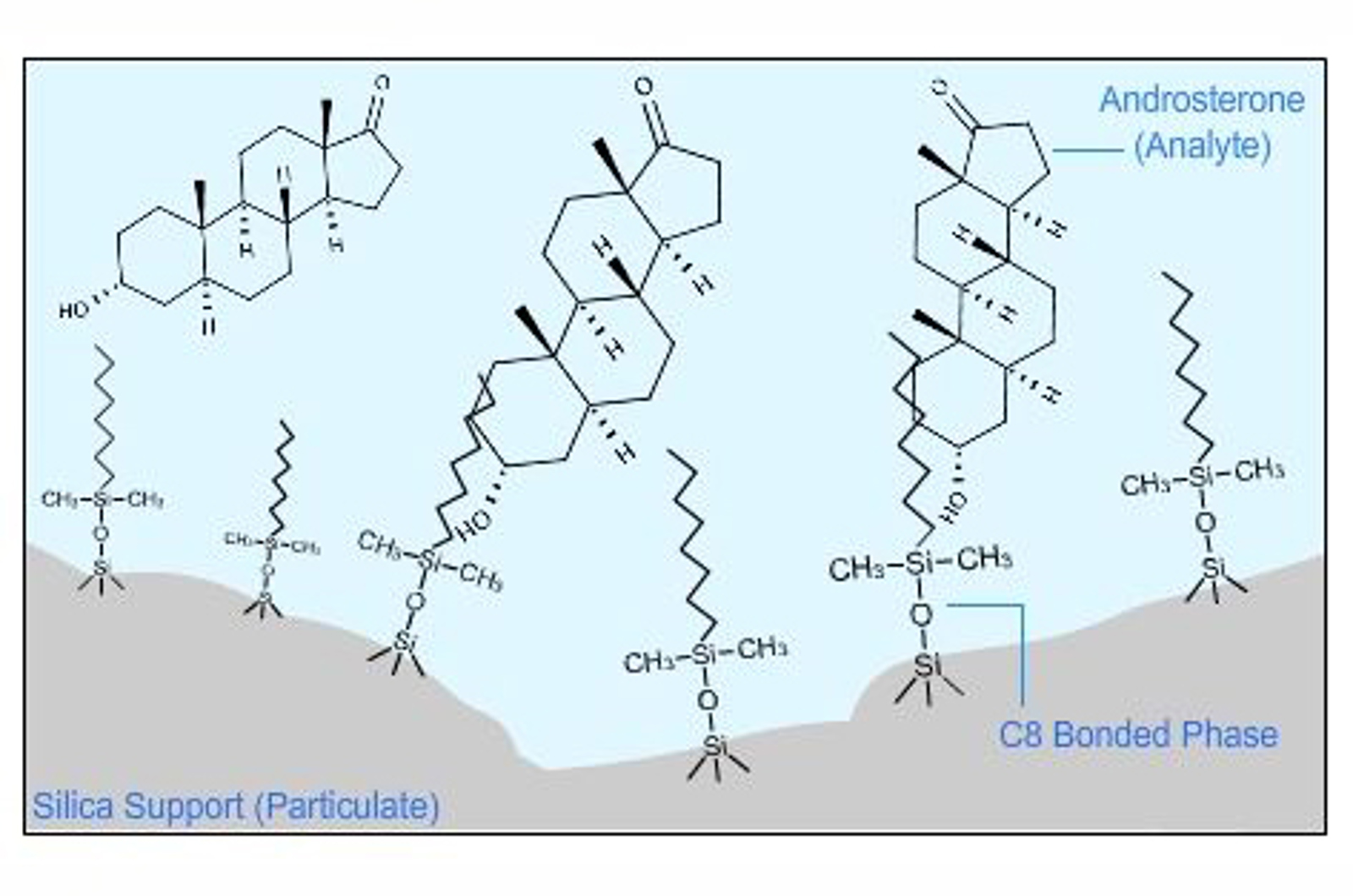
Introduction to Biopharmaceutical Analysis
This module will provide an overview of the different chromatographic techniques used in biopharmaceutical analysis.
Sponsored by 

Calculations 1 - Units and Unit Conversions
In this module we cover the common scientific units used, conversion between these units, and how we use these units in the practical preparation of common reagents.
Endorsed by 

Calculations 2 - Basic Result Calculations
This module will consider the basic calculations required for reporting results.
Endorsed by 

Quantitation and Calibration
This module will provide an understanding of the mathematical methods which are used to quantitate and calibrate chromatographic data.
Endorsed by 
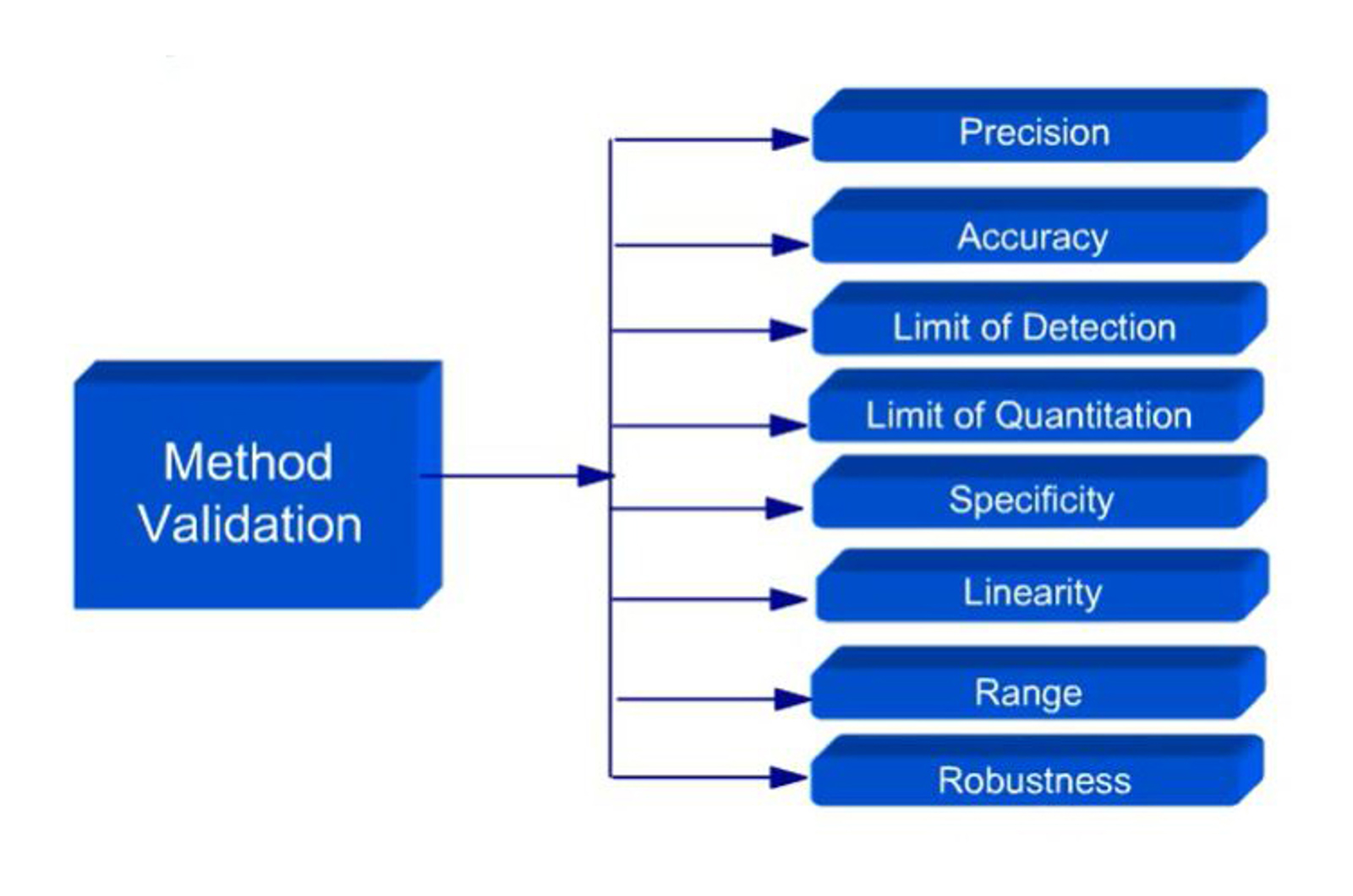
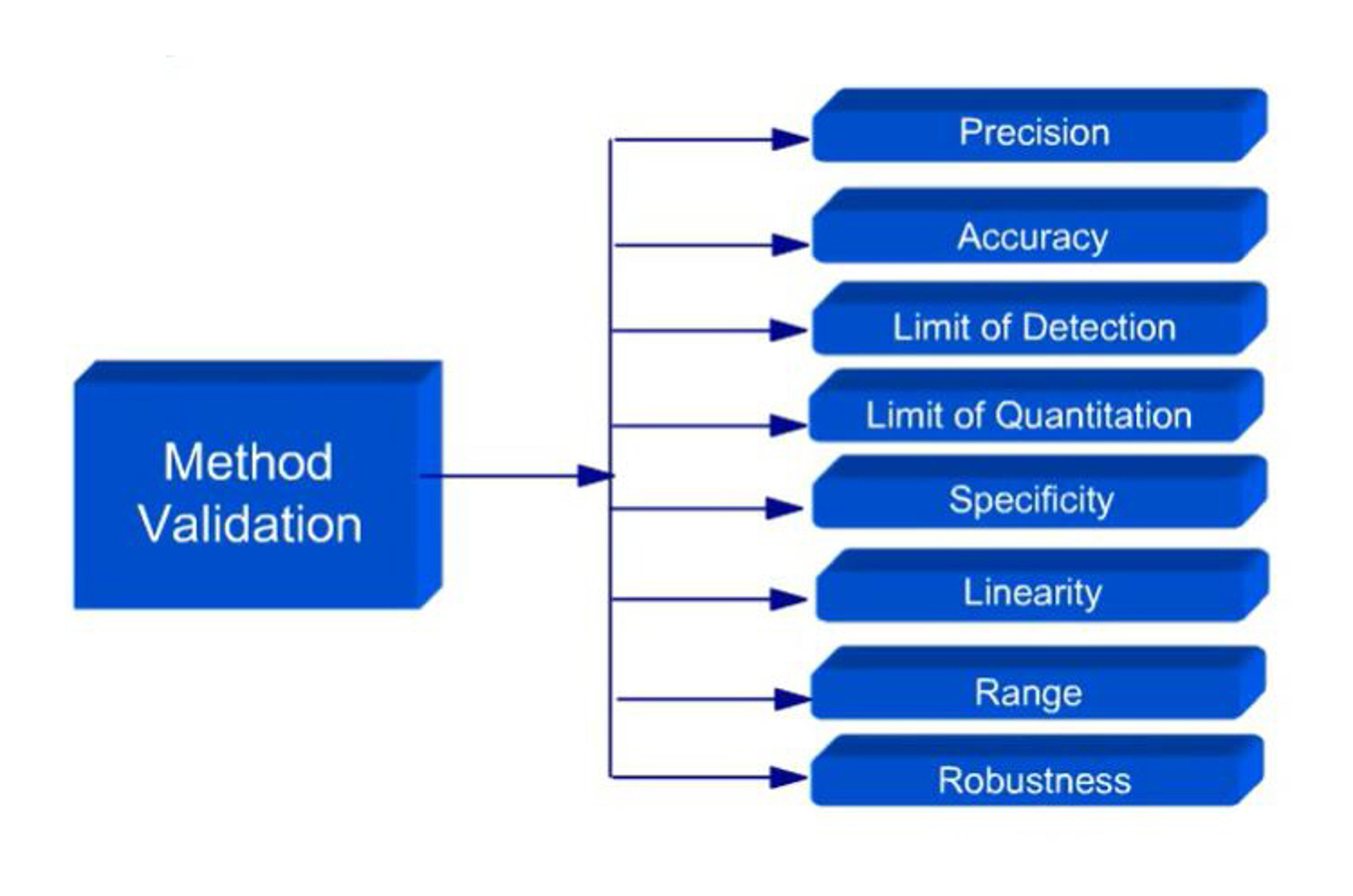
Method Validation - Principles
This module introduces the principles of analytical method validation. Each of the key parameters which are tested during a validation protocol are discussed in order to provide an understanding of what is being asked of the analyst and analytical method.
Endorsed by